Being a savvy car owner goes beyond just admiring the sleek exterior. A crucial aspect of responsible car ownership is understanding the mechanics that keep you moving. While the engine and interior might be more familiar, the Parts Underneath A Car are equally vital for performance, safety, and overall vehicle longevity. Knowing these components empowers you to make informed maintenance decisions and understand potential repair costs.
Let’s delve into the world beneath your vehicle, exploring the key systems and components that work tirelessly out of sight.
Engine Components: The Powerhouse and its Underpinnings
The engine is the heart of your car, and while much of it resides under the hood, several critical components extend downwards and are considered parts underneath the car in terms of their location and interaction with the chassis.
Cylinder Block and Pistons: The Foundation of Power
The cylinder block, the engine’s core structure, often sits relatively high in the engine bay, but its lower sections and related ancillaries are definitely parts underneath the car in terms of spatial awareness. Inside the block are cylinders where pistons move. These pistons, driven by combustion, are fundamental in converting fuel energy into the motion that propels your vehicle. This piston-cylinder interaction is the origin point of your car’s power, much of which is then transferred to parts situated beneath the car.
Crankshaft and Camshaft: Rotational Motion and Valve Timing
The crankshaft and camshaft are also central to the engine’s operation. The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion – the driving force. While the camshaft manages valve timing for combustion. These parts, although within the engine block, contribute to the power delivery that’s channeled downwards to the transmission and drivetrain, which are definitively parts underneath the car.
Intake and Exhaust Manifolds: Breathing and Emission Control
The intake and exhaust manifolds are crucial for engine breathing. The intake manifold draws air in for combustion, and the exhaust manifold expels gases. The exhaust manifold is a key component that leads to the entire exhaust system, which runs almost entirely underneath the car. These manifolds ensure efficient combustion, and the exhaust system, a very prominent set of parts underneath a car, is critical for emissions control. Electric vehicles, notably, do not have these manifolds or a traditional exhaust system.
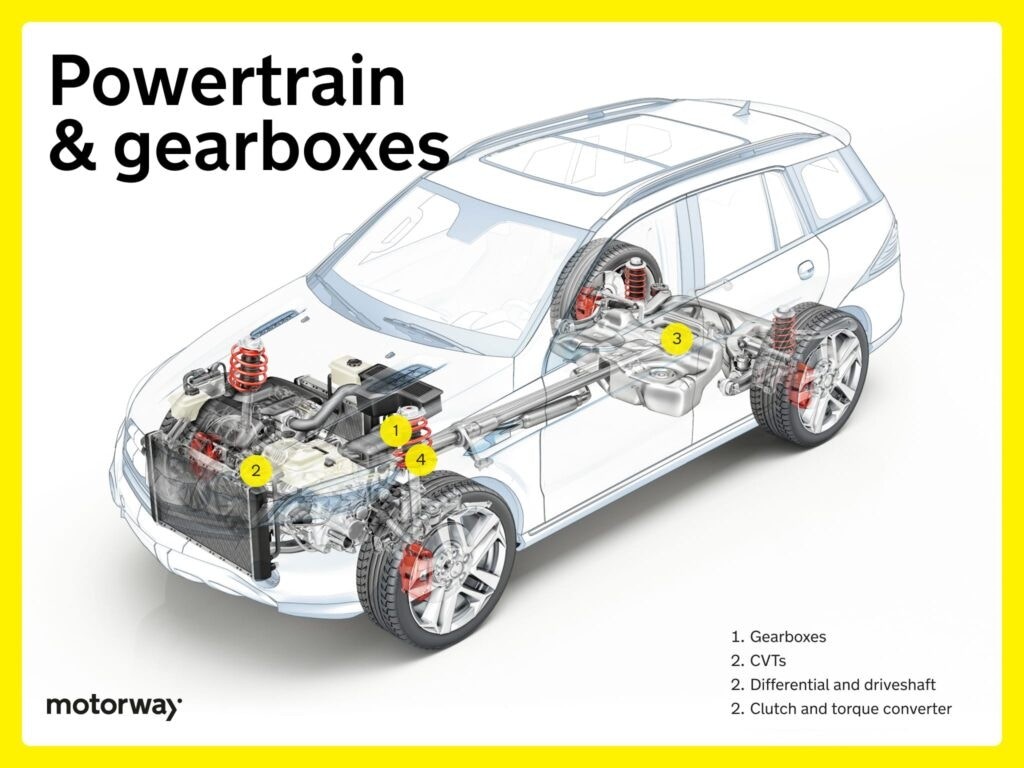
Powertrain and Gearboxes: Transferring Power Below
The powertrain is the system that transmits engine power to the wheels, and many of its key components are located directly underneath the car.
Gearboxes/Transmissions: Managing Speed and Torque
Gearboxes, also known as transmissions, are essential parts underneath a car responsible for managing engine speed and torque to suit driving conditions.
Manual Gearboxes: Driver Control
Manual gearboxes give the driver full control over gear selection, using a clutch to engage and disengage gears. This system allows drivers to adapt to varied conditions, all managed through a unit located underneath the car.
Automatic Gearboxes: Automated Shifting
Automatic gearboxes simplify driving by automatically shifting gears. These transmissions, located underneath the car, use a torque converter for smooth gear changes without driver intervention.
CVTs: Seamless and Efficient
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) offer an infinite range of gear ratios via pulleys and belts. Located as parts underneath a car, CVTs provide seamless acceleration and enhance fuel efficiency by dynamically adjusting to driving demands.
Differential and Driveshaft: Distributing Power to the Wheels
The driveshaft and differential are vital parts underneath a car in the powertrain. The driveshaft carries power from the transmission towards the wheels, running along the undercarriage. The differential then ensures even power distribution to the wheels, especially during turns.
Clutch and Torque Converter: Engagement and Power Transfer
The clutch (in manual transmissions) and torque converter (in automatics) are key for managing power flow from the engine to the transmission. The clutch allows for gear changes, while the torque converter provides smooth power transfer in automatic systems. Both are integral to the powertrain system located underneath the vehicle.
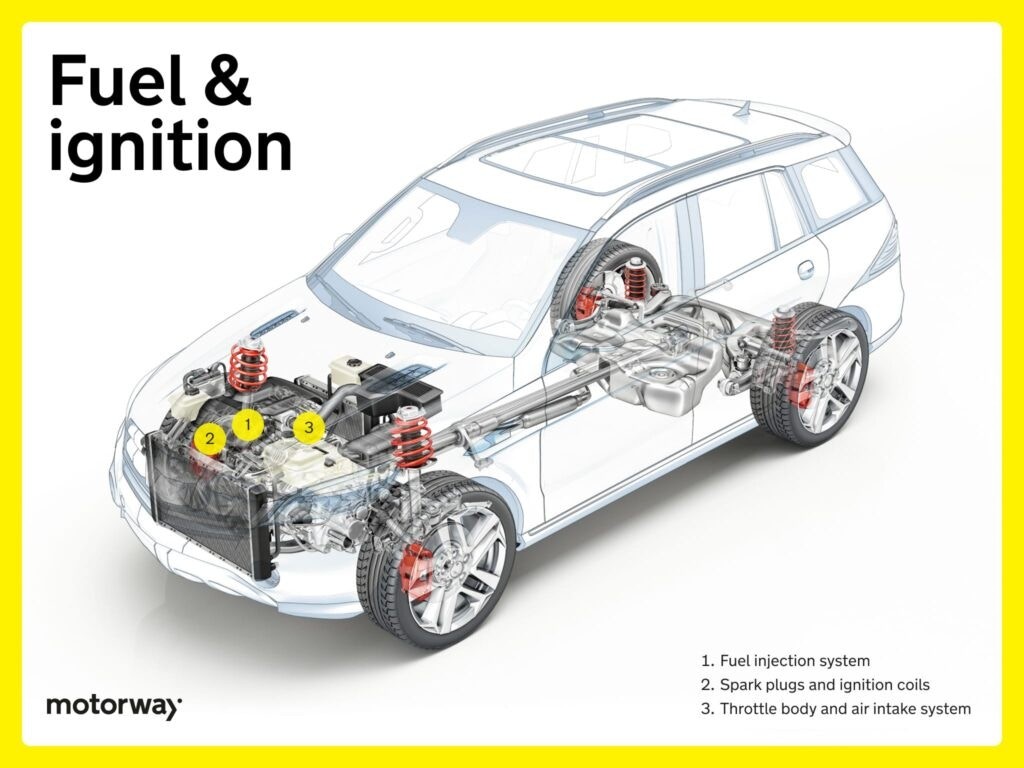
Fuel and Ignition Systems: Powering Combustion
The fuel and ignition systems are essential for starting and running the engine. While some components are in the engine bay, the fuel lines and aspects of the exhaust are definitely parts underneath a car.
Fuel Injection System: Precise Fuel Delivery
Modern engines use fuel injection systems for optimal combustion. Fuel injectors precisely deliver fuel into cylinders, enhancing efficiency. Fuel lines, running underneath the car, supply this system, making them parts underneath a car to consider. This system is more efficient and reliable than older carburetor systems.
Spark Plugs and Ignition Coils: Initiating Combustion
Spark plugs and ignition coils are critical for igniting the air-fuel mixture. Spark plugs create the spark, and ignition coils amplify voltage. While these are located within the engine, their function is to initiate the combustion process that drives the components located underneath.
Throttle Body and Air Intake System: Airflow Management
The throttle body and air intake system control airflow to the engine. The throttle manages air quantity, and the intake system ensures clean air supply. These systems regulate engine ‘breathing,’ vital for performance. The air intake often starts higher up, but interacts with systems that are considered parts underneath a car.
Cooling and Lubrication: Maintaining Optimal Temperatures
Cooling and lubrication systems prevent engine overheating and wear. Many components of these systems are located low in the vehicle, making them parts underneath a car.
Radiator and Cooling Fans: Heat Dissipation
Radiators and cooling fans prevent engines from overheating. Radiators dissipate heat from coolant, and fans enhance airflow. The radiator is often at the front, but cooling lines and aspects of the system extend underneath the car.
Water Pump and Hoses: Coolant Circulation
Water pumps and hoses circulate coolant, regulating engine temperature. The water pump drives coolant flow, and hoses allow coolant movement throughout the engine and cooling system, many of these hoses running as parts underneath a car.
EV Battery Cooler System: Electric Vehicle Thermal Management
Electric vehicles use battery cooler systems for battery and motor temperature regulation. These systems, similar in function to radiators, are crucial for EV efficiency and battery longevity, and are often situated as parts underneath a car.
Oil Pump and Oil Filter: Engine Lubrication and Cleanliness
Oil pumps circulate engine oil for lubrication, and oil filters remove impurities. These systems extend engine life by ensuring smooth operation and are connected to the engine block, which is spatially related to parts underneath a car.
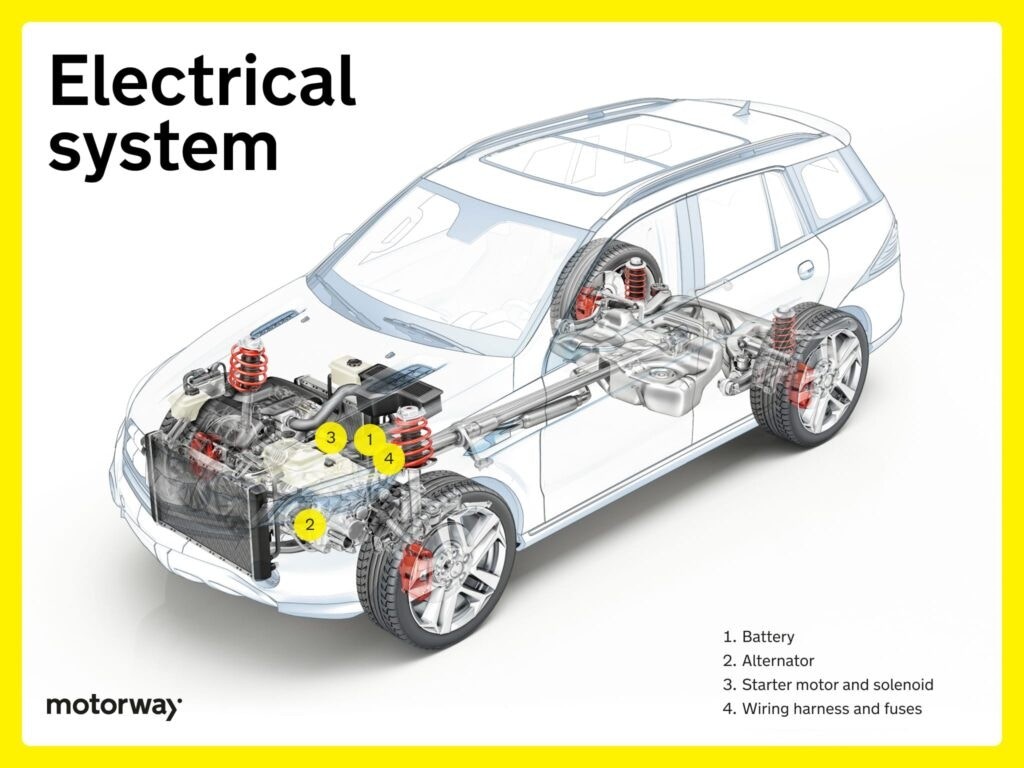
Electrical System: Powering the Vehicle
The electrical system powers all vehicle functions, from starting the engine to running accessories. Many wiring harnesses and components run along the chassis and are parts underneath a car.
Battery: Initial Power Source
The car battery provides initial energy to start the engine and power electrical systems. All cars, including EVs, have batteries. Battery cables and some battery placement can be considered related to parts underneath a car.
Alternator: Recharging and Power Supply
Alternators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, recharging the battery and powering the electrical system while the engine runs. It regulates voltage for consistent power supply and is connected to the engine, influencing systems that are parts underneath a car.
Starter Motor and Solenoid: Engine Ignition
Starter motors and solenoids work together to start the engine. The solenoid activates the starter motor, which turns the engine to initiate combustion. These parts are crucial for starting the car and are positioned in relation to the engine and chassis, influencing parts underneath a car.
Wiring Harness and Fuses: Electrical Distribution and Protection
Wiring harnesses distribute electricity throughout the vehicle, and fuses protect against overloads. These run throughout the vehicle, including as parts underneath a car, ensuring safe and organized electrical flow.
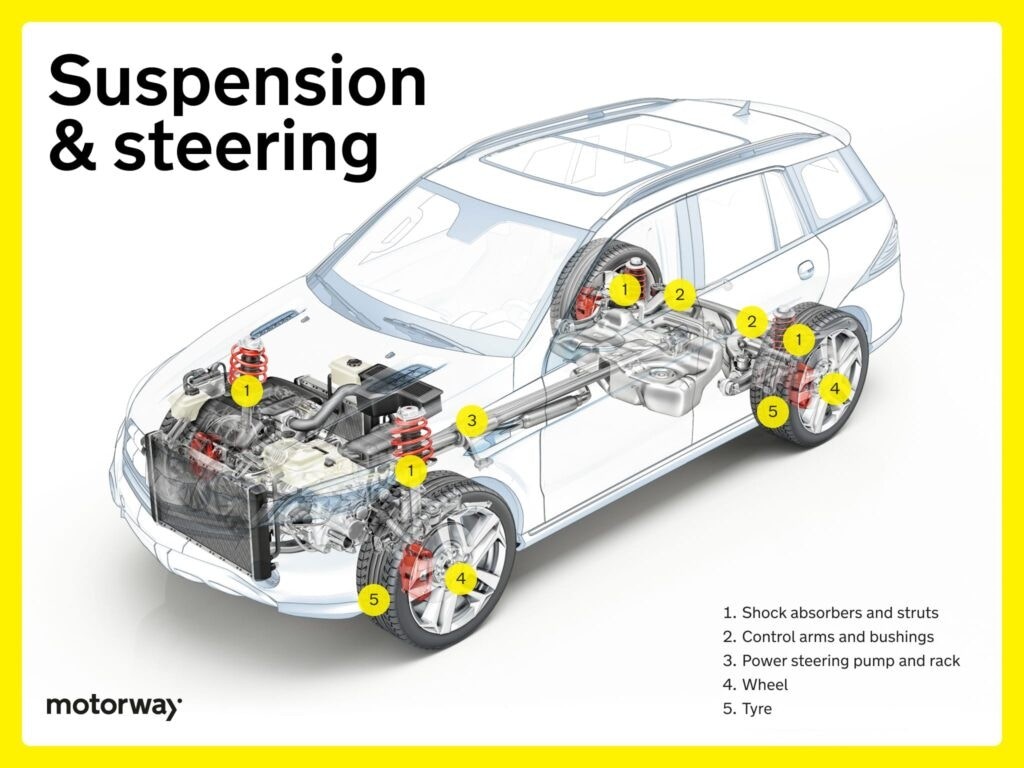
Suspension and Steering: Ride Comfort and Control
The suspension and steering systems are critical for handling, stability, and ride comfort. These are primarily located underneath the car and are quintessential parts underneath a car.
Shock Absorbers and Struts: Damping and Support
Shock absorbers and struts are vital for suspension. Shock absorbers dampen vibrations, providing a smoother ride. Struts offer structural support and shock absorption. These parts underneath a car enhance ride comfort and stability.
Control Arms and Bushings: Stability and Handling
Control arms connect the suspension to the frame, and bushings provide flexibility. This combination absorbs road imperfections, maintains tyre alignment, and ensures balanced handling. These are core parts underneath a car for chassis stability.
Power Steering Pump and Rack: Effortless Steering
Power steering pumps generate hydraulic pressure, and steering racks convert it into controlled motion, making steering easier. These parts underneath a car provide precise and smooth maneuverability.
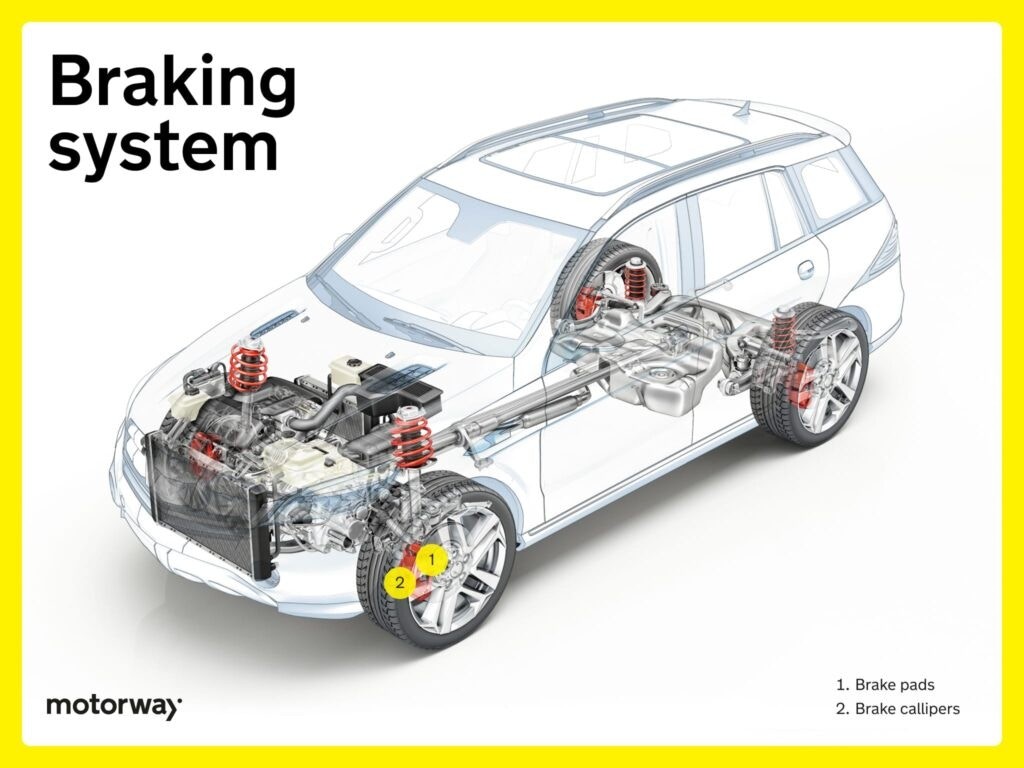
Braking System: Ensuring Safety
The braking system is paramount for safety, allowing controlled deceleration. The majority of the braking system is located at the wheels and along the undercarriage, making them key parts underneath a car.
Brake Pads: Friction for Deceleration
Brake pads create friction against brake rotors, converting kinetic energy into heat for deceleration. These are wear items and crucial for braking performance, located at each wheel as parts underneath a car.
Brake Calipers: Applying Brake Force
Brake calipers house pistons that clamp brake pads onto rotors upon brake pedal application. Their precision ensures responsive braking, contributing to overall safety and are located at each wheel as parts underneath a car.
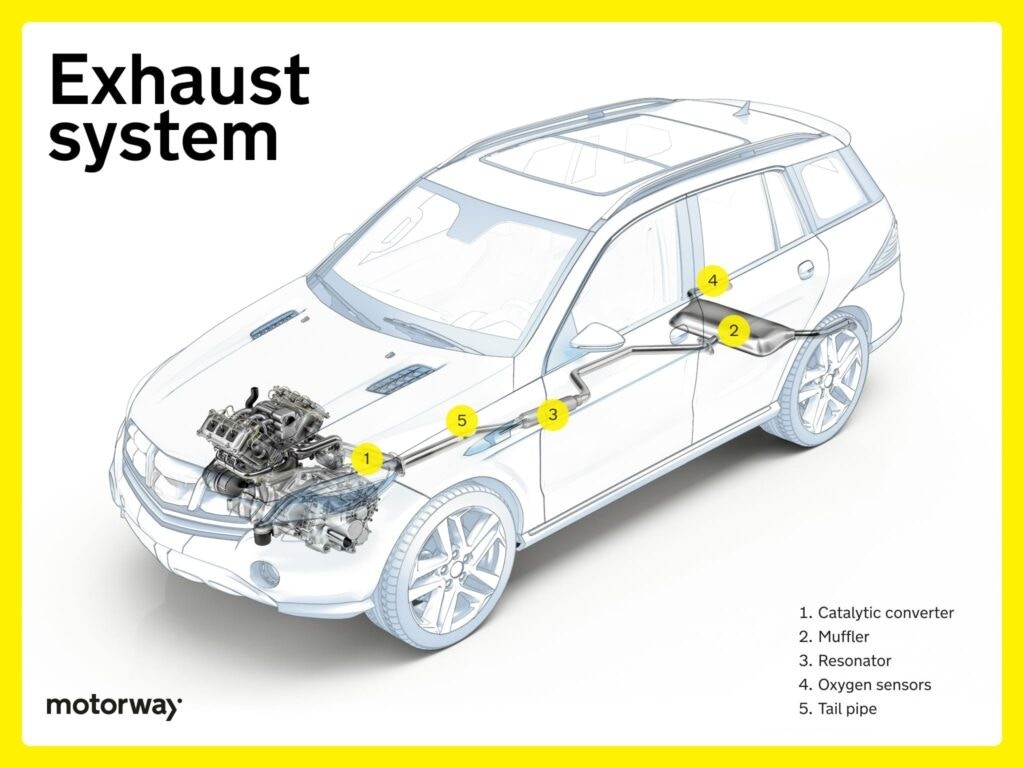
Exhaust System: Emission Control and Noise Reduction
The exhaust system removes combustion gases and reduces emissions and noise. This system runs almost entirely underneath the car, making it a prominent set of parts underneath a car.
Catalytic Converter: Reducing Harmful Emissions
Catalytic converters transform harmful gases into less harmful substances, reducing vehicle emissions and contributing to cleaner air. This is a key component within the exhaust system parts underneath a car.
Muffler and Resonator: Noise Management
Mufflers reduce exhaust noise, and resonators fine-tune sound frequencies. Together, they manage exhaust noise for a more pleasant driving experience. These are significant parts underneath a car in the exhaust system.
Oxygen Sensors: Monitoring Exhaust Gases
Oxygen sensors monitor oxygen levels in exhaust gases, providing data to the engine control unit. This information optimizes fuel injection and reduces emissions. These sensors are positioned within the exhaust system parts underneath a car.
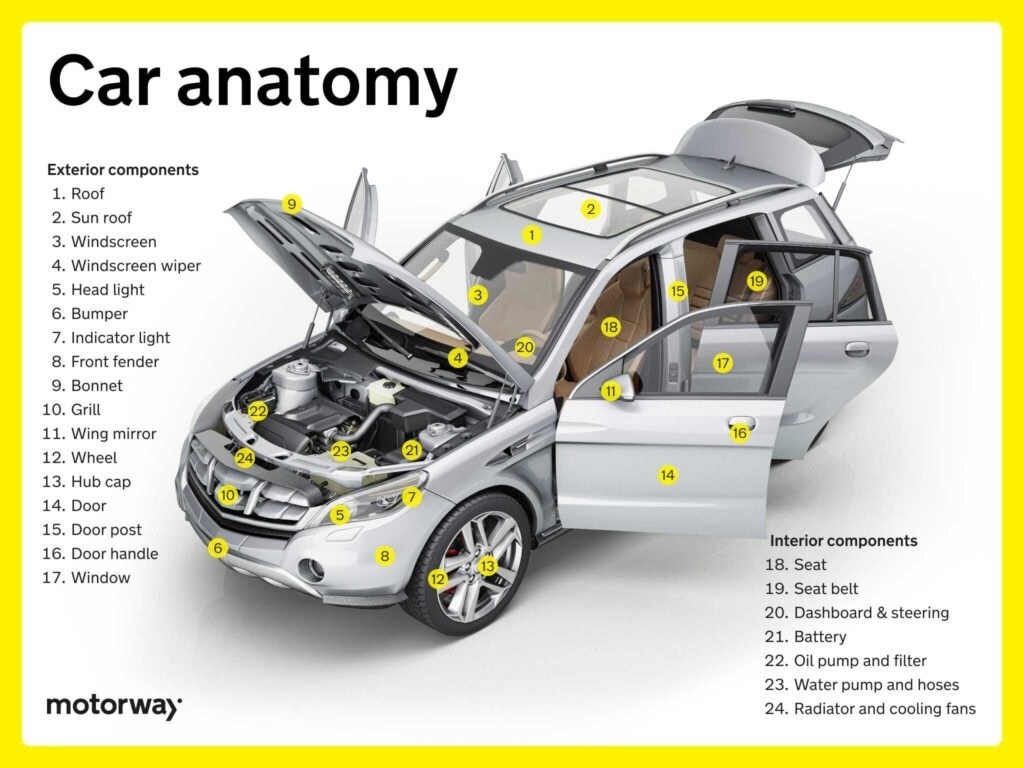
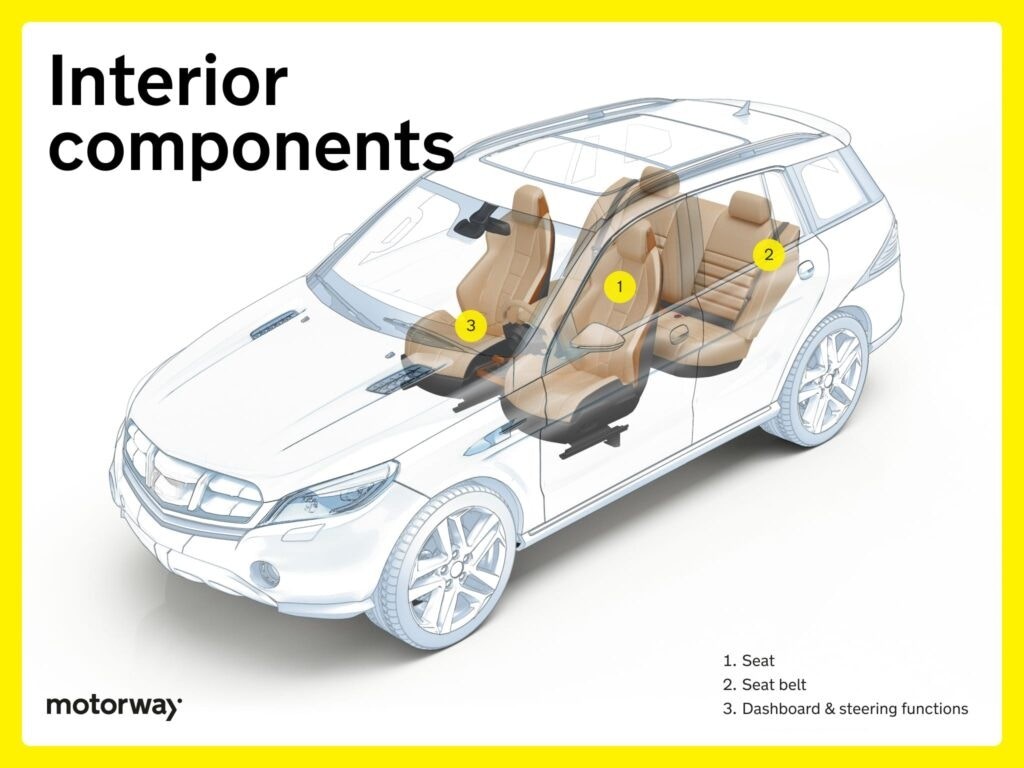
Interior Components: Driver and Passenger Comfort (Less Relevant to “Underneath”)
Interior components focus on comfort and convenience, and are generally not considered parts underneath a car.
Seats & Their Belts: Safety and Comfort
Seats offer comfort and support, and seat belts ensure occupant safety. These are interior features, not parts underneath a car.
Dashboard & Steering Functions: Driver Interface
Dashboards display vital information, and steering wheels integrate controls. These are also interior features, not parts underneath a car.
Exterior Components: Vehicle Aesthetics and Protection (Less Relevant to “Underneath”)
Exterior components define the car’s appearance and offer protection, and are mostly not considered parts underneath a car except for perhaps underbody panels.
Features & Controls on Doors: Convenience and Access
Door features include window controls, locks, and mirrors. These are exterior and interior door components, not directly parts underneath a car.
Wheels and Tyres: Road Contact and Performance
Wheels and tyres are the direct link to the road and crucial for performance and safety. While wheels are on the sides, tyres are very much related to the ground and interact with parts underneath a car like suspension.
Types of Tyres and Their Functions
| Type of tyre | Function |
|---|---|
| Summer tyres | Optimal grip and handling in warm, dry, and wet conditions. |
| Winter tyres | Enhanced traction on snow and ice in cold climates. |
| All-season tyres | Balanced performance in varied conditions, wet and dry. |
| Performance tyres | Superior handling, grip, and responsiveness for sporty driving. |
| Off-Road tyres | Rugged treads for enhanced traction on challenging terrains. |
| Run-flat tyres | Reinforced sidewalls for continued driving after a puncture. |
| Touring tyres | Smooth, comfortable ride for long journeys with low noise. |


Wheel Construction Guide: Alloy vs. Steel Wheels
- One-piece construction: Simple, common design for alloy and steel wheels.
- Two-piece construction: Center and rim bolted or welded, often in performance wheels.
- Three-piece construction: Customizable modular design popular in aftermarket wheels.
- Forged construction: Stronger and lighter wheels for high-performance use.
- Multi-piece construction: Versatile, customizable sizing.
Material choices include:
- Alloy wheels: Lightweight, better heat dissipation, enhanced appearance.
- Steel wheels: Robust, durable, cost-effective, suitable for rugged conditions.
Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): Safety and Efficiency
TPMS monitors tyre pressure, warning of deviations for safety, fuel efficiency, and tyre lifespan. Sensors are located within the wheel/tyre assembly, interacting with parts underneath a car in terms of data transmission and general wheel well location.
FAQs about Parts Underneath a Car
What parts are under a car?
Crucial parts underneath a car include the engine (lower components), transmission, suspension, exhaust system, driveshaft, differential, fuel lines, and braking system components. These systems are essential for vehicle functionality and performance.
How many car parts are on a car?
Modern cars can have over 30,000 parts, encompassing numerous systems. EVs generally have fewer parts due to simpler powertrains. Many of these parts, particularly in the systems mentioned above, are located as parts underneath a car.
What are the important parts of a vehicle?
Important vehicle parts include the engine, transmission, brake system, steering system, suspension, and electrical components. Many of these systems have significant parts underneath a car.
What parts of a car can be sold separately?
Engines, transmissions, body panels, and specific electrical parts can be sold separately, offering flexibility for repairs and upgrades. Some parts underneath a car, like exhaust components or suspension parts, are commonly sold individually.
Why is there a shortage of car parts?
Car part shortages can result from supply chain disruptions, increased demand, manufacturing issues, and global events affecting production and distribution. This can impact availability of parts underneath a car as much as any other component.
Need to Sell Your Car?
Want to learn more about car ownership, maintenance, and selling your car? Explore our guides here for information on various topics from Clean Air Zones to car tax.