Being a responsible car owner goes beyond just driving; it’s about understanding what keeps your vehicle running smoothly and safely. While the world of car mechanics might seem complex, grasping the essentials of your car’s anatomy, especially the crucial Car Under Parts, empowers you to make informed maintenance and repair decisions. Knowing your vehicle inside and out helps you identify potential issues early, understand repair costs, and ensure your car remains reliable.
One critical aspect of car ownership is recognizing which parts are vital for safety and which are essential for performance and longevity. This guide will illuminate the key mechanical components that make up your car, focusing on the car under parts and their significance. From the engine’s intricate systems to the chassis components beneath the body, we’ll explore the inner workings of your vehicle.
Let’s delve into the world of car under parts, starting with the heart of your vehicle – the engine.
Engine Components: Powering Your Ride
The engine is arguably the most complex system within your car, and many of its vital car under parts work tirelessly to generate power.
Cylinder Block and Pistons: The Heart of Combustion
The cylinder block serves as the engine’s robust foundation, housing the cylinders – hollow tubes where the magic of combustion happens. Within these cylinders, pistons, secured by piston rings, move up and down. This reciprocating motion is fundamental, converting the explosive energy from fuel combustion into mechanical force that propels your vehicle forward. The precise interaction between pistons and cylinders is paramount, making it the primary source of your car’s power generation.
Crankshaft and Camshaft: Orchestrating Motion
Deep within the engine’s workings, the crankshaft and camshaft play synchronized roles. The crankshaft transforms the linear, up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational energy, providing the driving force that ultimately turns your wheels. Simultaneously, the camshaft expertly manages the timing of valve openings, ensuring precise and efficient combustion. Working in harmony, these car under parts synchronize the internal combustion process with accurate mechanical movements, contributing to the smooth and powerful motion of your car.
Intake and Exhaust Manifolds: The Breathing System
Imagine the intake and exhaust manifolds as the lungs of your car. The intake manifold draws in fresh air, rich in oxygen needed for combustion, while the exhaust manifold expels the spent gases produced after combustion, channeling them out through the exhaust system. These car under parts are essential for optimizing your engine’s performance, ensuring a balanced mix of power and fuel efficiency. It’s important to note that electric vehicles, which operate without internal combustion, do not have intake and exhaust manifolds.
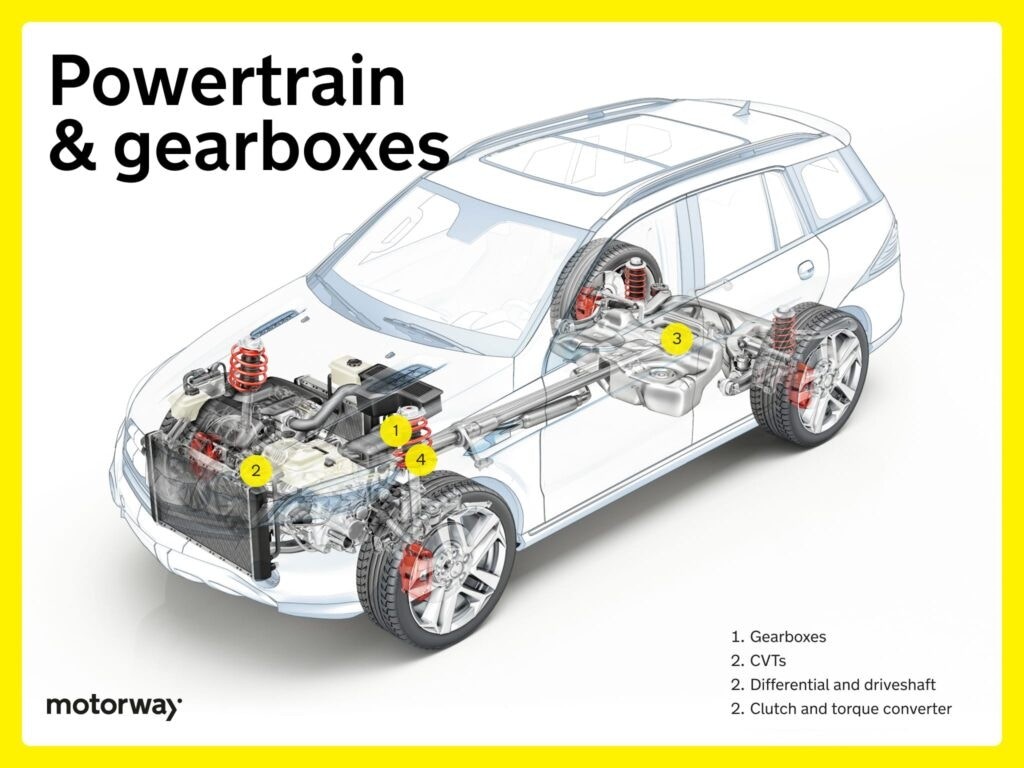
Powertrain and Gearboxes: Transferring Power to the Wheels
The powertrain system, including the gearbox, is responsible for taking the power generated by the engine and delivering it to the wheels, making your car move.
Different Types of Gearboxes (Transmission): Managing Speed and Torque
The gearbox, also known as the transmission, is a vital car under part that allows you to control your car’s speed and torque by changing gears.
Manual Gearboxes: Driver Control at Your Fingertips
Manual gearboxes put the driver in direct control of gear selection. By manually engaging and disengaging gears using a clutch pedal and gear stick, drivers can adapt to various driving conditions. This level of control is crucial for responding to situations like slippery roads, accelerating, or decelerating, offering a more engaged driving experience.
Automatic Gearboxes: Seamless Gear Shifting
Automatic gearboxes simplify driving by automatically shifting gears smoothly, eliminating the need for manual clutch and gear stick operation. Inside an automatic gearbox is a torque converter, a fluid coupling mechanism that ensures smooth gear transitions. This system provides convenience and ease of driving, especially in stop-and-go traffic.
CVTs (Continuously Variable Transmissions): Infinite Gear Ratios
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) represent an advanced gearbox technology. Using a system of pulleys and belts, CVTs offer an infinite range of gear ratios. This results in exceptionally smooth and continuous acceleration, eliminating the stepped gear changes of traditional gearboxes. CVTs are designed to optimize fuel efficiency and dynamically adapt to changing driving conditions, making them a fuel-conscious and performance-oriented choice.
Differential and Driveshaft: Distributing Power Evenly
Within the powertrain, the differential and driveshaft work in concert. The driveshaft is the component that transmits power from the transmission to the wheels. The differential plays a critical role in ensuring that power is distributed evenly to the wheels, especially when turning. This allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, preventing wheel slippage and ensuring smooth cornering. Together, these car under parts create a harmonious system for your car’s motion and maneuverability.
Clutch and Torque Converter: Engaging and Transferring Power
In the realm of gearboxes and power transmission, the clutch and torque converter are key players. In manual transmissions, the clutch allows the driver to engage and disengage the engine from the gearbox, enabling precise gear changes and control. In automatic transmissions, the torque converter takes over this role, smoothly transferring power from the engine to the transmission, ensuring seamless gear shifts and a comfortable, dynamic driving experience.
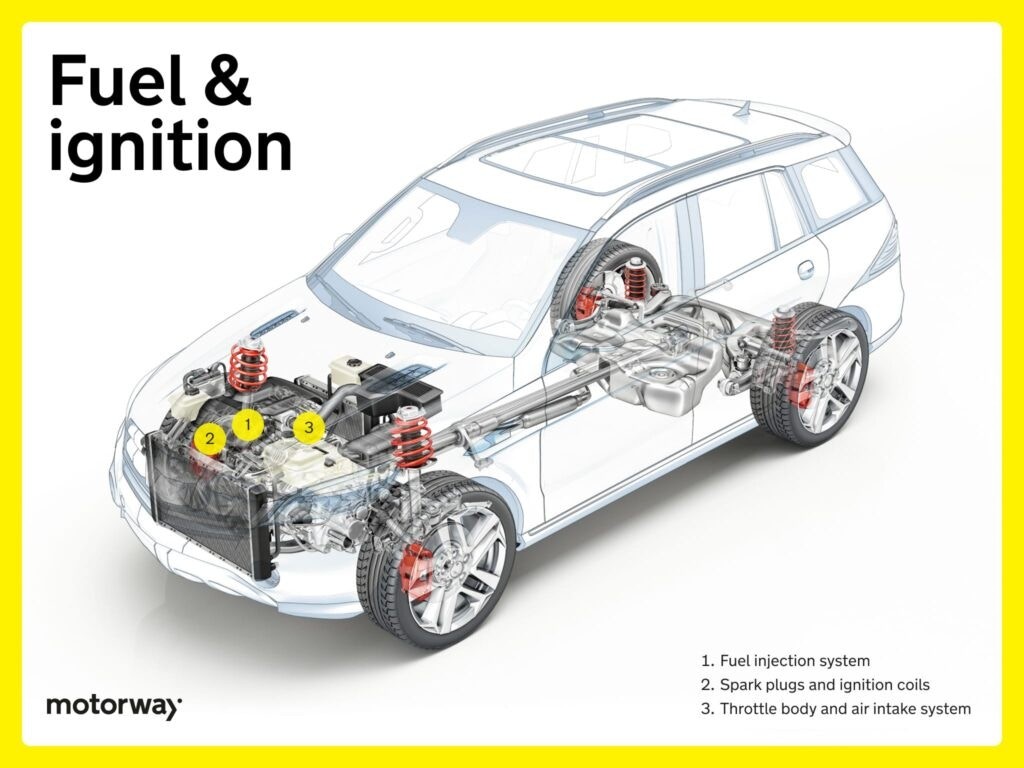
Fuel and Ignition Systems: Starting the Combustion
The fuel and ignition systems are responsible for delivering fuel to the engine and initiating the combustion process that creates power.
Fuel Injection System: Precise Fuel Delivery
A cornerstone of modern engines is the fuel injection system. Fuel injectors are precision nozzles that spray fuel directly into the engine cylinders in a highly controlled manner. This system offers significant improvements over older carburettor systems, providing enhanced fuel efficiency, increased power output, and reduced emissions. Fuel injection ensures optimal combustion by precisely managing the fuel-air mixture.
Spark Plugs and Ignition Coils: Creating the Spark
The ignition system relies on spark plugs and ignition coils working together to ignite the fuel-air mixture within the engine cylinders. Spark plugs generate the electrical spark needed to initiate combustion, while ignition coils amplify the voltage from the car’s electrical system to create a powerful spark. The synchronized operation of these car under parts is crucial for efficient and rapid ignition, leading to optimal engine performance, responsiveness, and fuel economy.
Throttle Body and Air Intake System: Controlling Airflow
The throttle body and air intake system collaborate to regulate the amount of air entering the engine. The throttle body acts as a valve, controlling how much air flows into the engine based on your accelerator pedal input. The air intake system ensures that the engine receives a clean and sufficient supply of air, filtering out contaminants. Working together, these car under parts manage the engine’s “breathing,” a vital aspect for achieving peak power, fuel efficiency, and overall engine performance.
Cooling and Lubrication: Maintaining Optimal Temperature and Smooth Operation
Maintaining the right temperature and ensuring smooth movement of parts are crucial for engine health and longevity. Cooling and lubrication systems are designed to achieve this.
Radiator and Cooling Fans: Preventing Overheating
The radiator and cooling fans are primary components in preventing engine overheating. The radiator dissipates heat from the engine coolant as it circulates through its fins. Cooling fans enhance this process by forcing airflow across the radiator, expelling excess heat. These car under parts work together to maintain the engine at an optimal operating temperature, preventing damage from overheating and ensuring efficient performance.
Water Pump and Hoses: Circulating Coolant
The water pump and hoses are additional car under parts essential to the cooling system. The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and cooling system, ensuring continuous heat absorption and dissipation. Hoses provide the pathways for coolant to travel between the engine, radiator, and other cooling components.
EV Battery Cooler System: Thermal Management for Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) require a different cooling approach, focusing on managing the temperature of the battery pack and electric motor. The battery cooler, similar in function to a traditional radiator, dissipates heat from the battery coolant. The cooling system further enhances heat expulsion using airflow. Maintaining optimal temperature is critical in EVs for maximizing battery life, efficiency, and overall performance of the electric powertrain.
Oil Pump and Oil Filter: Ensuring Lubrication and Cleanliness
The oil pump and oil filter are vital for engine lubrication. The oil pump circulates engine oil throughout the engine, ensuring that moving parts are constantly lubricated, reducing friction and wear. The oil filter removes impurities and contaminants from the oil, keeping it clean and effective. Together, these car under parts contribute significantly to extending engine life and maintaining smooth operation.
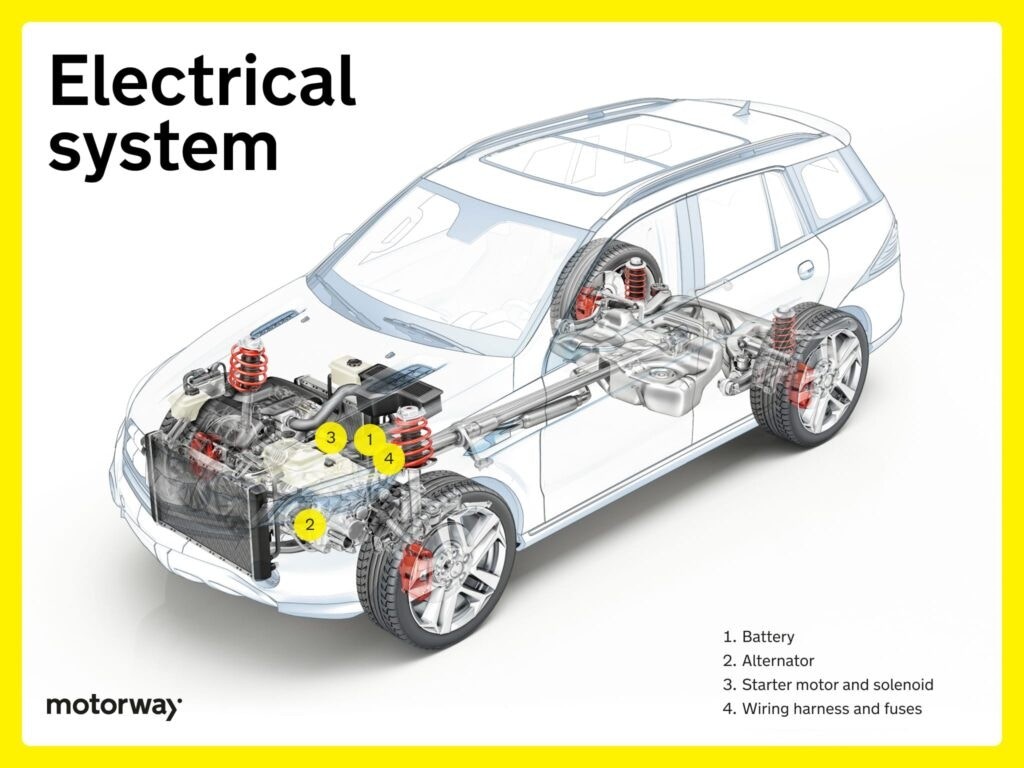
Electrical System: Powering Car Functions
The electrical system is the nerve center of your car, providing power for everything from starting the engine to operating lights and accessories.
Battery: The Initial Power Source
The car battery is the primary source of electrical energy in your vehicle. It provides the initial power to start the engine and supplies electricity to various electrical systems when the engine is not running. All cars, including EVs (which also have large traction batteries for driving), rely on a 12V battery for starting and accessory power. A failing battery can lead to starting problems and electrical malfunctions.
Alternator: Recharging and Powering
The alternator is an engine-driven generator that converts mechanical energy from the engine’s rotation into electrical energy. It recharges the battery while the engine is running and provides power to the car’s electrical system, including lights, radio, and other accessories. Crucially, the alternator regulates voltage to maintain a consistent electrical supply, preventing battery overcharging and ensuring electrical components receive the correct voltage.
Starter Motor and Solenoid: Initiating Engine Start
The starter motor and solenoid work together to crank the engine and initiate the combustion process. The solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when you turn the ignition key. The starter motor then uses electrical energy to turn the engine’s crankshaft, starting the engine. This coordinated action transforms electrical energy into the mechanical motion needed to begin the engine’s operation.
Wiring Harness and Fuses: Electrical Pathways and Protection
The wiring harness is a network of wires that distributes electricity throughout the vehicle, connecting all electrical components. Fuses are safety devices strategically placed within the wiring harness to protect against electrical overloads. If excessive current flows through a circuit, the fuse blows, interrupting the circuit and preventing damage to components. Together, these car under parts ensure a safe and organized distribution of electrical power throughout the car.
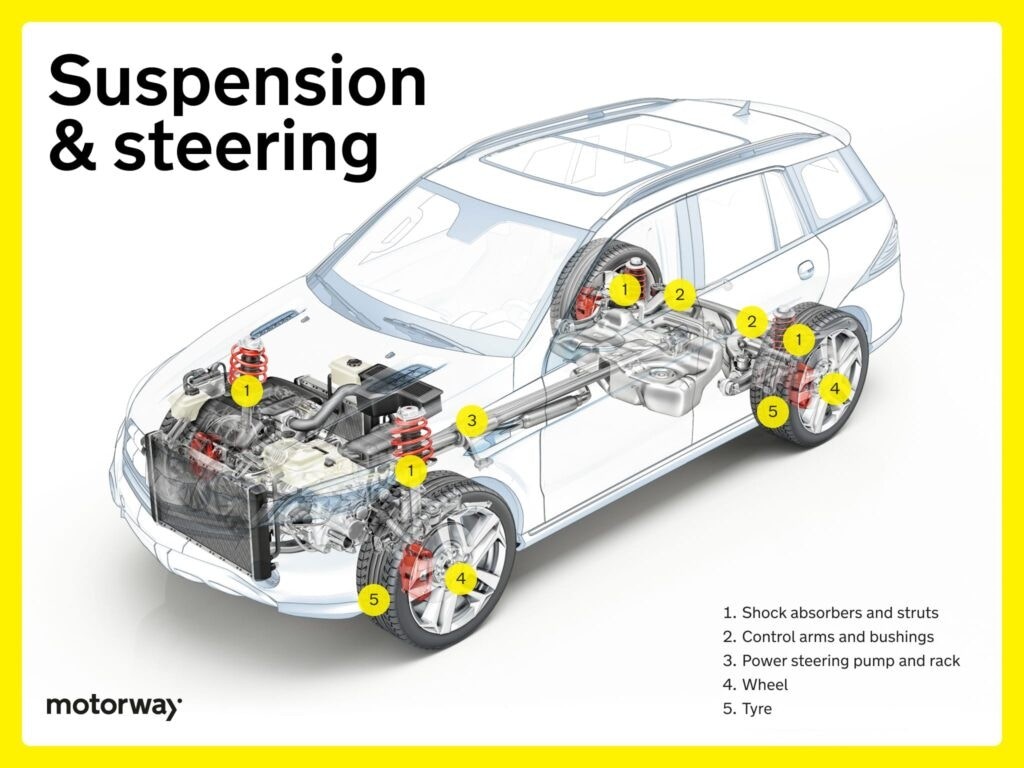
Suspension and Steering: Ensuring Ride Comfort and Control
The suspension and steering systems are crucial for ride comfort, handling, and vehicle control, especially when navigating varying road conditions.
Shock Absorbers and Struts: Damping Bumps and Vibrations
Shock absorbers and struts are key components of the suspension system. Shock absorbers are designed to dampen shocks and vibrations from road irregularities, providing a smoother ride by controlling wheel movement. Struts, often found at the front and sometimes rear, combine shock absorption with structural support, contributing to vehicle stability. These car under parts enhance driving comfort by minimizing the impact of bumps and uneven surfaces.
Control Arms and Bushings: Stability and Handling
Within the chassis, control arms and bushings work together to provide stability and smooth handling. Control arms link the suspension to the car’s frame, allowing for controlled wheel movement. Bushings, made of flexible materials, are inserted into control arm joints, providing cushioning and flexibility. This combination absorbs road imperfections, maintains proper wheel alignment, and contributes to a balanced and comfortable ride.
Power Steering Pump and Rack: Effortless Steering
The power steering pump and rack are essential for responsive and effortless steering. The power steering pump generates hydraulic pressure, which is then used by the power steering rack to assist in turning the wheels. The rack converts this hydraulic pressure into controlled motion, making steering easier, especially at low speeds. These car under parts provide precise and smooth maneuverability, enhancing driving ease and control.
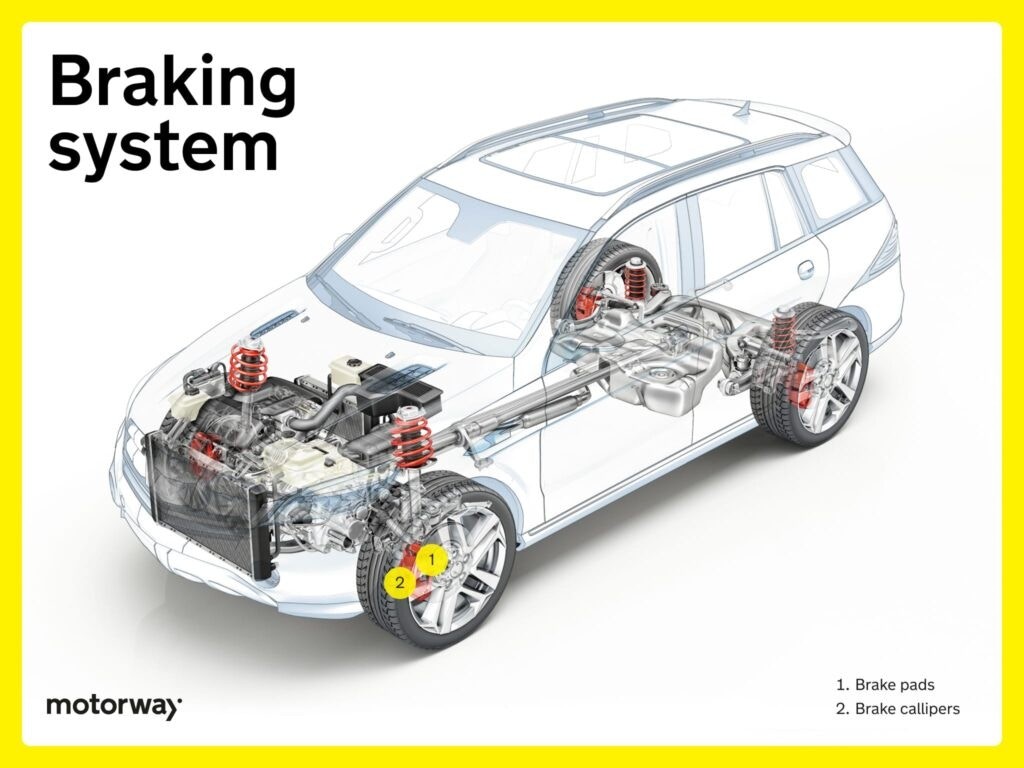
Braking System: Ensuring Safety Through Controlled Stops
The braking system is paramount for safety, allowing you to control your car’s speed and bring it to a stop effectively and reliably.
Brake Pads: Creating Friction for Deceleration
Brake pads are frictional components that press against the brake rotors when you apply the brakes. Typically made of composite materials, they convert kinetic energy into heat through friction, causing the car to slow down. Their robust design ensures reliable braking performance and contributes to both safety and the longevity of the braking system. Brake pads are subject to wear over time and require periodic replacement.
Brake Calipers: Applying Pressure to Brake Pads
Brake calipers are located around the brake rotors. They house pistons that, when hydraulic pressure from the brake system is applied, clamp the brake pads against the rotor. This clamping action generates the friction needed for controlled deceleration. The precision of brake calipers ensures responsive and reliable braking performance, vital for overall driving safety.
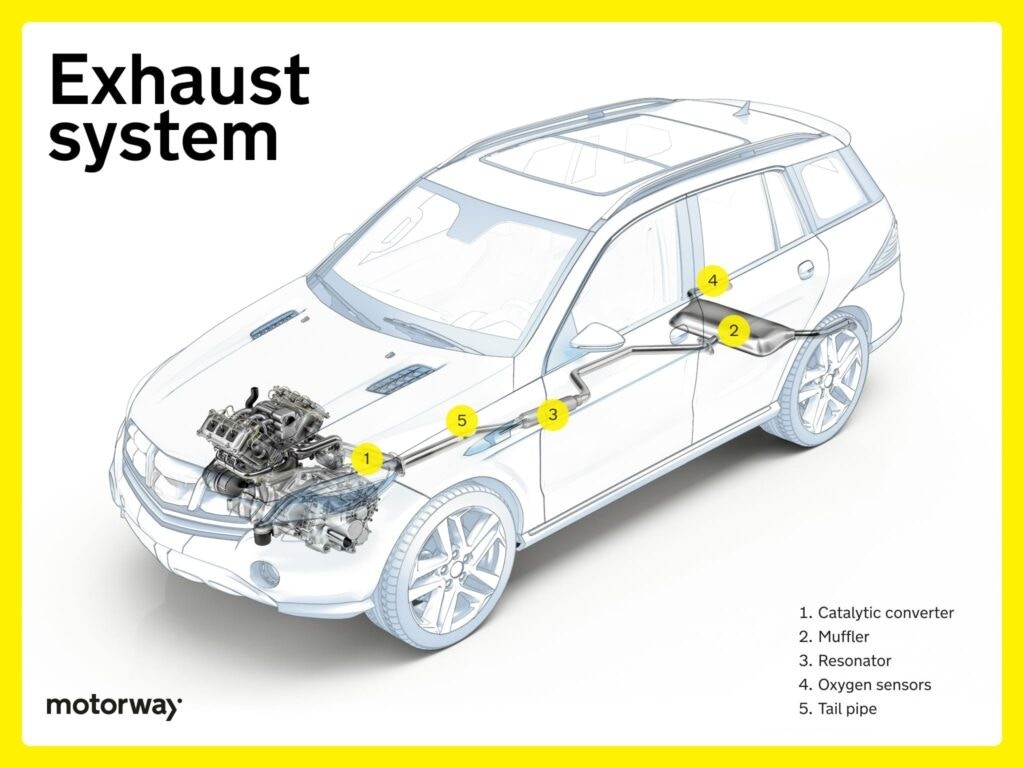
Exhaust System: Managing Emissions and Noise
The exhaust system is responsible for safely channeling exhaust gases away from the engine, reducing harmful emissions, and minimizing noise.
Catalytic Converter: Reducing Harmful Emissions
The catalytic converter is a key car under part within the exhaust system of internal combustion engines. It uses chemical catalysis to transform harmful gases like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen. This ingenious device significantly reduces vehicle emissions, contributing to cleaner air and environmental health.
Muffler and Resonator: Quieting Exhaust Noise
The muffler and resonator work together to manage exhaust noise. The muffler’s primary function is to reduce the overall loudness of the exhaust sounds. The resonator fine-tunes sound frequencies, further minimizing unwanted noise and adjusting the exhaust note. By reducing noise, these car under parts contribute to a more comfortable and pleasant driving experience and help meet noise regulations.
Oxygen Sensors: Monitoring Exhaust Gases
Oxygen sensors are positioned in the exhaust system to monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. This data is crucial for the engine control unit (ECU), the car’s computer. The ECU uses oxygen sensor readings to precisely adjust fuel injection, optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions.
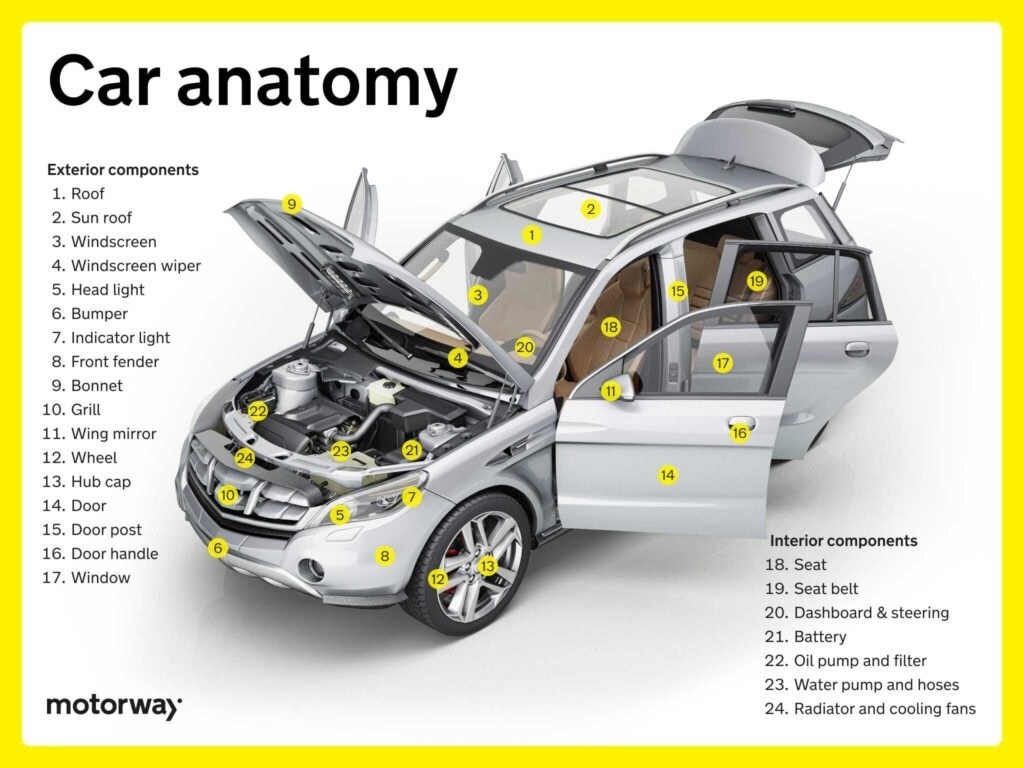
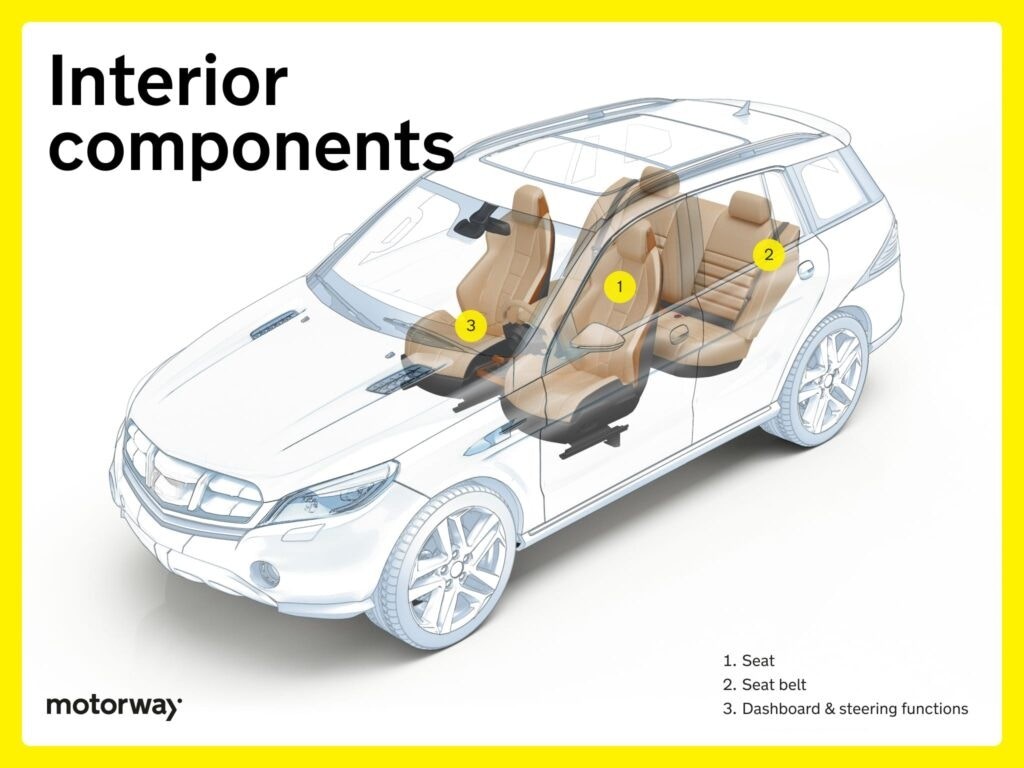
Interior Components: Comfort and Convenience Inside
Interior components contribute to the comfort, convenience, and aesthetics of your car’s cabin.
Seats & Seat Belts: Occupant Comfort and Safety
Car seats are designed for comfort and support, available in various materials and configurations. Seat belts are essential safety devices, securing occupants during travel. Modern seat belts often include pretensioners that tighten the belt in a collision and force limiters that reduce the force exerted on the occupant’s chest.
Dashboard & Steering Functions: Driver Command Center
The dashboard serves as the driver’s visual command center, displaying essential information such as speed, fuel level, engine temperature, and warning lights. It provides a comprehensive snapshot of the car’s operational status. The steering wheel integrates various controls, including power-assisted steering, turn signals, windshield wipers, and multimedia system controls, putting essential functions within easy reach.
Exterior Components: Protecting and Styling the Car’s Body
Exterior components protect the car’s body, contribute to its aerodynamics, and define its styling.
Features & Controls on Doors: Convenience and Safety
Car doors are equipped with features and controls that enhance convenience and safety. Standard features include electric window controls, door locks (manual or power), and mirror adjustments. Some vehicles incorporate advanced features like keyless entry systems, power-operated doors, and integrated safety lighting, providing a more streamlined and user-friendly experience.
Wheels and Tyres: Connecting to the Road
Wheels and tyres are the crucial interface between your car and the road surface, directly impacting handling, braking, and ride comfort.
Types of Tyres and Their Functions
| Type of tyre | Function |
|---|---|
| Summer tyres | Designed for warm weather, offering excellent grip and handling in both dry and wet conditions. |
| Winter tyres | Engineered for cold temperatures, featuring specialized treads for superior traction on snow and ice. |
| All-season tyres | Versatile tyres providing a balance of traction and durability in a range of weather conditions, both wet and dry. |
| Performance tyres | Designed for sporty driving, prioritizing enhanced handling, grip, and responsiveness at higher speeds. |
| Off-Road tyres | Built for challenging terrains, featuring rugged treads and reinforced sidewalls for maximum traction and durability on unpaved surfaces. |
| Run-flat tyres | Equipped with reinforced sidewalls, allowing continued driving at reduced speeds for a limited distance after a puncture. |
| Touring tyres | Focused on providing a smooth and comfortable ride, ideal for long journeys with low noise and good handling. |


Wheel Construction Guide: Alloy vs. Steel Wheels
Wheel construction methods and materials influence wheel weight, strength, and aesthetics.
- One-piece construction: The wheel is made from a single piece of material, commonly alloy or steel. This is typical for both alloy and steel wheels.
- Two-piece construction: The wheel comprises two main parts: the center and the outer rim, typically bolted or welded together. Often found in performance or custom wheels.
- Three-piece construction: The wheel has three separate pieces: the center, outer rim, and inner hoop. This modular design offers customization options, popular in aftermarket wheels.
- Forged construction: Forged wheels are made from a single block of metal compressed under high pressure, resulting in a stronger and lighter wheel compared to cast wheels, often used in high-performance and racing applications.
- Multi-piece construction: Combines multiple components for design flexibility and customization, often including a center section, outer rim, and bolts.
Material choices also impact wheel characteristics:
- Alloy wheels: Made from aluminum or magnesium alloys, they are lighter than steel wheels, improving heat dissipation and vehicle appearance.
- Steel wheels: Constructed from steel for robustness and durability. While heavier than alloy wheels, they are cost-effective and suitable for rugged conditions.
Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): Maintaining Optimal Tyre Pressure
The Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is a safety feature that continuously monitors tyre air pressure using sensors in each tyre. It transmits real-time pressure data to the car’s computer, issuing warnings if tyre pressure drops below optimal levels. TPMS promotes safety, fuel efficiency, and extends tyre life by ensuring proper tyre inflation.
FAQs About Car Under Parts
What parts are under a car?
Beneath a car, you’ll find essential car under parts including the engine, transmission, suspension system, exhaust system, and fuel system. These systems work collaboratively to ensure the car’s functionality and performance.
How many car parts are on a car?
The number of parts in a car can vary significantly depending on the model and complexity, but modern vehicles can contain over 30,000 individual parts. This highlights the intricate engineering involved in car design. Electric vehicles typically have fewer parts due to their simpler powertrains.
What are the important parts of a vehicle?
Key car under parts and systems include the engine, transmission, brake system, steering system, suspension, and electrical components. Each plays a crucial role in vehicle safety, performance, and reliability.
What parts of a car can be sold separately?
Many car under parts can be sold individually, including engines, transmissions, body panels, and specific electrical components. The demand and availability of these parts influence their resale potential.
Why is there a shortage of car parts?
Car part shortages can arise from various factors, including supply chain disruptions, increased demand, manufacturing challenges, and global events impacting production and distribution networks.
Need to Sell Your Car?
Want to learn more about car ownership, maintenance, and selling your vehicle? Explore our guides here for information on topics ranging from Clean Air Zones to car tax, and plate changes to part exchange.