Wheels are fundamental to every car, acting as the crucial link between your vehicle and the road. From the most basic sedan to high-performance sports cars, the principle remains the same: wheels enable movement. Understanding the components of a car wheel is beneficial for vehicle maintenance, repair, and simply expanding your automotive knowledge.
This guide will break down the various Car Wheel Parts Names With Pictures, providing a detailed look at each component and its function. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a curious car owner, this comprehensive overview will enhance your understanding of this essential automotive system.
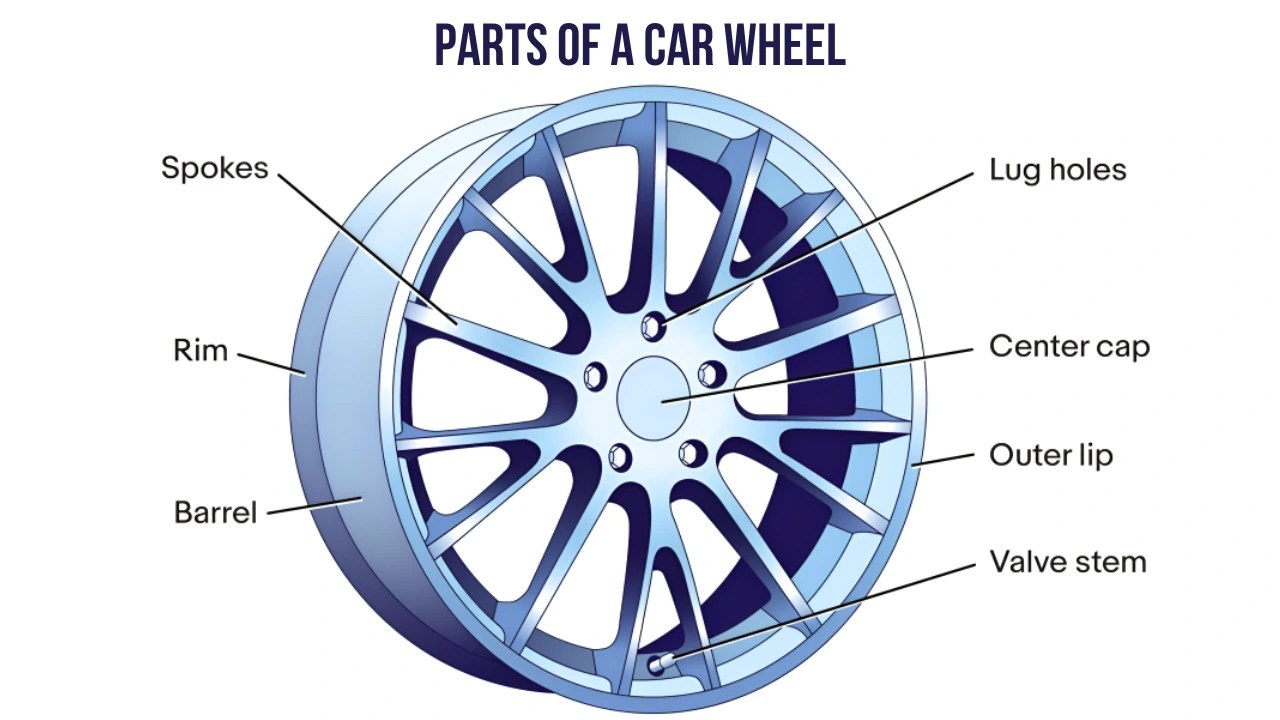 Diagram of car wheel parts with labels pointing to rim, tire, hub, spokes, and valve stem
Diagram of car wheel parts with labels pointing to rim, tire, hub, spokes, and valve stem
Understanding the Anatomy of a Car Wheel
A car wheel is more than just a simple circle; it’s a complex assembly of parts working in harmony. While the terms “wheel” and “tire” are often used interchangeably, they are distinct components. The wheel itself is typically composed of the rim and the hub, onto which the tire is mounted. Let’s delve into the specific parts that make up a complete car wheel assembly:
#1. Tire
The tire is arguably the most recognized part of the wheel. It’s the rubber component that encircles the rim and makes direct contact with the road surface. Tires are filled with air, providing cushioning and grip, which are essential for a comfortable and safe ride. Modern tires are sophisticated pieces of engineering, designed to perform in diverse conditions, from dry highways to wet and snowy roads. They play a critical role in handling, braking, and overall vehicle stability.
#2. Rim
The rim is the metal structure that provides the foundational shape and support for the tire. Think of it as the skeleton of the wheel assembly. The tire is mounted onto the rim, and the rim’s shape and dimensions are crucial for ensuring a proper and secure fit. Rims are typically manufactured from steel or aluminum alloy, chosen for their strength and durability. They come in a vast array of styles and finishes, contributing significantly to a vehicle’s aesthetic appeal.
#3. Hub
The hub is the central part of the wheel, acting as the crucial connection point to the vehicle itself. It’s the component that attaches to the car’s axle, allowing the wheel to rotate freely while remaining securely fastened to the vehicle. The hub is also often integrated with other critical components like brake rotors, calipers, and wheel bearings. It’s a robust and precisely engineered part that bears significant load and stress during vehicle operation.
#4. Spokes
Spokes are structural elements that radiate outwards from the central hub to the outer rim. They are responsible for distributing load and providing structural integrity to the wheel. Spoke design also plays a significant role in wheel aesthetics, with variations in number, shape, and pattern. While spoke design can influence wheel weight to a degree, modern manufacturing focuses more on materials and construction methods for weight reduction.
#5. Outer Lip (Dish)
The outer lip, sometimes referred to as the dish, is the area of the wheel that extends outwards from the spokes towards the edge of the rim. The depth of the dish is primarily an aesthetic feature. Deep-dish wheels, where the spokes are set back significantly from the outer edge, are a popular styling choice. However, a very deep dish can make the wheel face more susceptible to damage from impacts.
#6. Barrel
The barrel is the main cylindrical part of the rim that forms the inner structure of the wheel. It’s the section where the tire is mounted and sealed. The barrel includes several key features essential for tire installation and retention:
- Drop Center: The narrowest diameter section within the barrel. The drop center is designed to allow for tire mounting and demounting without excessive stretching of the tire bead wires.
- Barrel Edges (Flanges): The flared edges at the outer ends of the barrel. These flanges are crucial for retaining the tire on the rim and preventing it from slipping off, especially under load and cornering forces.
#7. Beads
Beads are the flat, raised areas located just inside the flanges on the barrel. These are the precise points where the tire’s bead – the reinforced edge of the tire – seats against the wheel rim. The bead and bead seat form an airtight seal, essential for maintaining tire pressure.
#8. Flanges
As mentioned earlier, flanges are the flared edges on the inboard and outboard sides of the rim’s barrel. They are critical safety features, preventing the tire from detaching from the wheel rim during operation, particularly under lateral forces experienced during cornering.
#9. Mounting Humps
Mounting humps are small circumferential ridges located on the bead seat area, just inboard of the flanges. These humps are designed to further secure the tire beads in place, preventing them from slipping inwards towards the drop center, especially during hard cornering or in low-pressure situations.
#10. Drop Center
The drop center, as previously defined within the barrel section, is the reduced diameter section of the rim. It is a crucial design element that facilitates tire mounting and demounting. By having a smaller diameter section, it allows one bead of the tire to be pushed into the drop center, providing enough slack to lever the opposite bead over the rim flange without damaging the tire bead wires.
#11. Center Cap
The center cap is a removable cover that fits over the center bore of the wheel on the outboard side. Its primary function is aesthetic, concealing the hub and often featuring the vehicle manufacturer’s logo or the wheel brand. In some modern vehicles, the center cap also provides a degree of protection to the lug nuts from dirt and debris.
#12. Valve Stem
The valve stem is a small, usually metal, fitting that protrudes through a hole in the rim. It houses a valve core and provides the access point for inflating or deflating the tire with air or nitrogen. The valve stem is a critical component for maintaining proper tire pressure, which is vital for safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity.
#13. Lug Nuts
Lug nuts are threaded fasteners that are used to secure the wheel to the wheel studs. They are tightened to a specific torque to ensure the wheel is firmly and safely attached to the vehicle’s hub assembly. The number of lug nuts varies depending on the vehicle and wheel design, typically ranging from four to eight.
#14. Wheel Studs
Wheel studs are threaded bolts that are permanently mounted to the vehicle’s hub. They protrude outwards from the hub and pass through the mounting holes in the wheel. Lug nuts are then screwed onto the wheel studs to clamp the wheel securely against the hub.
#15. Wheel Bearings
Wheel bearings are located within the hub assembly and allow the wheel to rotate smoothly and with minimal friction. They are crucial for efficient wheel rotation and overall vehicle handling. Wheel bearings are designed to withstand significant loads and require periodic inspection and replacement as part of routine vehicle maintenance.
#16. Wheel Spacers
Wheel spacers are aftermarket components installed between the wheel and the hub. They are used to increase the wheel offset, effectively pushing the wheels further outwards from the vehicle. Spacers are often used for aesthetic purposes, to improve wheel fitment with aftermarket wheels, or to create more clearance for brake components.
#17. Wheel Seal
Wheel seals are used to prevent contaminants like dirt, water, and debris from entering the wheel bearing assembly. They also prevent grease from leaking out of the bearings. Maintaining effective wheel seals is important for prolonging the life of wheel bearings.
#18. Wheel Bolts
In some vehicles, particularly European models, wheel bolts are used instead of wheel studs and lug nuts. Wheel bolts thread directly into the hub to secure the wheel. The function is the same as wheel studs and lug nuts, but the fastening method is different.
#19. Wheel Locks
Wheel locks are specialized lug nuts or bolts designed to prevent wheel theft. They typically require a unique key for removal, providing an added layer of security for expensive wheels and tires.
#20. TPMS Sensor (Tire Pressure Monitoring System)
The TPMS sensor is a small electronic device often integrated into the valve stem or wheel rim. It monitors the air pressure inside the tire and transmits this information to the vehicle’s onboard computer, alerting the driver to low tire pressure conditions. TPMS sensors are a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles.
#21. Rim Flange
The rim flange, in a broader context, can refer to the entire flared edge of the rim barrel, encompassing both the inboard and outboard flanges. It’s the outermost part of the rim that directly interfaces with the tire bead.
#22. Bead (Tire Bead)
While “bead” was already mentioned in the context of the rim’s bead seat, it’s important to reiterate the tire bead. The tire bead is the reinforced edge of the tire that is designed to seat securely against the rim’s bead seat. It’s constructed of strong, often steel, wires encased in rubber, providing the necessary strength and sealing capability.
#23. Wheel Balancing Weights
Wheel balancing weights are small weights that are attached to the wheel rim to correct any imbalances in the wheel and tire assembly. These imbalances can cause vibrations at higher speeds. Balancing weights ensure smooth and vibration-free driving.
#24. Wheel Valve Cap
The wheel valve cap is a small plastic or metal cap that screws onto the end of the valve stem. Its primary purpose is to protect the valve core from dirt and debris and to prevent air leaks.
#25. Dust Cap
The dust cap is a protective cover that fits over the outer end of the wheel hub. It’s designed to keep dust, dirt, and moisture out of the wheel bearing assembly, contributing to bearing longevity.
Conclusion
Understanding the names and functions of car wheel parts is more than just automotive trivia; it’s practical knowledge that empowers you to better maintain your vehicle and communicate effectively with mechanics. From the tire to the valve stem, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient vehicle operation. By familiarizing yourself with these parts, you’re taking a step towards becoming a more informed and proactive car owner.