The era when vehicles operated without electrical components is long behind us. Early automobiles relied on gas-powered lights, hand cranks for starting, and bells instead of horns. However, the automotive landscape drastically changed around 1920 when battery-powered electric starters became standard in almost every car.
Since then, Electrical Parts Of A Car have become indispensable. The electrical system is not merely for starting the engine; it’s critical for overall vehicle operation and safety. Understanding these components and their functions is crucial for every car owner.
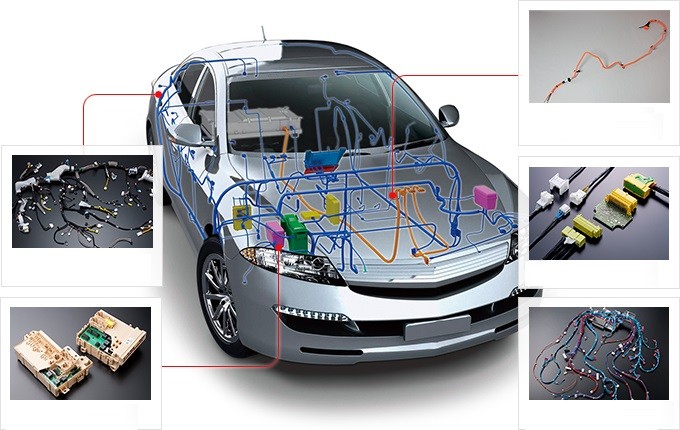 Diagram showcasing essential electrical parts of a car, including battery, alternator, and starter motor
Diagram showcasing essential electrical parts of a car, including battery, alternator, and starter motor
Key Electrical Components of a Car
Modern vehicles incorporate a complex network of electrical parts. Here are some of the most vital components:
Alternator: In older car models, battery charging relied on gas-powered systems. Today, the alternator, also known as a dynamo in some contexts, is the standard. Connected to the engine via a belt or gear, the alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This generated electricity serves a dual purpose: it continuously recharges the car battery and provides power to all other electrical components while the engine is running.
Battery: Often considered the heart of a car’s electrical system, the battery is an essential electrical part of a car. Its primary function is to provide the initial surge of power needed by the starter motor to crank the engine. Beyond engine starting, the battery acts as a power reservoir. It can supply energy to various accessories like the audio system, headlights, and air conditioning, even when the engine is turned off. The battery is truly the backbone of the vehicle’s electrical network.
Starter Motor: The starter motor has a singular yet critical role: initiating engine operation. This robust, battery-powered motor engages with the engine’s flywheel, rotating the crankshaft at a speed sufficient to start the combustion process. Starters require a significant jolt of electrical current for a brief period. To ensure longevity and efficient operation, it’s advisable to switch off non-essential electrical loads like headlights and the audio system before starting the engine.
Ignition System (Fuel Pump Switch Implied): For gasoline engines, the ignition system, which includes components like the ignition coil, is crucial for generating the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture. While the original text mentions a “fuel pump switch,” this is more relevant to diesel engines where continuous fuel injection is necessary for operation. In both gasoline and diesel engines, the electrical system plays a key role in managing the fuel delivery and combustion process.
Cooling Fans: Traditional cooling fans were mechanically driven by the engine. Modern vehicles, especially after advancements in areas like 4WD systems, frequently utilize electric cooling fans, also known as radiator fans. These fans are powered by the car’s electrical system, allowing them to operate even after the engine is switched off. This is particularly useful in preventing overheating after engine shutdown, especially in hot conditions or after heavy use.
Air Conditioner Blower: The air conditioning system in modern cars relies on an electric blower fan. Located within the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system, this fan circulates air through the vents and into the cabin, providing cooling and ventilation. The blower’s speed is typically controlled by a switch or knob on the dashboard, allowing for adjustable airflow.
Lighting System: From headlights and taillights to interior cabin lights, the entire lighting system in a car is electrically powered. Modern car lights are designed to be energy-efficient while providing ample illumination for safety and visibility. Being battery-powered, car lights can be used even when the engine is not running, though prolonged use can drain the battery. This is a significant advancement from older gas-powered lighting systems.
Motors (Wipers and Windows): Numerous electric motors are used throughout a vehicle for various functions. Windshield wipers, essential for safe driving in inclement weather, are powered by an electric motor. Similarly, power windows, a standard feature in most modern cars, are operated by individual electric motors located in each door. These motors are typically powered by both the battery and the car’s electrical system when the engine is running.
Other Important Automotive Electrical Components
Beyond these major components, numerous other automotive electrical components play crucial roles in a vehicle’s operation:
-
On-Board Computer (ECU): The Engine Control Unit (ECU), often referred to as the on-board computer, is the brain of the modern car. It’s a sophisticated electronic control system that manages and monitors various engine and vehicle functions, from fuel injection and ignition timing to emissions control and transmission operation.
-
Fuse Box and Relays: The fuse box houses fuses, which are safety devices that protect electrical circuits from overloads. Relays are electrically operated switches that allow low-current circuits to control high-current circuits, essential for managing power distribution to various components.
-
Combination Switch: Typically located on the steering column, the combination switch integrates controls for multiple functions like headlights, turn signals, windshield wipers, and sometimes cruise control, into a single unit for driver convenience.
-
Wiring and Signal Transmission: A complex network of wires, connectors, and harnesses forms the nervous system of the car’s electrical system. This wiring network transmits electrical power and signals throughout the vehicle, connecting all the electrical components and enabling them to communicate and function together.
These electrical parts are fundamental to a car’s functionality. Malfunctions in any of these components can lead to significant operational issues. Experts recommend seeking immediate professional help from a qualified mechanic if you suspect any electrical problems to prevent further damage and ensure safe vehicle operation. Fortunately, automobile parts manufacturing companies widely produce these electrical components, making replacements readily available.