After exploring the exterior parts of a car in our previous article, it’s natural to be curious about what’s inside. The interior of your car is more than just seats and a steering wheel; it’s a complex system of components working together to ensure a comfortable, safe, and enjoyable driving experience. In this guide, we’ll delve into the Names Of Parts Inside A Car, explaining their functions and importance.
Understanding the names and roles of these interior car parts is valuable for several reasons. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, planning to buy a new vehicle, considering upgrades, or simply want to be more knowledgeable about your car, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview. Knowing these components can help you make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and customizations, ultimately contributing to a safer and more personalized driving experience. Many of these interior parts can be enhanced with aftermarket accessories, from custom LED lighting to advanced audio systems, allowing you to personalize your vehicle and improve your time on the road.
Key Interior Car Parts and Their Names
Here’s a list of the essential names of parts inside a car, which we will explore in more detail:
- Steering Wheel and Horn
- Ignition System
- Pedals (Accelerator, Brake, Clutch)
- Gear Shifter/Selector
- Dashboard
- Hazard Lights Button
- Seat Belts
- Airbags
- Rearview Mirrors (Interior and Exterior)
- Parking Brake (Emergency Brake)
- Turn Signal Lever (Indicator Stalk)
- Center Console
- Glove Compartment
- Power Window and Door Lock Controls
- Interior Door Handle
- Audio System
- Infotainment Screen (Central Control Screen)
- Sun Visors
- Car Seats
- Floor Mats
- Roof and Headliner
Detailed Look at Car Interior Parts
Let’s examine each of these names of parts inside a car more closely, understanding their function and significance.
#1. Steering Wheel and Car Horn
The steering wheel is arguably the most fundamental control inside your car. It’s the primary interface for the driver to control the vehicle’s direction. The steering wheel translates the driver’s rotational movements into the turning of the front wheels via a series of mechanical and hydraulic (or electric in modern cars) linkages.
Beyond steering, modern steering wheels often integrate various controls for convenience and safety, including cruise control, audio system adjustments, and even heating elements for colder climates. Customizing your steering wheel with a new cover is a popular interior modification. These covers come in various materials and designs, offering enhanced grip, comfort, and aesthetic appeal.
The horn, activated by pressing a button on the steering wheel, is a critical safety feature. It allows the driver to audibly alert other road users to their presence, warn of potential hazards, or communicate in various driving situations.
#2. Ignition System
The ignition system is the starting point for your car’s engine. Typically located on the steering column or dashboard, the ignition switch is where you insert your key or press a start button to bring the car to life.
When you turn the key or press the start button, the ignition system engages, initiating a sequence of events that ultimately starts the engine. This system provides power to the starter motor, which cranks the engine, and also activates the ignition system to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders, initiating combustion and engine operation.
#3. Pedals
Located in the driver’s footwell, the pedals are essential controls for managing the car’s speed and braking. In most cars, you’ll find two or three pedals:
- Accelerator Pedal (Gas Pedal): The pedal on the right, often the smaller one, is the accelerator. Pressing this pedal controls the amount of fuel delivered to the engine, directly influencing the car’s speed.
- Brake Pedal: Positioned to the left of the accelerator, the brake pedal is typically larger. Pressing the brake pedal activates the car’s braking system, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
- Clutch Pedal (Manual Transmissions Only): In vehicles with a manual gearbox, a third pedal, the clutch, is located to the left of the brake pedal. The clutch pedal is used to disengage the engine from the transmission, allowing the driver to change gears smoothly. Automatic cars do not have a clutch pedal.
The pedal arrangement in a manual car, from left to right, is clutch, brake, and accelerator. In automatic cars, it’s simply brake and accelerator.
#4. Gear Shifter/Selector
The gear shifter (for manual transmissions) or gear selector (for automatic transmissions) is typically located in the center console area, between the driver and front passenger seats. This control allows the driver to select different gears for various driving conditions.
In a manual transmission vehicle, the gear shifter is a lever used in conjunction with the clutch pedal to manually change gears. The shift knob often displays a pattern indicating gear positions.
For automatic transmissions, the gear selector, sometimes referred to as the “PRNDL” (Park, Reverse, Neutral, Drive, Low), allows the driver to choose driving modes. While the specific letters or symbols might vary, the function remains the same: to select the appropriate mode for driving, reversing, parking, or neutral idling.
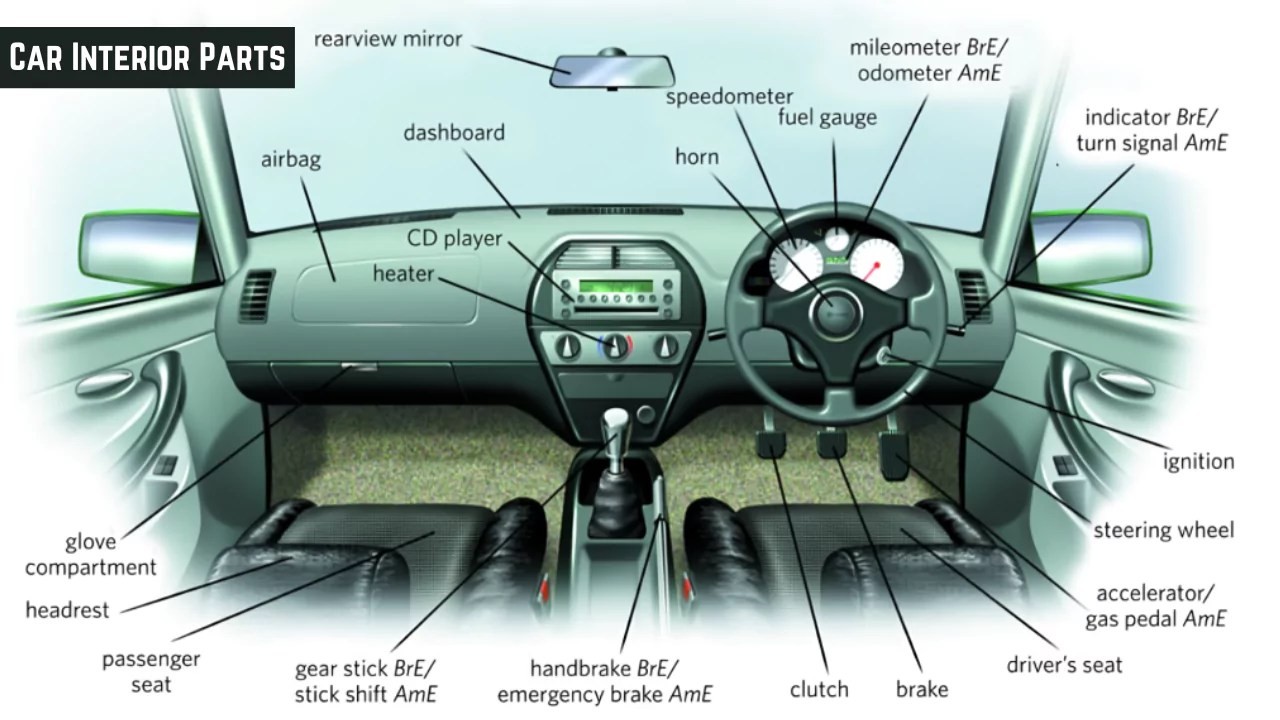 interior car parts names with diagram
interior car parts names with diagram
#5. Dashboard
The dashboard is a prominent interior component situated at the front of the car, beneath the windshield. It serves as a central panel housing crucial vehicle information displays and controls, and it acts as a visual and physical separation between the engine bay and the passenger cabin.
Dashboard designs vary significantly across car models and brands, reflecting different styles and levels of sophistication. A modern dashboard typically integrates several key instrument panels:
- Fuel Gauge: Indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the tank, allowing drivers to monitor fuel levels and plan for refueling.
- Speedometer: Displays the vehicle’s current speed, helping drivers maintain safe and legal speeds. It can be analog with a needle or digital.
- Tachometer (RPM Gauge): Shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM). This is particularly useful in manual transmission vehicles for optimal gear shifting and for monitoring engine performance and potential strain.
- Temperature Gauge: Displays the engine’s coolant temperature. It warns of potential overheating, which could indicate engine problems or low coolant levels.
In addition to these gauges, the dashboard also houses various warning lights and indicator lights that alert the driver to potential issues or the status of different vehicle systems, such as low oil pressure, check engine light, or airbag system alerts.
#6. Emergency Flashers
Emergency flashers, or hazard lights, are activated by a button, usually marked with a red triangle, on the dashboard or steering column. When activated, they cause all four turn signal lights to flash simultaneously.
Hazard lights are used to warn other drivers of an emergency situation, such as a breakdown, accident, or when the car is parked in a hazardous location. They are a crucial safety feature for increasing vehicle visibility in emergencies.
#7. Car Seat Belts
Seat belts are fundamental safety devices designed to restrain occupants during a collision, significantly reducing the risk of serious injury or death. They work by securing the occupant to the car seat, preventing ejection from the vehicle and minimizing impact with the car’s interior or other occupants.
Proper seat belt use is crucial for their effectiveness. Unbelted occupants are at a much higher risk of being ejected from the vehicle during a crash, or becoming projectiles within the car, potentially injuring themselves and others.
#8. Airbags
Airbags are supplemental restraint systems that work in conjunction with seat belts to provide additional protection in a crash. Sensors detect the severity of a collision, and if it’s significant enough, the airbags are instantly inflated with gas in milliseconds.
Airbags cushion occupants, preventing them from hitting hard interior surfaces like the steering wheel, dashboard, or windshield. They are designed for one-time use and must be replaced after deployment by a qualified repair shop using genuine OEM parts to ensure proper functionality in future collisions. Counterfeit airbags pose a serious safety risk as they may malfunction or deploy improperly.
#9. Rearview Mirrors
Rearview mirrors are essential for driver visibility, providing a view of the road and surrounding traffic behind the vehicle. Regulations mandate that passenger cars have an interior rearview mirror and exterior rearview mirrors on both the driver and passenger sides.
- Interior Rearview Mirror: Mounted centrally to the dashboard or windshield, it is a flat, unit magnification mirror, providing a true-size reflection of the scene behind the car.
- Exterior Rearview Mirrors: Located on the doors, these mirrors are typically convex to provide a wider field of view, although this can slightly distort distance perception. They are adjustable to suit different drivers’ viewing preferences.
#10. Parking Brake
The parking brake, also known as the emergency brake, is an independent braking system designed to hold the vehicle stationary when parked. Unlike the primary hydraulic braking system used for stopping the car while driving, the parking brake is usually mechanically operated and acts on the rear wheels.
While primarily for parking, the parking brake can also be used as an emergency brake if the primary brakes fail. In such a situation, gradually applying the parking brake can help slow down and stop the vehicle. It’s recommended to use the parking brake every time you park, regardless of the terrain or transmission type, as a safety precaution.
#11. Turn Signal Lever
The turn signal lever, or indicator stalk, is located on the steering column and is used to activate the turn signals (indicators). Moving the lever up or down signals the intention to turn right or left, respectively.
Turn signals are crucial for communicating with other road users, indicating planned lane changes or turns. Proper and timely use of turn signals is essential for safe driving and preventing accidents.
#12. Center Console
The center console is the area in the middle of the front cabin, between the driver and passenger seats. In most modern cars, it’s positioned behind the gear shifter/selector. It often incorporates storage compartments, cupholders, and various vehicle controls.
The center console can house features like:
- Storage bins or compartments
- Cupholders
- Accessory power outlets (cigarette lighter, USB ports)
- Audio system controls
- Climate control (HVAC) system controls
- Infotainment system controls or displays
In essence, the center console serves as a central hub for various convenience and control functions within the car’s interior.
#13. Glove Compartment
The glove compartment, or glove box, is a storage compartment built into the dashboard on the passenger side, above the footwell. Despite its name, it’s used for general storage rather than just gloves.
Common items stored in the glove compartment include:
- Owner’s manual
- Vehicle registration and insurance documents
- Maps or navigation guides
- Flashlight
- Napkins or tissues
- Tire pressure gauge
The glove compartment provides a convenient and enclosed space to keep essential documents and small items organized and within reach.
#14. Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Power windows and door locks are electrically operated systems that allow for convenient control of the car’s windows and doors. Controls for these features are typically located on the door panels or center console.
- Power Window Controls: Buttons or switches that raise and lower the car windows electronically, replacing manual crank handles.
- Power Door Lock Controls: Buttons or switches that simultaneously lock or unlock all car doors, providing centralized door security.
#15. Interior Door Handle
The interior door handle is used to open the car door from the inside. Pulling the handle disengages the door latch mechanism, allowing the door to be pushed open. Modern interior door handles are often made of plastic for durability and safety. The mechanisms connecting interior and exterior door handles are located inside the door panel.
#16. Audio System
The car audio system is responsible for providing entertainment and information through sound. It comprises components such as:
- Speakers
- Amplifier (to boost audio signal)
- Source unit (head unit, radio, CD player, etc.)
Modern car audio systems can be highly sophisticated, incorporating features like Bluetooth connectivity, smartphone integration, and high-fidelity sound reproduction.
#17. Infotainment Screen
The infotainment screen, also known as the central control screen or multimedia display, is a prominent feature in contemporary car interiors. It serves as a central interface for a wide range of functions, integrating information and entertainment.
Infotainment systems combine features such as:
- Navigation
- Audio and media playback
- Smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto)
- Vehicle settings and information displays
- Backup camera display
- Climate control interface
These systems are essentially in-car computers, offering a centralized and interactive way to manage various vehicle functions and access information and entertainment.
#18. Sun Visors
Sun visors are hinged flaps located above the windshield, on the interior roof lining. They are designed to be flipped down to block glare from the sun, enhancing driver and passenger visibility and comfort during sunny conditions.
#19. Car Seats
Car seats provide support, comfort, and safety for vehicle occupants. They are typically constructed with a strong frame, often made of metal, and padded with cushioning materials for comfort and impact absorption.
Many car seats offer adjustability features, including:
- Seat height adjustment
- Seatback angle adjustment
- Lumbar support adjustment
These adjustments allow occupants to personalize their seating position for optimal comfort and ergonomics. Car seat covers are a popular accessory for protecting seats from wear and tear, and for customizing the interior aesthetic. Regular cleaning and conditioning (for leather or fabric seats) can help maintain seat condition and longevity.
#20. Floor Mats
Floor mats are designed to protect the car’s interior carpeting from dirt, moisture, and wear. They are removable for easy cleaning and replacement.
Car floor mats come in various materials, such as rubber, carpet, and all-weather materials. Some mats use fixation points to secure them in place. In vehicles with permanent rubber flooring, like some commercial or off-road vehicles, floor mats may be less common or unnecessary.
#21. Roof and Headliner
The car roof provides structural integrity to the vehicle, contributing to rollover protection and overall vehicle rigidity. It also protects the cabin from weather elements.
The headliner is the fabric or material lining the interior roof of the car. It serves multiple purposes:
- Insulation: Provides thermal and acoustic insulation, helping to regulate cabin temperature and reduce noise levels.
- Aesthetics: Conceals the car’s structural roof and wiring, providing a finished interior appearance.
- Headroom and Safety: Contributes to interior headroom and can offer a degree of impact protection in certain collisions.
The roof and headliner together form an essential part of the car’s interior structure, contributing to safety, comfort, and aesthetics.
FAQs About Car Interior Parts
What are the basic names of interior car parts?
The most fundamental names of parts inside a car include: Steering Wheel, Ignition, Pedals, Gear Shifter, Dashboard, Seat Belts, and Airbags. These are essential for basic vehicle operation and safety.
What is an interior panel in a car for?
Interior car panels serve multiple functions beyond just covering the door’s inner structure. They protect the window mechanism when lowered, conceal electrical wiring for windows and door locks, and contribute to the interior’s aesthetic finish.
What is the ceiling inside a car called?
The ceiling inside a car is called the headliner. It’s a fabric or composite material that covers the roof’s interior, providing insulation, sound dampening, and a finished look to the cabin.
What is the purpose of the dashboard in a car?
The dashboard is a critical interior component that houses essential instrument panels (speedometer, fuel gauge, etc.) and warning lights. It provides the driver with vital information about the vehicle’s operation and acts as a partition between the front of the car and the cabin.
What materials are commonly used for car interiors?
Modern car interiors utilize a variety of materials, including polymers for lightweight seats, instrument panels, and door panels; durable upholstery fabrics like nylon and polyester; vinyl; and premium materials like leather for seating and trim.
What are the main types of car interior upholstery?
The primary types of car upholstery are:
- Nylon Upholstery: A common and durable fabric choice.
- Polyester Upholstery: Another popular and versatile fabric option.
- Vinyl Upholstery: A durable and easy-to-clean synthetic material.
- Leather Upholstery: A premium and luxurious natural material.
This comprehensive guide should give you a solid understanding of the names of parts inside a car and their functions. Knowing these components enhances your car knowledge and allows you to appreciate the intricate design and engineering that goes into your vehicle’s interior.