Wheel bearings and hub assemblies are crucial for your vehicle’s performance, often working silently in the background. These essential components, though small and often overlooked, ensure smooth wheel rotation and are vital for safe driving. When wheel bearings wear out, timely replacement with high-quality parts is essential to maintain your vehicle’s optimal operation.
To help you better understand these components, we’ve created a detailed guide outlining the various parts of wheel bearings and hubs and their functions within your car wheel assembly. Let’s explore the anatomy of these vital parts.
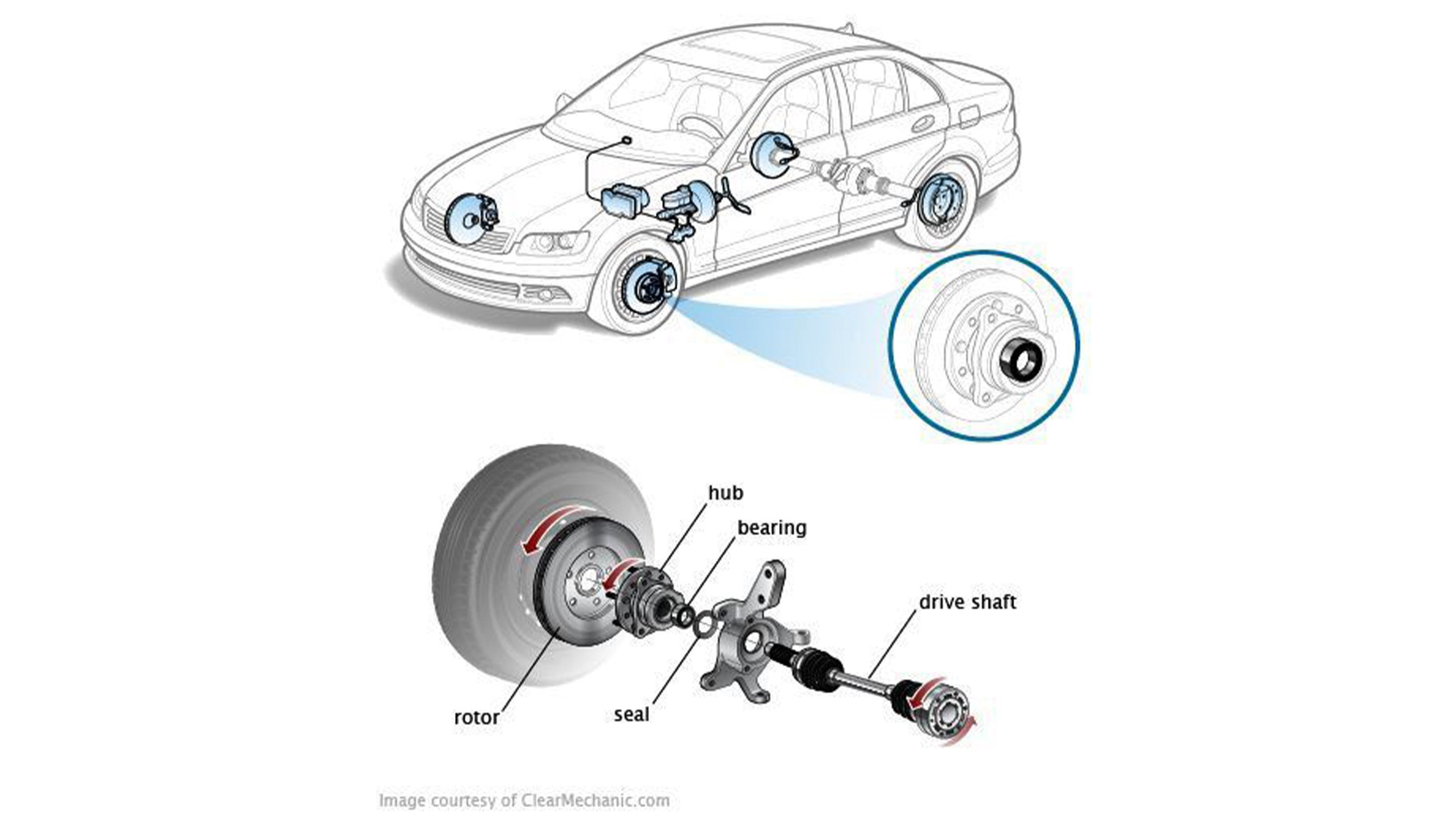
Locating Wheel Bearings in Your Vehicle’s Assembly
The diagram below illustrates the typical positioning of wheel bearings and hub assemblies in a standard vehicle. Each wheel incorporates a hub, bearing, and rotor, connected via a seal to the drive shaft through the axle shaft. This basic design principle remains consistent across different vehicle sizes, from compact cars to large trucks. For instance, while a Ford F-150 wheel bearing will be physically larger, its structure and function are similar to that of a Ford Explorer wheel bearing.
Alt text: Diagram showing car wheel assembly parts including the wheel bearing and hub location connected to the drive shaft and rotor.
The Function of Wheel Bearings in Car Wheel Assembly
Wheel bearings play a fundamental role in enabling your vehicle’s wheels to rotate with minimal friction. This smooth rotation is essential when engine torque is transferred to the wheels, facilitating movement. As a wheel bearing deteriorates, the corresponding wheel encounters increased resistance in rotation. This can lead to handling issues and potentially cause damage to the suspension system over time.
Typically, a worn wheel bearing will produce a noticeable rattling or grinding sound, providing ample warning before serious problems arise. Prompt replacement of a failing wheel bearing is crucial. Addressing this issue promptly prevents performance degradation and avoids more expensive mechanical repairs down the line.
Exploring the Components of Wheel Bearing & Hub Assemblies
A car wheel assembly comprises several key parts working in harmony. The primary components of the wheel bearing and hub assembly include the bearings themselves, the hub, the rotor, seals, and the drive shaft. Each component is designed to withstand the forces generated during braking and cornering, ensuring vehicle stability and control under normal driving conditions.
Alt text: Close-up of two car wheel bearings showcasing their metallic rings and rolling elements, essential parts of the wheel assembly.
Bearings: Enabling Wheel Rotation
Bearings typically consist of balls or tapered rollers contained within a metal ring. These rolling elements facilitate smooth movement on the axle shaft and fit snugly within the hub. Due to the constant stress and load they endure, wheel bearings are often more susceptible to wear and tear compared to other components in the wheel assembly. Regular inspection and timely replacement are vital for maintaining optimal vehicle performance.
Alt text: Car wheel hub assembly highlighting the mounting studs for wheel attachment and the central hole designed to house the wheel bearing.
Hub: The Wheel Assembly Connector
The hub serves as the central link, connecting the wheel directly to the vehicle’s axle. It also acts as the housing for the wheel bearings, protecting them and ensuring proper alignment. The hub is usually constructed from robust metal, often shaped as a disc with a slightly raised center section incorporating several studs for wheel mounting. A central bore in the hub is precisely machined to accommodate the wheel bearing.
Hubs can experience significant stress when the bearings they contain fail. A compromised hub can severely impact vehicle handling and safety. Therefore, prompt hub replacement is crucial when bearing failure occurs to maintain vehicle control and prevent further damage to the car wheel assembly.
Alt text: Image of a brake rotor, a critical car wheel assembly part responsible for braking performance.
Rotor: The Braking Force
Rotors are essential components of your vehicle’s braking system. When you apply the brakes, calipers squeeze brake pads against the rotors. This generates friction, slowing down the wheel’s rotation and bringing your vehicle to a stop. Effective rotors are vital for safe and responsive braking.
Alt text: Illustrative diagram of a car wheel assembly brake system, showing the brake rotor attached to the wheel hub with the brake pad and caliper.
Brake rotors endure considerable thermal and mechanical stress due to frequent energy absorption during braking. Consequently, they are subject to wear and require periodic replacement. Driving with worn brake rotors can mimic the symptoms of a failing wheel hub, such as vibrations during braking. However, a faulty hub or worn bearings might also cause a slight pull to one side. A professional mechanic can accurately diagnose the issue and identify the specific car wheel assembly part requiring replacement.
Alt text: Assortment of various car wheel bearing seals, designed to protect bearings from contaminants and retain lubricant.
Seals: Protecting Wheel Bearings
Seals are positioned between the bearings and the drive shaft in your car wheel assembly. Their primary function is to prevent contaminants, such as dirt, water, and road debris, from entering the bearing assembly and causing premature wear. These seals are critical for extending the lifespan of the wheel bearings.
Equally importantly, seals retain the grease that lubricates the bearings within the hub assembly. This lubricant is vital for minimizing friction and heat, thereby prolonging the operational life of both the hub and bearings. Regular inspection of seals and timely replacement of deteriorated seals are essential preventative maintenance steps.
Alt text: Schematic diagram illustrating the different parts of a car drive shaft, including the connection to the transmission, axle shaft, and differential, integral to the wheel assembly system.
Drive Shaft: Powering the Wheels
The drive shaft is a crucial component responsible for transmitting engine torque to the wheels, enabling vehicle movement. The transmission directs kinetic energy from the engine through the drive shaft to the differential. The differential then rotates the axle shafts, which are connected to the wheel hubs on each side of the vehicle, ultimately driving the wheels.
Drive shafts can sustain damage due to various factors, including wear and tear in wheel bearings or hub assemblies. Symptoms of drive shaft issues often include excessive vibrations during acceleration or braking and may be accompanied by a knocking sound, indicating a problem within the car wheel assembly system.
Understanding Your Car Wheel Assembly for Optimal Maintenance
Gaining a solid understanding of your car’s wheel bearings, hubs, and related components, and their respective functions, is paramount for maintaining your vehicle in good working condition. Utilize the knowledge gained from this guide to proactively monitor these critical Car Wheel Assembly Parts. When necessary, ensure you replace worn components with high-quality aftermarket parts to guarantee continued vehicle reliability and safety.