Connecting to your vehicle’s OBD2 port is usually a straightforward process, essential for diagnostics and using various automotive apps and tools. However, it’s important to be aware of potential issues that can arise during connection, ensuring both your adapter and vehicle systems function correctly. This guide will explain how to connect to the OBD2 pin safely and effectively, and what to do if you encounter unexpected problems, especially with certain vehicle models.
Understanding the OBD2 Connector and Pin Layout
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface found in most modern vehicles. It allows communication with the car’s computer system for reading diagnostic trouble codes, accessing sensor data, and performing various functions. The connector typically has 16 pins, each assigned for specific purposes like power, ground, CAN bus, and manufacturer-specific diagnostics. Locating your OBD2 port is the first step. It’s commonly found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, but the exact position can vary depending on your car’s make and model. Refer to your vehicle’s manual if you are unsure of its location.
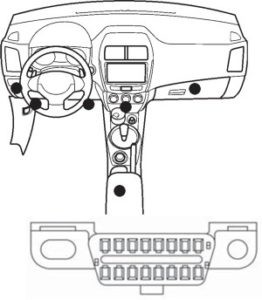
Alt text: Diagram showing potential locations of the OBD2 diagnostic connector in a vehicle cabin.
Potential Issues When Connecting OBD2 Adapters: Focus on Toyota Models
While generally safe, connecting an OBD2 adapter can sometimes lead to unexpected behavior, particularly in some Toyota vehicles. A known issue involves the activation of a diagnostic mode when an OBD2 adapter is plugged in. This is not caused by a faulty adapter in itself, but rather how certain Toyota models are designed to react to pin connections within the OBD2 port.
The Toyota ABS Issue: Diagnostic Mode and Warning Lights
In specific Toyota models, connecting a standard OBD2 adapter can inadvertently trigger a diagnostic mode. A common symptom of this is a constantly flashing ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) warning light on the dashboard. This flashing light indicates that the ABS function might be disabled as the vehicle enters this diagnostic state. Driving with ABS disabled is a safety concern, as it significantly affects braking performance, especially in emergency situations.
Why This Happens? Pin Shorting and Diagnostic Mode Activation
The root cause of this issue in some Toyota vehicles lies in the design of certain OBD2 adapters. Some generic adapters may create a short circuit between specific pins in the OBD2 connector, particularly pins 13 and 14. In affected Toyota models, this short circuit can be misinterpreted by the car’s control unit as a signal to activate a special diagnostic mode. This activation happens immediately upon turning the ignition ON with the adapter connected and is not triggered by any specific OBD2 application or software, but by the physical pin connection itself.
Solutions to Avoid OBD2 Connection Problems with Specific Vehicles
If you encounter the ABS warning light or suspect your Toyota is entering a diagnostic mode when connecting an OBD2 adapter, here are a few recommended solutions:
Solution 1: OBD2 Adapter Pin Modification
One effective solution is to physically modify your OBD2 adapter by removing the 13th and 14th pins from the connector. Carefully removing these pins will prevent the unintended short circuit, thus avoiding the diagnostic mode activation in susceptible Toyota models. This modification allows you to use the adapter without triggering the issue.
Solution 2: Using a Special OBD2 Adapter Connector
Alternatively, you can purchase a specialized OBD2 adapter that is designed to prevent this pin shorting issue. These adapters are often engineered with internal modifications or circuitry to avoid activating diagnostic modes in sensitive vehicles. Using a compatible adapter eliminates the need for manual pin removal and ensures safe connection.
Solution 3: Delayed OBD2 Adapter Connection
A temporary workaround, although less convenient, is to connect the OBD2 adapter a few seconds after turning the ignition ON or starting the engine. By delaying the connection, you might prevent the control unit from initiating the diagnostic mode upon startup. However, this method requires consistent timing every time you start your vehicle and is not as reliable as the other solutions.
Important Considerations When Connecting to OBD2 Pin
Keep in mind that modifying your OBD2 adapter by removing pins might limit its compatibility with other car brands or models. Some vehicles may require those specific pins for proper diagnostics. If you choose to remove pins, ensure you understand the potential limitations and consider having a separate, unmodified adapter for diagnosing other vehicles. Always prioritize safety and verify the functionality of your vehicle’s systems after connecting or disconnecting any OBD2 device. If you are uncertain about any step, consult with a qualified automotive technician.
