Understanding the different parts of a car is essential knowledge for any vehicle owner, enthusiast, or anyone interested in automotive mechanics. Whether you’re trying to describe a problem to a mechanic, learning about car maintenance, or simply expanding your automotive vocabulary, knowing the names and locations of car parts is incredibly useful.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the major components of a car, using clear descriptions and helpful visuals to aid your understanding. Let’s dive into the world of automotive anatomy and explore the essential parts that make your vehicle run.
Exploring Car Part Names and Locations
Let’s begin by categorizing car parts based on their general location on the vehicle. This will help you systematically learn and remember different components.
Inside the Car: Interior Car Parts
The interior of your car is where you interact with the vehicle most directly. Knowing the names of these parts is crucial for comfortable and safe driving.
| English | Description |
|---|---|
| Accelerator Pedal | Controls the car’s speed by regulating fuel flow to the engine. |
| Brake Pedal | Used to slow down or stop the vehicle by applying pressure to the brakes. |
| Clutch Pedal | (Manual transmissions) Disengages the engine from the transmission to allow gear changes. |
| Gear Shift/Selector | Used to select different gears for driving, neutral, and reverse. |
| Glove Compartment | A storage space built into the dashboard, often used for documents and small items. |
| Handbrake/Parking Brake | A lever or pedal used to engage the rear brakes for parking, preventing the car from rolling. |
| Horn | A sound device used to warn others. |
| Floor Mats | Removable coverings for the car floor to protect the carpet. |
| Rearview Mirror | Provides a view of the road and traffic behind the vehicle. |
| Seatbelt | A safety device designed to secure the occupant against harmful movement during a collision or sudden stop. |
| Seats | Places for the driver and passengers to sit. |
| Steering Wheel | Used to control the direction of the vehicle. |
| Power Steering System | Assists the driver in steering by reducing the effort needed to turn the wheel. |


Further Exploration: For a deeper understanding of vehicle safety, research “automotive safety features” to learn about advancements beyond seatbelts.
Outside the Car: Exterior Car Parts
The exterior car parts are what you see when you look at a car from the outside. These parts contribute to the car’s aesthetics, aerodynamics, and safety.
| English | Description |
|---|---|
| Bumper | Front and rear protective bars designed to reduce damage in a low-speed collision. |
| Door Handles | Levers used to open and close the car doors. |
| Doors | Hinged panels that allow entry and exit from the vehicle. |
| Fenders (Front & Back) | Body panels that surround the wheel wells, protecting the car from road debris and reducing spray. |
| Grill | A decorative and functional panel at the front of the car, allowing air to flow to the radiator and engine. |
| Headlights | Powerful lights at the front of the car used to illuminate the road ahead at night or in low visibility. |
| Hood/Bonnet | The hinged cover over the engine compartment. |
| Hubcaps/Wheel Covers | Decorative covers for the wheels. |
| Indicator Lights/Turn Signals | Flashing lights to indicate the direction the car intends to turn. |
| License Plate | A plate displaying the car’s registration number for identification. |
| Side Mirrors/Outside Mirrors | Mirrors on the doors providing a view of the sides and rear of the vehicle. |
| Roof | The top covering of the car. |
| Sunroof/Moonroof | An opening in the car roof that can be opened to let in light and air. |
| Tail Light | Lights at the rear of the car, including brake lights, turn signals, and running lights for visibility. |
| Trunk/Boot | The main storage compartment at the rear of the car. |
| Wheels | Circular components that allow the car to move, typically fitted with tires. |
| Windows | Transparent panels in the car doors and body for visibility and weather protection. |
| Windshield | The large front window providing a clear view ahead. |
| Windshield Wipers | Mechanical arms with rubber blades used to clear rain, snow, and debris from the windshield. |
Did you know? The design of exterior car parts significantly impacts a vehicle’s fuel efficiency and handling due to aerodynamics.
Under the Hood: Engine and Mechanical Parts
The parts under the hood are the heart of your vehicle. Understanding these components is key to comprehending how a car operates.
| English | Description |
|---|---|
| Air Filter | Cleans the air entering the engine, removing dust and debris. |
| Alternator | Charges the battery and powers the electrical system when the engine is running. |
| Battery | Stores electrical energy to start the engine and power electrical components when the engine is off. |
| Belt (Serpentine/Drive Belt) | Transfers power from the engine to various components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. |
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. |
| Carburetor | (Older vehicles) Mixes air and fuel for combustion in the engine. (Replaced by fuel injection in modern cars). |
| Catalytic Converter | Reduces harmful emissions from the exhaust system. |
| Ignition Coil | Transforms the battery’s low voltage to the thousands of volts needed to create a spark in the spark plugs. |
| Combustion Chamber | The space in the engine cylinder where the air-fuel mixture is burned. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the drivetrain. |
| Fuel Pump | Pumps fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. |
| Ignition System | The system responsible for starting the combustion process in the engine. |
| Piston Rod/Connecting Rod | Connects the piston to the crankshaft, transmitting force. |
| Pulley | A grooved wheel that helps guide and tension belts. |
| Radiator | Cools the engine coolant to prevent overheating. |
| Exhaust Valve | A valve that allows exhaust gases to escape from the combustion chamber. |
| Thermostat | Regulates the engine’s temperature by controlling coolant flow. |
| Vacuum Diaphragm | Used in various systems for control and actuation, often in older emission control or transmission systems. |
| Valve | Controls the flow of fluids or gases within the engine and other systems. |
| Voltage Regulator | Maintains a constant voltage level in the electrical system. |
Explore Further: To deepen your knowledge, research “internal combustion engine” or “automotive mechanics” for detailed explanations of these systems.
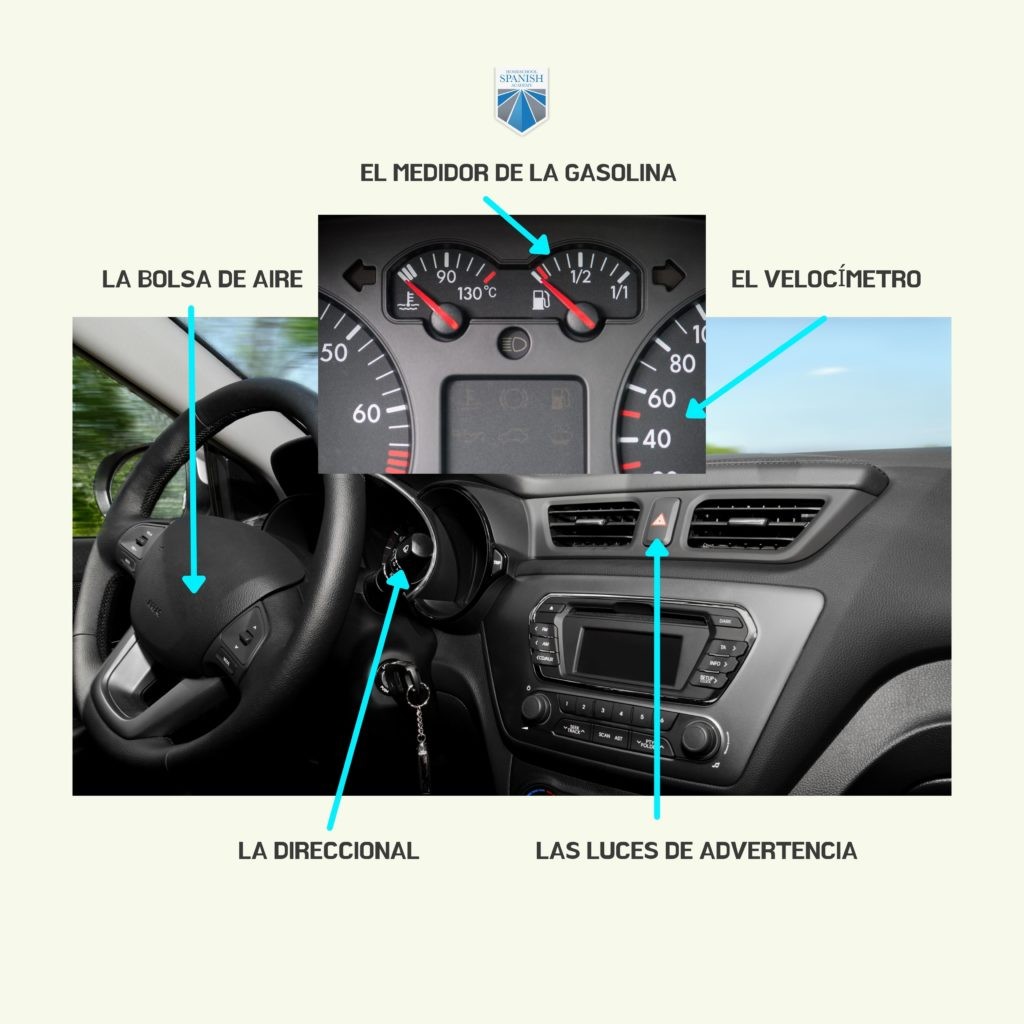
Instrument Panel: Dashboard Components
The instrument panel, or dashboard, provides crucial information about the car’s operation and status.
| English | Description |
|---|---|
| Airbag Indicator Light | Warns of issues with the airbag system. |
| Fuel Gauge/Gas Gauge | Indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the tank. |
| Speedometer | Displays the vehicle’s current speed. |
| Turn Signal Indicator | Lights on the dashboard that flash when turn signals are activated. |
| Warning Lights/Dashboard Lights | Various lights that illuminate to indicate potential problems or system status (e.g., engine light, oil pressure light). |
Safety Tip: Familiarize yourself with your car’s warning lights and their meanings in your owner’s manual.
Essential Car Maintenance Vocabulary
Beyond just naming parts, knowing verbs related to car maintenance and operation is equally important. Here are some key actions you might perform or discuss regarding your car:
| English Action | Description |
|---|---|
| To Accelerate | To increase the speed of the car. |
| To Reverse/Back Up | To move the car in the opposite direction of forward travel. |
| To Brake | To slow down or stop the car using the brakes. |
| To Change Lanes | To move the car from one lane to another on a multi-lane road. |
| To Fasten Seatbelt | To secure the seatbelt for safety. |
| To Fill Up the Tank/Refuel | To add fuel to the car’s fuel tank. |
| To Park | To stop and leave the car in a designated area. |
| To Run Out of Gas/Fuel | To deplete the car’s fuel supply. |
| To Slow Down | To decrease the speed of the car. |
| To Speed Up | To increase the speed of the car quickly. |
| To Start a Car | To initiate the engine’s operation. |
| To Start the Ignition | To begin the process of starting the engine. |
| To Stop the Car | To bring the car to a complete halt. |
Practical Application: Use these verbs when talking to a mechanic or reading car maintenance guides.
Expanding Your Automotive Knowledge
Learning about car parts and their names is a continuous process. As automotive technology evolves, new components and systems are introduced. By using this guide as a starting point and continuing to explore resources like online diagrams, repair manuals, and automotive websites, you can build a solid understanding of vehicle anatomy. This knowledge not only empowers you as a car owner but also opens up a deeper appreciation for the complexity and ingenuity of modern automobiles.