Being a responsible car owner goes hand in hand with understanding your vehicle. Proactive maintenance is key, but sometimes, diving into the mechanics of a car can feel like entering a maze of complex systems. If you’ve ever looked under the hood or glanced at a detailed car diagram, you might have been struck by the sheer number of components. But have you ever stopped to ask, How Many Parts Does A Car Have exactly?
It’s a question that might surprise you. While it’s impossible to give an exact figure that applies to every single vehicle on the road, the answer is: a lot. Modern cars are marvels of engineering, comprised of tens of thousands of individual parts working in harmony to get you from point A to point B safely and efficiently. Understanding this complexity can not only make you a more informed car owner but also deepen your appreciation for the incredible machines we rely on daily.
Let’s embark on a journey to explore the fascinating world of automotive components, breaking down the major systems and shedding light on just how many parts contribute to the functionality of your car.
Delving into the Major Car Systems and Their Components
To truly grasp the answer to “how many parts in a car?”, it’s helpful to categorize them by the main systems that make up a vehicle. Each of these systems is a complex assembly in itself, containing numerous individual components.
Engine: The Heart of the Machine
The engine is often considered the heart of a car, and for good reason. This powerhouse is responsible for generating the motion that propels your vehicle. When considering car engine components, you’re looking at a multitude of parts, all crucial for combustion and power generation.
Keeping your engine in top shape is vital for your car’s performance and longevity.
Key engine parts include:
- Cylinder Block and Pistons: The foundation of the engine, housing cylinders where pistons move to convert combustion energy into mechanical force.
- Crankshaft and Camshaft: Working in tandem, the crankshaft converts piston motion into rotational power, while the camshaft precisely controls valve timing for efficient combustion.
- Intake and Exhaust Manifolds: Managing airflow, the intake manifold brings in air, and the exhaust manifold expels gases after combustion.
The engine system alone can easily contain hundreds of parts when you consider every valve, gasket, sensor, and bolt that contributes to its operation.
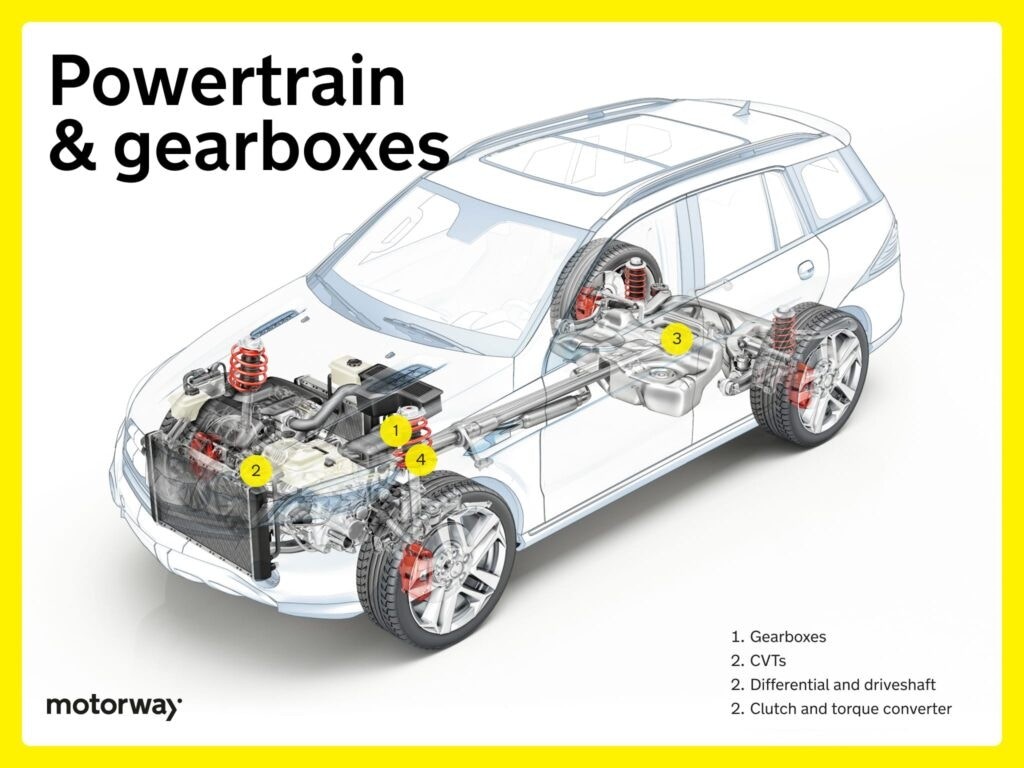
Powertrain and Gearboxes: Transferring Power to the Wheels
The powertrain system takes the power generated by the engine and transmits it to the wheels, enabling movement. Car powertrain and gearbox components are essential for controlling speed and torque.
The gearbox, or transmission, is a critical part of the powertrain system.
Key powertrain and gearbox components include:
- Gearboxes (Transmissions): Available in manual, automatic, and CVT variations, gearboxes manage gear ratios to optimize engine power for different driving conditions. Automatic gearboxes, in particular, are complex systems with numerous internal parts.
- Differential and Driveshaft: The driveshaft carries power from the transmission, and the differential distributes it evenly to the wheels, especially during turns.
- Clutch and Torque Converter: In manual transmissions, the clutch allows for gear changes, while automatic transmissions use a torque converter for smooth power transfer.
The transmission, especially automatic versions, is a highly intricate assembly with hundreds of moving parts, contributing significantly to the overall number of parts in a vehicle.
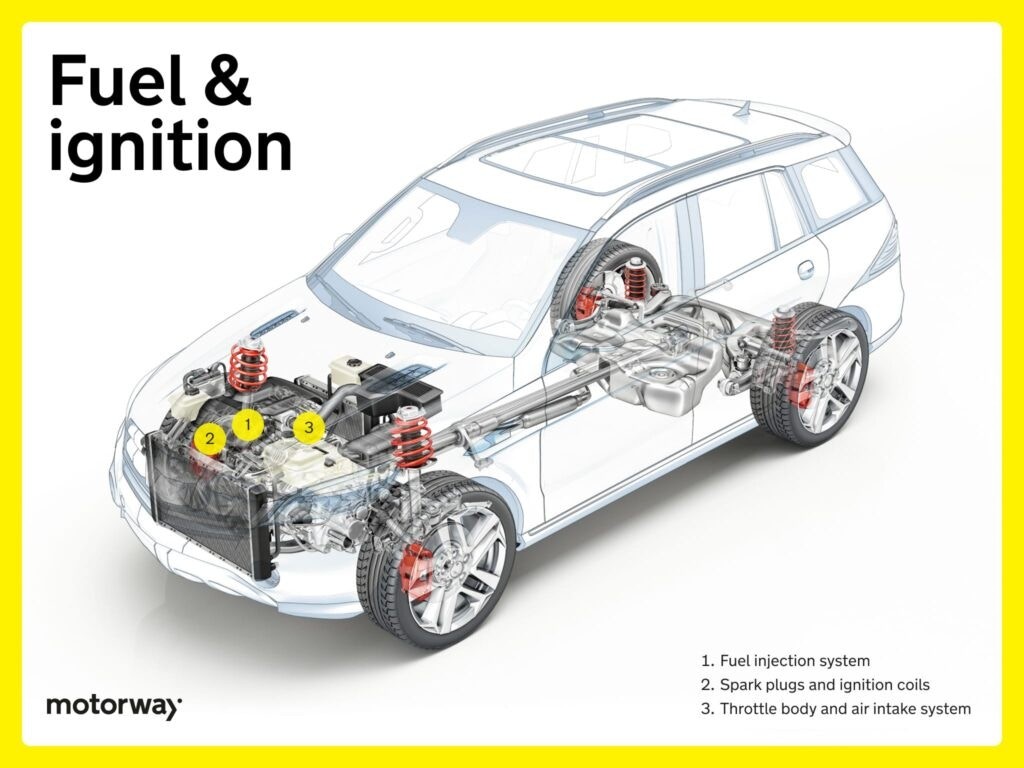
Fuel and Ignition Systems: Enabling Combustion
For internal combustion engine cars, the fuel and ignition systems are critical for starting and running the engine. The car fuel and ignition system ensures the engine receives the right mixture of fuel and air, and that combustion is initiated at the precise moment.
A well-functioning fuel system is crucial for avoiding breakdowns.
Key fuel and ignition components include:
- Fuel Injection System: Modern fuel injection systems precisely deliver fuel into the cylinders for efficient combustion.
- Spark Plugs and Ignition Coils: Spark plugs create the spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture, and ignition coils provide the necessary high voltage.
- Throttle Body and Air Intake System: These regulate airflow into the engine, controlling power output and efficiency.
These systems, with their injectors, pumps, sensors, and wiring, add a considerable count to the total car parts.
Cooling and Lubrication: Maintaining Optimal Temperature
To prevent overheating and ensure smooth operation, cars rely on cooling and lubrication systems. These systems are vital for the longevity and reliability of the engine and other components.
Key cooling and lubrication components include:
- Radiator and Cooling Fans: The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant, and fans enhance airflow to keep the engine at the right temperature.
- Water Pump and Hoses: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine, and hoses provide pathways for coolant flow.
- Oil Pump and Oil Filter: The oil pump circulates oil for lubrication, and the oil filter removes contaminants to keep the oil clean.
- EV Battery Cooler System: Electric vehicles have specialized cooling systems for their batteries and electric motors.
Even seemingly simple components like hoses and clamps add to the overall part count, and these systems include various sensors and control units as well.
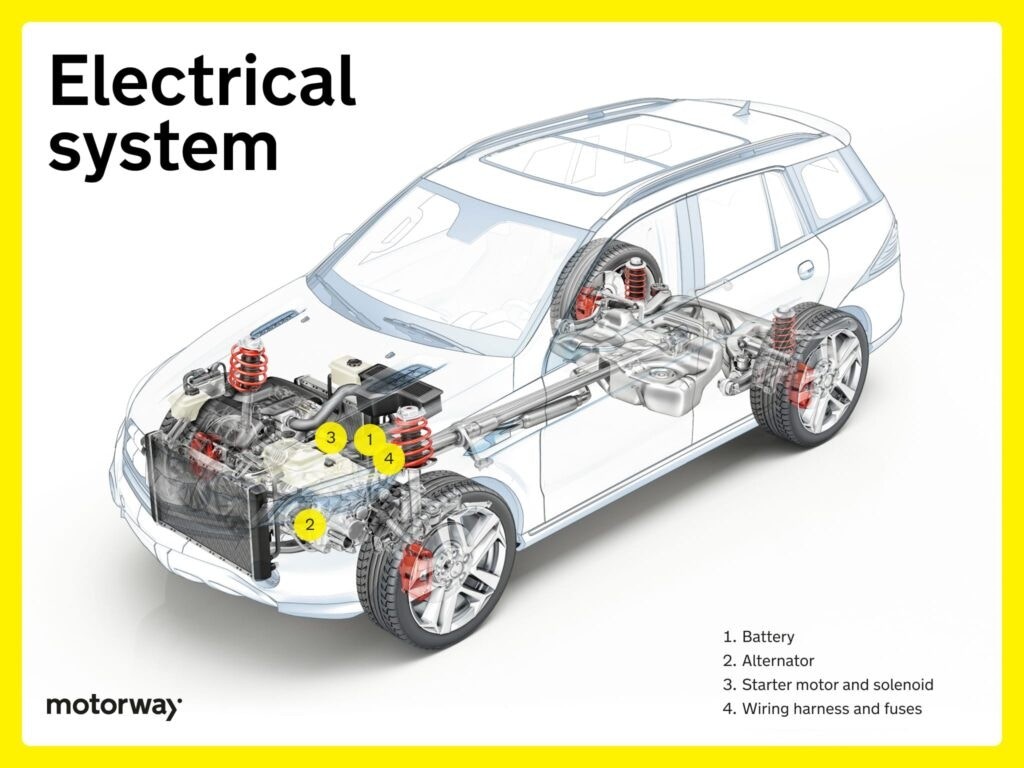
Electrical System: Powering Everything
The electrical system is the nervous system of your car, powering everything from the engine ignition to the infotainment system. Car electrical system components are spread throughout the vehicle, connecting and controlling various functions.
The electrical system underpins almost every function in a modern car.
Key electrical components include:
- Battery: Provides initial power to start the engine and power electrical accessories.
- Alternator: Recharges the battery and supplies power to electrical systems while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor and Solenoid: The starter motor turns the engine to initiate combustion.
- Wiring Harness and Fuses: Wiring harnesses distribute electricity throughout the car, and fuses protect circuits from overloads.
The complexity of modern car electronics, with extensive wiring, sensors, and control modules, means the electrical system alone contributes thousands of parts to the total parts of a car.
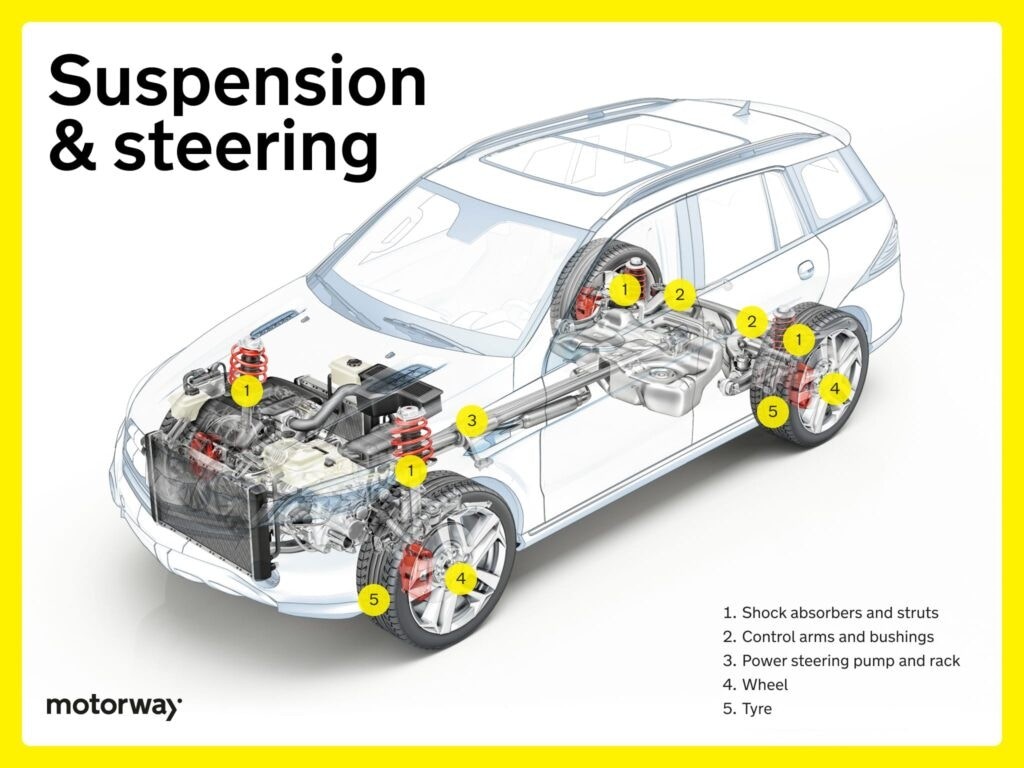
Suspension and Steering: Ensuring a Smooth and Controlled Ride
The suspension and steering systems are crucial for handling, stability, and ride comfort. These systems allow you to control the car and navigate various road conditions smoothly.
Suspension and steering systems are essential for vehicle maneuverability and comfort.
Key suspension and steering components include:
- Shock Absorbers and Struts: Dampen shocks and vibrations for a smoother ride.
- Control Arms and Bushings: Control arms connect suspension components, and bushings provide flexibility and reduce noise.
- Power Steering Pump and Rack: Power steering systems assist steering effort, making turning easier.
These systems, with their linkages, joints, and hydraulic components, add a significant number of parts to the car.
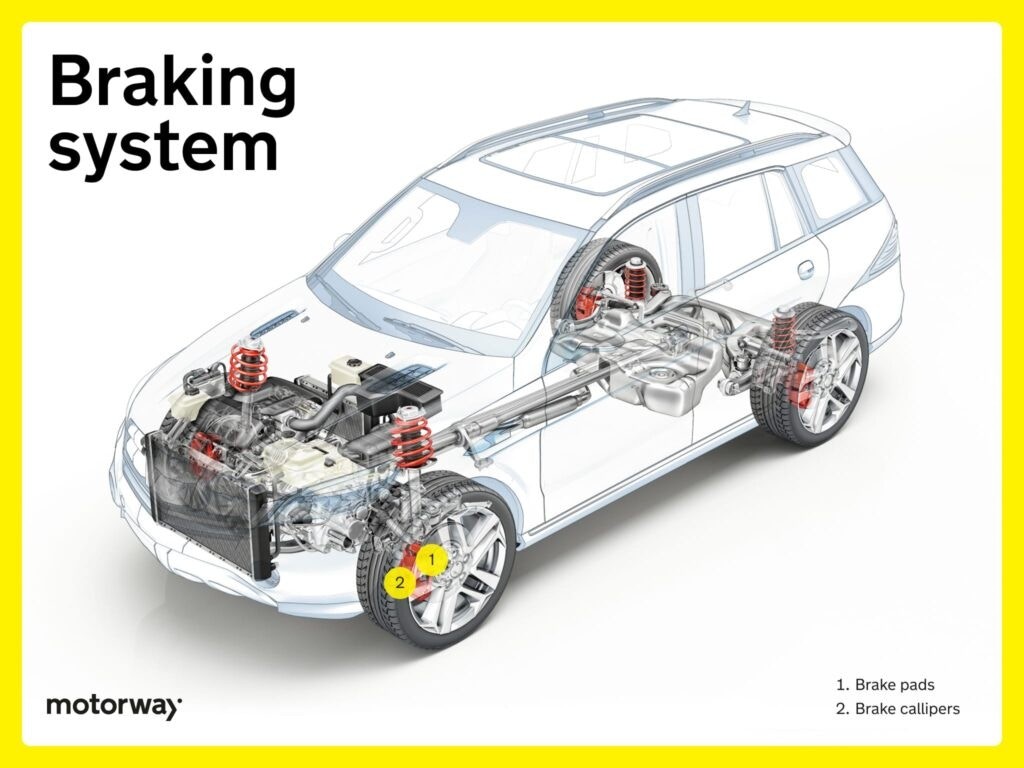
Braking System: Safety First
The braking system is arguably the most critical safety system in a vehicle. Reliable brakes are essential for controlled stopping and preventing accidents.
Regular checks of the braking system are vital for safety.
Key braking system components include:
- Brake Pads: Friction material that presses against rotors to slow the car.
- Brake Calipers: Hydraulic components that clamp brake pads onto rotors.
- Brake Rotors: Discs that brake pads grip to create friction.
While seemingly fewer in number compared to other systems, brake components are engineered to very high tolerances and are crucial for safety.
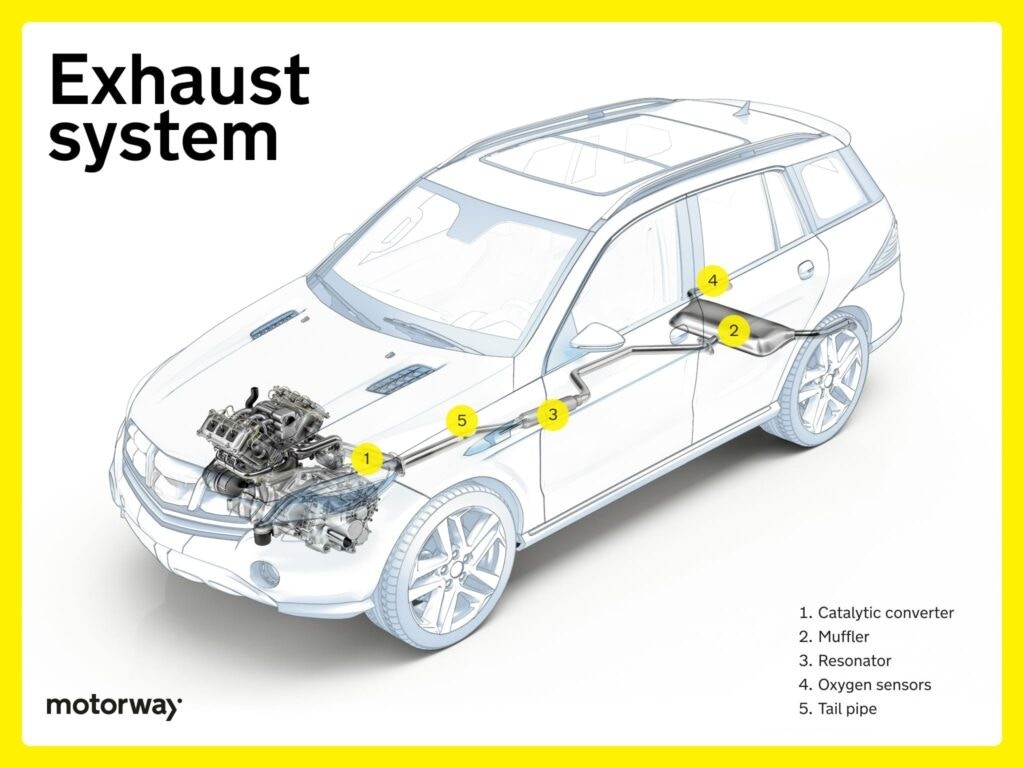
Exhaust System: Managing Emissions and Noise
The exhaust system is responsible for safely removing combustion gases from the engine, reducing harmful emissions, and minimizing noise.
A functioning exhaust system is important for both performance and environmental responsibility.
Key exhaust system components include:
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful pollutants in exhaust gases.
- Muffler and Resonator: Reduce exhaust noise for a quieter ride.
- Oxygen Sensors: Monitor exhaust gases to optimize engine efficiency and emissions control.
These components, along with pipes and hangers, contribute to the overall complexity of the vehicle.
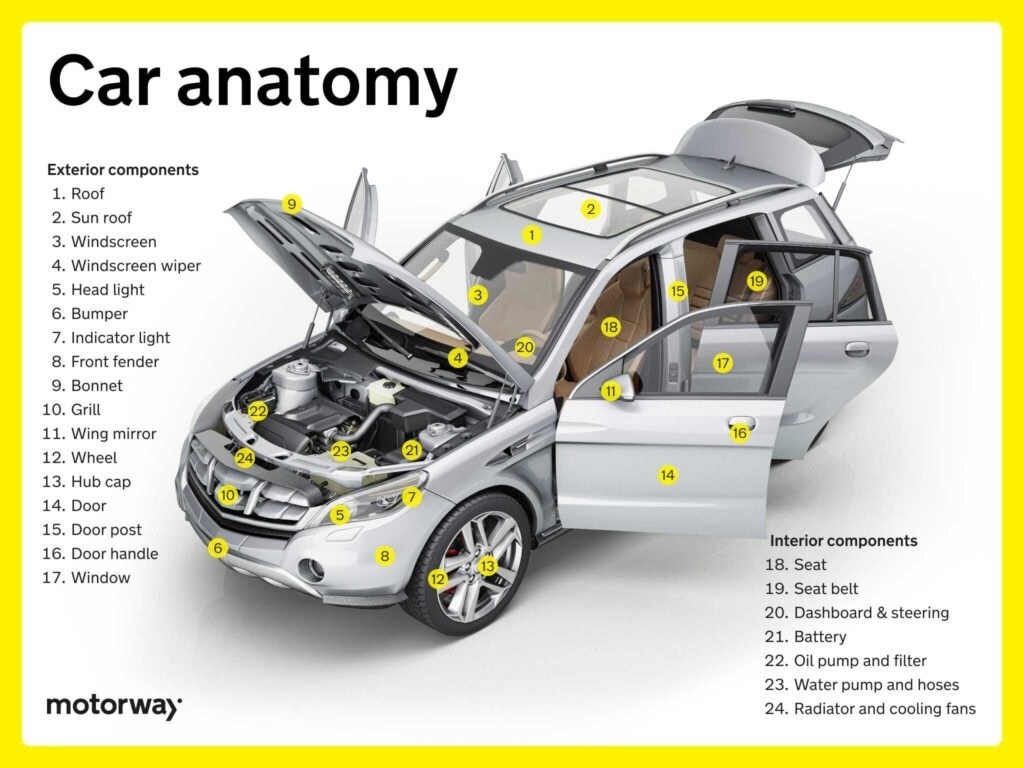
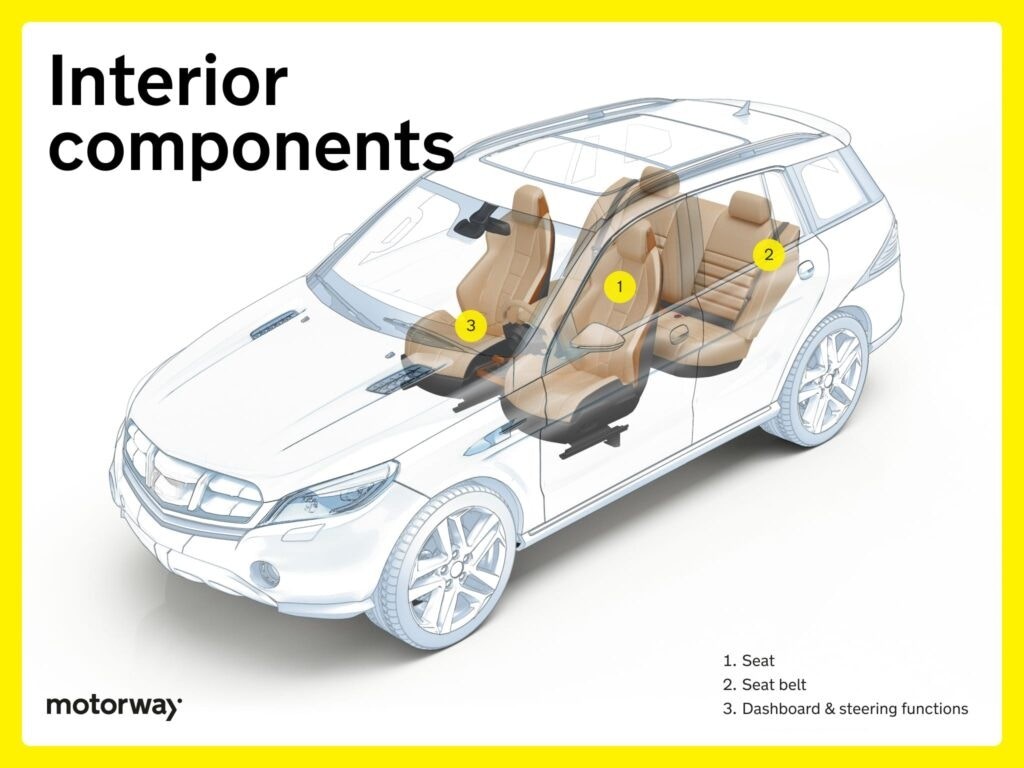
Interior and Exterior Components: Comfort, Aesthetics, and Functionality
Beyond the mechanical systems, a car has numerous interior and exterior components that contribute to comfort, aesthetics, and overall functionality.
Interior components greatly impact the driver and passenger experience.
Exterior components define the car’s look and provide protection.
Key interior components include:
- Seats and Seat Belts: Provide comfort and safety for occupants.
- Dashboard and Steering Functions: Display vital information and provide driver controls.
Key exterior components include:
- Doors, Windows, and Mirrors: Provide access, visibility, and weather protection.
- Body Panels and Trim: Shape the car’s aesthetics and protect internal components.
These categories encompass a vast array of parts, from simple screws and clips to complex electronic modules, all adding to the final car parts count.
Wheels and Tyres: The Point of Contact with the Road
Wheels and tyres are the car’s connection to the road, and they are critical for traction, handling, and ride comfort.
Key wheel and tyre components include:
- Tyres: Different types of tyres are designed for various conditions and purposes, each with its own construction and materials.
| Type of tyre | Function |
|---|---|
| Summer tyres | Crafted for warm weather, and excelling in both dry and wet conditions with optimal grip and precise handling. |
| Winter tyres | Engineered for cold climates, featuring specialised treads for improved traction on snow and ice-covered roads. |
| All-season tyres | Versatile performers suitable for various conditions, balancing traction and durability in both wet and dry weather. |
| Performance tyres | Designed for sportier driving, prioritising handling, grip, and responsiveness at higher speeds. |
| Off-Road tyres | Built for challenging terrains, featuring rugged treads and reinforced sidewalls for enhanced traction and durability. |
| Run-flat tyres | Equipped with reinforced sidewalls, enabling drivers to continue at reduced speeds for a limited distance even after a puncture. |
| Touring tyres | Focused on a smooth and comfortable ride, ideal for long-distance journeys with low road noise and good handling. |


- Wheels: Alloy and steel wheels have different construction types, affecting weight, durability, and aesthetics.
When it comes to wheel construction, there are several designs to consider:
- One-piece construction: The entire wheel is crafted from a single piece of material, typically alloy or steel. This design is commonly used for both alloy and steel wheels.
- Two-piece construction: In this design, the wheel consists of two main parts – the centre and the outer rim. These parts are usually bolted or welded together. Two-piece constructions are often found in performance or custom wheels.
- Three-piece construction: The wheel is composed of three separate pieces – the centre, the outer rim, and an inner hoop. This modular design allows for greater customization, making three-piece wheels a popular choice in the aftermarket scene.
- Forged construction: Forged wheels are made from a solid piece of metal that is compressed under high pressure. This process creates a wheel that is stronger and lighter compared to cast wheels. Forged wheels are often used in high-performance and racing applications.
- Multi-piece construction: This design combines multiple components, often including a centre section, an outer rim, and bolts. Multi-piece wheels offer versatility in terms of sizing and customization.
The choice of construction impacts factors such as weight, durability, and aesthetics, allowing drivers to select wheels that align with their performance and style preferences. You can also sometimes have a choice of material:
- Alloy wheels: Made from a mix of metals, often aluminium or magnesium. They are lightweight, providing better heat dissipation and enhancing a vehicle’s appearance.
- Steel wheels: Constructed from steel, ensuring robustness. Although heavier than alloy wheels, they are durable, cost-effective, and well-suited for rugged driving conditions.
- Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): A safety system that monitors tyre pressure and alerts the driver to any issues.
Even these seemingly simple systems contain sensors, valves, and electronic components that contribute to the overall count.
FAQs: Understanding Car Part Numbers
To further clarify the question of “how many parts are in a car?”, let’s address some frequently asked questions:
How many car parts are on a car?
While the exact number varies by model and complexity, a modern car typically has over 30,000 individual parts. This staggering number includes everything from major mechanical components to tiny fasteners, clips, and electronic elements. Some estimates even go as high as 50,000 parts for luxury or highly complex vehicles.
Does an electric car have fewer parts?
Yes, electric vehicles (EVs) generally have fewer parts than internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. This is primarily because EVs have a simpler powertrain, replacing the complex engine and transmission with an electric motor and battery system. While EVs still have thousands of parts, the reduction in mechanical components means they typically have fewer moving parts and are potentially less complex to manufacture and maintain in some aspects.
What are the important parts of a vehicle?
“Important” can be subjective, but critical parts are those that directly impact safety and functionality. These include:
- Engine: For generating power (in ICE cars).
- Transmission: For managing power delivery to the wheels.
- Braking System: For stopping the vehicle safely.
- Steering System: For controlling the vehicle’s direction.
- Suspension: For stability and ride comfort.
- Electrical System: For powering all electronic functions.
However, in reality, every part plays a role, and even a seemingly small component failure can impact the vehicle’s overall performance or safety.
What parts of a car can be sold separately?
Many car parts can be sold separately in the aftermarket, including:
- Engines and Transmissions: Major mechanical components are often rebuilt or reused.
- Body Parts: Panels, doors, bumpers, and lights are commonly replaced and sold individually.
- Electrical Parts: Alternators, starters, batteries, and electronic control units can be sold separately.
- Wheels and Tyres: These are often upgraded or replaced and sold individually or as sets.
The market for individual car parts is extensive, supporting repairs, customization, and vehicle recycling.
Why is there a shortage of car parts?
Car part shortages can occur due to various factors, including:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events, natural disasters, and economic factors can disrupt the complex international supply chains for automotive components.
- Increased Demand: Surges in car production or specific component demand can strain supply chains.
- Manufacturing Challenges: Production bottlenecks or shortages of raw materials can impact part availability.
- Global Events: Pandemics, trade disputes, and geopolitical instability can all contribute to part shortages.
These shortages can impact car production, repair times, and vehicle costs.
Appreciating Automotive Complexity
So, how many parts in a car? The answer is in the tens of thousands, highlighting the incredible complexity of modern vehicles. From the engine to the interior trim, every component plays a role in making your car function as intended. Understanding this intricate engineering can deepen your appreciation for the vehicles we use every day and emphasize the importance of proper maintenance and care.
Want to learn more about car ownership and maintenance? Explore more of our guides for valuable insights into keeping your vehicle in top condition.