Car batteries are the unsung heroes of our vehicles. They are the lifeblood, providing the necessary power to start your engine and keep all the electrical components running smoothly. Whether you drive a traditional fuel engine car or a modern electric vehicle, a functioning battery is absolutely crucial. Think of your car battery not just as a box, but as an energy reservoir. It diligently stores chemical energy and, upon ignition, instantly converts it into electrical energy, bringing your car to life. Understanding the Battery Parts Car is essential for any car owner.
This article dives deep into the intricate world of battery parts car. We will explore each component in detail, helping you understand how they contribute to the overall function of this vital automotive part.
What Exactly is a Car Battery?
In simple terms, a car battery is a device designed to convert chemical energy into electrical energy. Specifically, the car battery, also known as an automobile battery, stores chemical energy but is engineered for rapid conversion to electricity the moment you turn the ignition key.
Most car batteries are designed to be rechargeable, typically utilizing wet-cell technology. Regardless of the vehicle type, the fundamental role of all car batteries remains consistent: to power the vehicle and its array of electrical systems.
When you start your car, the battery delivers a surge of electric current. This initial jolt triggers the internal combustion engine (in fuel cars) or activates the electric motor (in EVs), setting your vehicle in motion. Beyond starting, the battery is also responsible for powering essential electrical accessories such as headlights, radio, windshield wipers, and more.
Components of a Typical Car Battery: A Detailed Breakdown
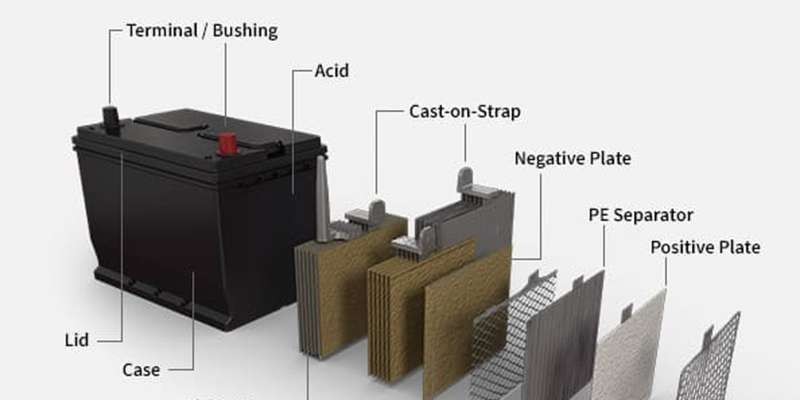
A standard car battery is housed within a protective battery case or box. However, the real magic happens inside, thanks to a collection of carefully engineered battery parts car. Let’s explore these essential components:
Battery Acid (Electrolyte)
Often referred to as the electrolyte, battery acid in a traditional lead-acid battery is a precisely formulated solution of sulfuric acid and water, typically ranging from 36% to 40% concentration. This mixture is crucial as it acts as the catalyst for the chemical reactions that generate the electric current needed to power your vehicle. The purity of this acid is paramount; contaminants can negatively impact its effectiveness in electricity production for your car battery.
The interaction between the battery acid and other battery parts car upon ignition is what produces the necessary voltage to start your engine. A weak or depleted battery acid solution can lead to insufficient voltage, hindering your car’s ability to start.
Battery Terminals (Bushings)
Battery terminals, sometimes called battery bushings, are the vital connection points that bridge the car battery to your vehicle’s electrical system. Like any electrical component, a car battery has two terminals: a positive terminal (+) and a negative terminal (-), connecting to the respective positive and negative straps of the battery end cells within. These battery parts car facilitate the flow of electricity to and from the battery.
Battery Case (Enclosure)
The battery case is a robust outer shell that encases the internal battery parts car in both fuel and electric vehicles. This protective enclosure is crucial for safeguarding the delicate internal components. For traditional fuel car batteries, the battery case and cast-on straps are often constructed from polypropylene resins, chosen for their durability and resistance to battery acid. In electric vehicles, EV battery cases are often made with lightweight yet strong aluminum alloys. The battery case provides critical protection against physical impacts, vibrations, and environmental factors, significantly extending the lifespan of the car battery.
Battery Plates (Positive and Negative)
A typical car battery contains both positive and negative battery plates. Each battery plate consists of a metallic grid structure. The positive battery plate is coated with lead dioxide, while the negative battery plate is made of spongy lead. A cast-on strap is positioned at the top of each battery plate, connecting each plate to the battery cells, forming part of the internal conductive pathway within the battery parts car system.
Battery Separator
The battery separator is a critical insulating component within car battery parts. As its name suggests, the battery separator is designed to physically separate the positive and negative battery plates within each cell. This prevents direct electrical contact and short circuits, which could damage the battery or cause failure. Battery separators are typically made from porous materials like polyethylene or other specialized plastic polymers that allow the electrolyte to flow freely while maintaining electrical isolation between the plates.
Working Principles: How Car Battery Parts Car Power Your Ride
The primary function of a car battery is to supply the electrical current necessary to power all of your vehicle’s electrical systems. Even when your car is turned off, the battery provides a small amount of energy to maintain certain functions, such as the car’s computer memory and alarm system. However, the real power surge is unleashed when you ignite the engine. Let’s break down the working principles of car battery parts car in action:
-
Chemical Reaction and Energy Conversion: When you turn the ignition key, a chemical reaction is initiated within the car battery. This reaction, facilitated by the battery acid and battery plates, transforms stored chemical energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy surge is then directed to the car’s starter motor.
-
Voltage Regulation and Stabilization: Once the engine is started, the car battery plays a vital role in voltage stabilization. It ensures a steady and regulated flow of electric current throughout the vehicle’s electrical system. Without this regulation, voltage fluctuations could lead to damage or malfunction of sensitive electronic components.
It’s important to note that starting a car engine typically requires only about 3% of the car battery’s total capacity. This is why car batteries are designed to deliver a high current burst for a short duration, primarily for starting, lighting, and ignition – often referred to as SLI batteries.
Exploring Different Types of Auto Batteries
The type of car battery in your vehicle can influence its overall performance and longevity. Choosing the right battery parts car and battery type is crucial for optimal vehicle operation. Here’s a brief overview of different types of vehicle batteries:
Primary Cell Batteries (Non-Rechargeable)
These are single-use, non-rechargeable batteries, like common AA or AAA batteries used in household devices. They are typically alkaline batteries composed of zinc and carbon. Primary cell batteries are not commonly found in automobiles because of their non-rechargeable nature and limited power capacity for vehicle applications. They are also becoming less popular due to environmental concerns related to disposal after single use.
Secondary Cell Batteries (Rechargeable)
Secondary cell batteries are rechargeable, making them ideal for automotive applications. They are composed of electrolytic materials, including the electrolyte and electrodes, which are essential battery parts car for powering vehicles. These are the standard battery type for cars, with common examples including:
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are the most traditional and widely used type of car battery, particularly in fuel engine vehicles. They were instrumental in pioneering rechargeable battery technology. Lead-acid batteries offer a high power-to-weight ratio, delivering significant power relative to their size. Beyond automotive use, they are also utilized in applications like hospitals and telecommunication towers as reliable backup power sources.
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are increasingly prevalent in automobiles, especially in electric vehicles and hybrid cars. Li-ion batteries boast a high energy density, meaning they can store a large amount of energy in a compact size. This characteristic allows EVs to achieve longer driving ranges on a single charge. Li-ion car batteries also exhibit a low self-discharge rate, meaning they retain their charge for extended periods, even when the vehicle is not in use.
Solid-state batteries are emerging as a promising advancement in battery parts car technology. Solid-state batteries aim to eliminate the need for a liquid electrolyte, hence the “solid-state” designation. They utilize solid, ceramic-like materials as the electrolyte. This innovative design offers potential advantages, including faster charging times, improved safety, and easier transportation. Solid-state batteries are rapidly gaining traction in the electric vehicle sector due to their enhanced performance characteristics.
Generally, secondary batteries are far more practical and environmentally conscious than primary batteries due to their rechargeable nature and extended lifespan.
Key Functions of Car Batteries: Beyond Just Starting
Car batteries perform several crucial functions that go beyond simply starting the engine. Here’s a summary of the essential roles of car batteries:
Engine Starting Powerhouse
Without a functional car battery, starting most car engines would be virtually impossible. The battery acts as the primary power source, storing chemical energy and instantaneously converting it to electrical energy upon ignition. This electrical power is then distributed to the starter motor and other essential battery parts car and vehicle systems required for engine startup.
Electrical Power Storage
The car battery serves as an energy reservoir, storing power that is needed to restart the car and operate various electrical accessories. A healthy battery should retain sufficient charge to power the vehicle even after periods of storage, ensuring reliable starting when needed. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over, recharging the car battery and replenishing the stored chemical energy for future use.
Collaboration with Alternator for Electrical Component Power
The alternator is responsible for continuously supplying power to the vehicle’s electrical systems while the engine is running, including lights, air conditioning, wipers, and the radio. However, the car battery provides the initial power surge to activate the alternator and subsequently assists in powering these electrical components, especially when the electrical load exceeds the alternator’s output or at low engine speeds.
Voltage Regulation and System Protection
Modern car batteries are designed with features that contribute to voltage regulation within the vehicle’s electrical system. In situations where other car components might generate voltage spikes or surges, the battery can act as a buffer, absorbing excess energy and preventing damage to sensitive electronics. This voltage regulation function enhances the overall reliability and longevity of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Conclusion: Maintaining Your Battery Parts Car for Optimal Performance
For your vehicle to operate at its best, ensuring your car battery and its battery parts car are in optimal condition is paramount. Missing or malfunctioning battery parts car, such as damaged electrodes or depleted electrolyte, will compromise battery function. The robust battery case is essential for protecting internal components, preventing leaks, and ensuring user safety by containing potentially hazardous materials. Regular battery maintenance and understanding the role of each battery part car will contribute to a longer battery lifespan and reliable vehicle performance.
FAQs About Battery Parts Car
What are the basic components of a car battery (battery parts car)?
The fundamental battery parts car include the electrolyte (typically sulfuric acid in lead-acid batteries or lithium salts in Li-ion batteries), positive plates (anode), and negative plates (cathode). The battery case is also a critical component, providing protection and containment for all internal battery parts car. The case is essential for safety, preventing leaks of hazardous materials and ensuring the battery’s structural integrity.
What is the liquid inside a car battery (battery parts car)?
In a traditional lead-acid car battery, the liquid is the electrolyte, often referred to as battery acid due to its acidic nature. It’s a solution of sulfuric acid and water. In lithium-ion car batteries, the liquid electrolyte is a solution of lithium salts, such as LiPF6, LiClO4, or LiBF4, dissolved in organic solvents.