Experiencing issues with your 2004 Chevy Silverado’s OBD2 port? If you’re trying to diagnose a “Service Engine Soon” light or other trouble codes and your scanner isn’t powering up, a blown fuse is the most common culprit. This guide will walk you through locating and troubleshooting the OBD2 fuse on your 2004 Chevy Silverado, getting you one step closer to resolving your automotive issues.
Understanding the OBD2 Port and Its Fuse
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is crucial for modern vehicle maintenance. It allows mechanics and DIYers to connect scan tools and retrieve diagnostic trouble codes, monitor engine performance, and ensure your Silverado is running optimally. This port requires power to function, and like many electrical components in your truck, it’s protected by a fuse.
When the OBD2 port loses power, it’s often due to a blown fuse. This fuse is designed to protect the diagnostic system from electrical surges or shorts. Identifying and replacing this fuse is a straightforward first step in diagnosing OBD2 port issues.
Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2004 Chevy Silverado
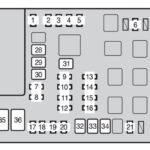
The fuse box location in a 2004 Chevy Silverado can vary slightly depending on the specific model and trim, but generally, you’ll find the primary fuse box under the hood.
-
Under-Hood Fuse Box: Open your Silverado’s hood and locate the main fuse box. It’s typically a black plastic box, often on the driver’s side near the engine compartment. The location is usually detailed in your owner’s manual.
-
Fuse Box Diagram: Once you’ve found the fuse box, open the lid. Inside the lid, you should find a fuse diagram. This diagram is essential for identifying the correct fuse for your OBD2 port.
-
Identifying the OBD2 Fuse: Look for labels on the diagram that might indicate “OBD,” “Diagnostic,” “DLC” (Data Link Connector), or similar terms. Unfortunately, there isn’t one universally labeled fuse for the OBD2 port across all 2004 Silverado models. You may need to consult your owner’s manual for the precise fuse name and number. Common fuses to check in this area are often related to the cigarette lighter or auxiliary power outlets, as these circuits are sometimes linked to the OBD2 power supply.
-
Checking the Fuse: Once you believe you’ve located the correct fuse, use a fuse puller (often found in the fuse box itself or your Silverado’s toolkit) or needle-nose pliers to carefully remove the fuse. Inspect the fuse visually. A blown fuse will typically have a broken wire inside.
-
Testing with a Multimeter (Optional but Recommended): For a more definitive test, use a multimeter to check fuse continuity. If there’s no continuity, the fuse is blown and needs replacement.
Troubleshooting Beyond the Fuse
If you replace the fuse and it blows again immediately, or if the OBD2 port still doesn’t power up, you may have a more complex electrical issue. Here are a few potential culprits:
- Short Circuit: A short circuit in the wiring related to the OBD2 port or circuits sharing the same fuse can cause fuses to blow repeatedly.
- Wiring Damage: Inspect the wiring around the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, fraying, or corrosion.
- Aftermarket Accessories: Incorrectly installed aftermarket accessories, particularly those drawing power from the vehicle’s electrical system, can sometimes interfere with the OBD2 port circuit. Consider if any recent modifications have been made to your Silverado’s electrical system.
- OBD2 Port Damage: While less common, the OBD2 port itself could be damaged, causing a short.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a non-functional OBD2 port on your 2004 Chevy Silverado often starts with checking the fuse. By locating the correct fuse box, using the fuse diagram, and visually inspecting or testing the fuse, you can quickly rule out a simple blown fuse. If a new fuse doesn’t solve the problem, it’s advisable to consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair any underlying electrical issues to ensure your Silverado’s diagnostic system is functioning correctly.