Experiencing trouble connecting to your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) port can be frustrating, especially when you need to pass an emissions test or diagnose a check engine light. This article delves into a real-world scenario of a non-functional OBD2 port in a 2012 Toyota Tacoma and explores troubleshooting steps, focusing on the crucial role of the OBD fuse and the potential fix using a powered scan tool.
Diagnosing the Dead OBD2 Port: Step-by-Step Troubleshooting
When your OBD2 scanner fails to power up or connect, a systematic approach is key to pinpointing the issue. Here’s a breakdown of troubleshooting steps, starting with the simplest checks:
1. Verify Your Scan Tool and Cable
The first and easiest step is to rule out any issues with your diagnostic equipment. A faulty scan tool or a damaged cable can mimic problems with your vehicle’s OBD2 system.
- Test with a Different Scanner: If possible, try using a different OBD2 scanner. Borrow one from a friend or visit an auto parts store or repair shop, as they often have scanners available for testing.
- Inspect Cables and Connectors: Carefully examine the cable for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or bent pins in the connectors.
2. Check the OBD Fuse: Your First Line of Defense
The OBD2 port is protected by a fuse, and a blown fuse is a common culprit for a non-functional port. For many vehicles, including the Toyota Tacoma mentioned in the original story, this fuse is often located in the engine bay fuse box.
- Locate the OBD Fuse: Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the precise location of the OBD fuse. In the case of the 2012 Toyota Tacoma, the fuse box is in the engine compartment on the driver’s side.
- Identify the Correct Fuse: Look for the fuse labeled “OBD” or “Diagnostic.” In the original example, Fuse #7 (7.5 amp) was identified as the OBD fuse. While some online discussions mention Fuse #19 (20A EFI), a blown EFI fuse is likely to cause more significant vehicle issues beyond just the OBD port.
- Inspect and Test the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse for a broken filament. Even if it looks intact, it’s best to test it with a fuse tester or by swapping it with a fuse of the same rating from a non-essential circuit.
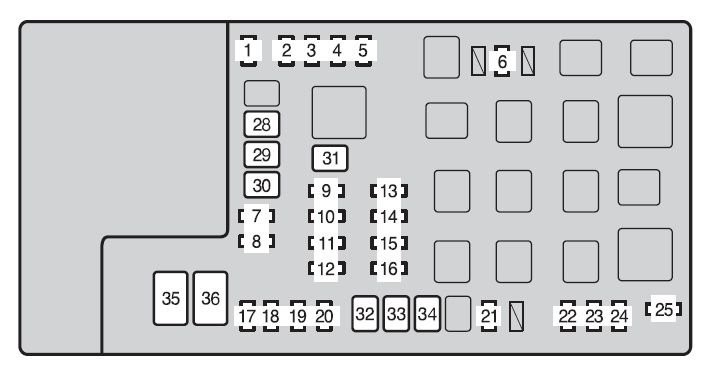 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Engine bay fuse box layout of a 2012 Toyota Tacoma, highlighting the location for potential OBD fuse inspection.
3. Wiring Inspection: Tracing the OBD2 Circuit
If the fuse is intact, the next step involves checking the wiring that connects the OBD2 port to the fuse box and the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
- Visual Inspection: Look for any obvious signs of damage to the wiring harness, such as cuts, chafing, or corrosion, especially around the OBD2 port and fuse box.
- Continuity Testing: If you have experience with automotive electrical systems, you can use a multimeter to perform continuity tests on the wiring between the fuse box, OBD2 port pins, and ECU. However, this step may require wiring diagrams and should be approached with caution or by a qualified technician.
4. Battery Reset: A Simple System Refresh
Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve minor electrical glitches.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery terminal for about 30 seconds, then reconnect it. This can reset the vehicle’s computer systems and potentially restore OBD2 port functionality.
5. The Powered OBD Scanner Solution: Bypassing a Power Issue
In the original story, the user discovered that a powered OBD scanner, which uses its own battery to supply power, was able to connect to the OBD2 port when unpowered scanners failed.
- Understanding the Issue: This suggests a potential issue with the power supply to the OBD2 port from the vehicle’s electrical system. There are specific pins in the OBD2 port that are supposed to provide power to the scanner. If there’s a voltage drop or interruption in this power supply, a standard scanner might not function.
- Powered Scanner as a Workaround: A powered scanner bypasses this issue by drawing power from its own battery, ensuring it has sufficient power to operate and communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
6. ECU Issues: A Less Likely Scenario
While a faulty ECU could theoretically cause OBD2 port problems, it’s generally less common than fuse or wiring issues. ECU problems often manifest with other significant vehicle performance issues. This should be considered as a last resort after ruling out other possibilities.
Real-World OBD2 Port Mystery: The Tacoma Story
The original author’s experience perfectly illustrates this troubleshooting process. Initially, the smog check station and their personal Bluetooth OBD2 scanner failed to connect to their 2012 Toyota Tacoma. After basic checks, the problem seemed elusive. However, a visit to the Toyota dealership revealed that their professional, powered scan tool worked flawlessly. This pointed directly to a power supply issue with the OBD2 port itself.
Interestingly, the dealership visit also involved a recall service related to the air injection pump system. While seemingly unrelated, electrical system glitches can sometimes be interconnected. The dealership’s powered scan tool and potentially a battery port on their smog machine allowed them to bypass the power issue and complete the smog test.
Conclusion: Unraveling OBD2 Port Problems
A non-functional OBD2 port can stem from various issues, but starting with the simple checks, especially the OBD fuse, is crucial. The experience shared highlights the effectiveness of using a powered OBD scanner as a diagnostic tool and a potential workaround for power supply problems to the OBD2 port. While the exact root cause in the original story remains unresolved, the powered scanner provided a practical solution. Further investigation into the specific power pins of the OBD2 port might reveal the underlying electrical fault for a more permanent fix.