Being a responsible car owner means taking a proactive approach to maintenance. However, understanding the complex mechanical parts of your car can feel overwhelming when you need to make informed repair decisions.
It’s crucial to know which car parts can be dangerous if they malfunction and which are relatively inexpensive to maintain.
Understanding your car’s components is key to proper maintenance and managing associated costs.
Let’s explore the inner workings of a car, from pistons to spark plugs, and understand the essential components that make up the anatomy of any vehicle.
Engine Components
Maintaining your engine in good condition is vital for preserving your car’s value and keeping running costs low.
Cylinder Block and Pistons
The cylinder block is the engine’s structural backbone, a robust framework that houses the cylinders. These cylinders are hollow tubes where the controlled combustion process takes place.
Pistons, fitted with piston rings inside these cylinders, move up and down. They are critical in converting the explosive energy from combustion into mechanical force, which propels the vehicle. This piston-cylinder interaction is the heart of the engine, generating the power that drives your car.
Crankshaft and Camshaft
Deep within the engine, the crankshaft and camshaft are essential for its operation. The crankshaft converts the pistons’ vertical motion into rotational energy, providing the driving force for the vehicle.
Simultaneously, the camshaft precisely controls the timing of the engine valves opening and closing, ensuring efficient combustion. Together, they synchronize the combustion events with precise mechanical movements, resulting in the smooth, propulsive motion of the car.
Intake and Exhaust Manifolds
These components act like the lungs of your car, managing airflow for the engine. The intake manifold draws in fresh air for combustion, while the exhaust manifold expels the gases produced after combustion, routing them out through the exhaust system.
Working together, they optimize the engine’s performance by ensuring a balanced and efficient combustion process. It’s important to note that electric vehicles do not have intake and exhaust manifolds as they operate without internal combustion engines.
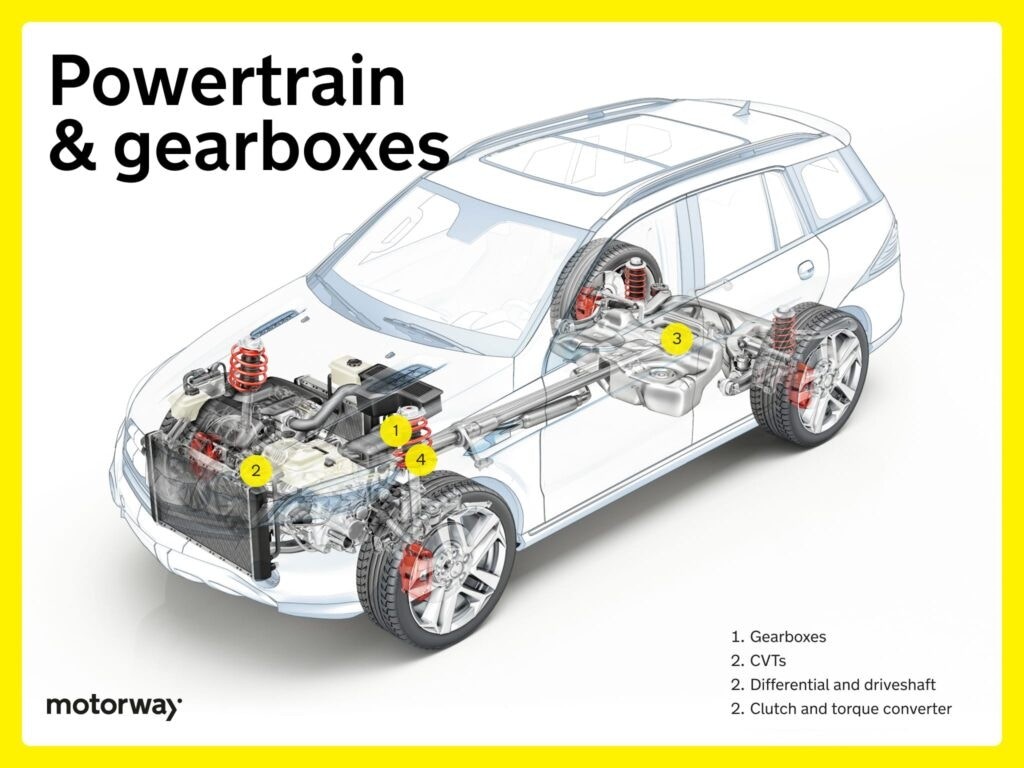
Powertrain and Gearboxes
The gearbox is a critical component, especially in manual cars, requiring smooth operation and careful maintenance.
Different Types of Gearboxes, Also Known as Transmissions
Manual Gearboxes
Manual gearboxes put the driver in control of gear selection.
They require the driver to manually engage and disengage gears using a clutch pedal and gear stick. This system allows drivers to adapt to various driving conditions, such as road grip, acceleration needs, and deceleration.
Automatic Gearboxes
Automatic gearboxes simplify driving by automatically shifting gears without driver intervention. This eliminates the need for a clutch pedal or manual gear shifting.
These gearboxes use a torque converter, a type of fluid coupling, to ensure smooth gear changes.
CVTs (Continuously Variable Transmissions)
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) represent an advanced type of gearbox. Using pulleys and belts, CVTs offer a virtually infinite range of gear ratios. This results in seamless and continuous acceleration.
This design not only improves fuel efficiency but also dynamically adjusts to changing driving conditions, making CVTs a performance-oriented and efficient choice.
Differential and Driveshaft
In a car’s power delivery system, the differential and driveshaft perform distinct yet interconnected roles. The driveshaft transmits power from the transmission to the wheels.
The differential then ensures that power is distributed appropriately to the wheels, especially when turning, allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds. Together, they create a harmonious system for vehicle motion and maneuverability.
Clutch and Torque Converter
Within the transmission system, the clutch and torque converter are crucial for managing power flow. In manual transmissions, the clutch enables the driver to engage and disengage gears for precise control.
In automatic transmissions, the torque converter smoothly transfers engine power to the transmission, ensuring seamless gear shifts and a dynamic driving experience.
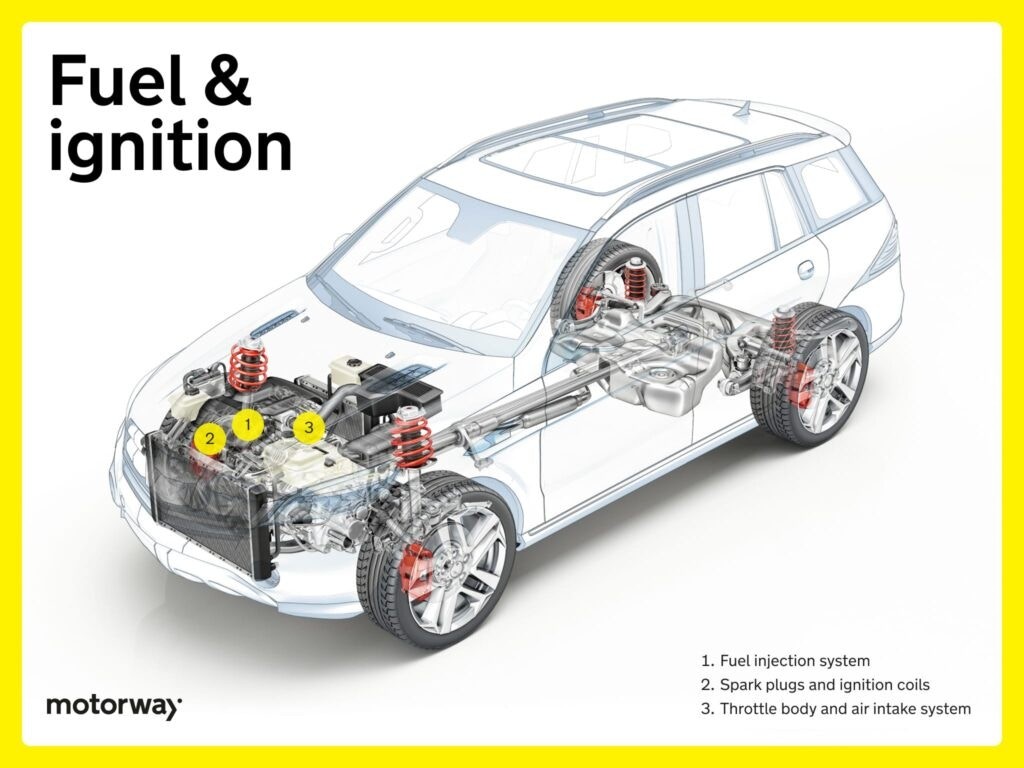
Fuel and Ignition Systems
A well-functioning fuel system is essential for your internal combustion engine car to avoid dangerous breakdowns.
Fuel Injection System
The fuel injection system is a vital part of modern engines, ensuring optimal combustion. Fuel injectors precisely spray fuel into the engine cylinders, enhancing both engine efficiency and power output.
This technology replaced older carburettors, which were prone to issues like clogging. Fuel injectors offer superior fuel distribution, improved engine performance, and reduced emissions.
Spark Plugs and Ignition Coils
The ignition system comprises spark plugs and ignition coils. They work in tandem to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinders. Spark plugs generate the spark needed for combustion, while ignition coils amplify the voltage to create a strong spark.
Synchronization between these parts is crucial for efficient and rapid ignition, which is essential for optimal engine performance, responsiveness, and fuel economy.
Throttle Body and Air Intake System
The throttle body and air intake system work together to regulate airflow into the engine. The throttle body controls the amount of air entering the engine, while the air intake system ensures a clean and efficient air supply by filtering out impurities.
Together, they manage the engine’s “breathing,” which is fundamental for achieving maximum power, fuel efficiency, and overall engine performance.
Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Radiator and Cooling Fans
The radiator and cooling fans are the primary components in preventing engine overheating.
The radiator dissipates heat from the engine coolant, while cooling fans enhance airflow across the radiator, helping to expel excess heat. These components ensure the engine operates at an optimal temperature, preventing damage and promoting efficient performance.
Water Pump and Hoses
The water pump and hoses are additional cooling system elements vital for regulating engine temperature. The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine, absorbing heat, while hoses provide pathways for the coolant to travel.
This circulation ensures consistent temperature regulation, preventing overheating and maintaining engine efficiency.
EV Battery Cooler System
Electric vehicles utilize a different cooling system specifically designed for the battery and electric motor. The battery cooler, similar to a traditional radiator, dissipates heat from the battery coolant, while the cooling system enhances airflow to remove heat.
Maintaining optimal temperature is crucial in EVs for the longevity and efficiency of both the battery pack and the electric motor.
Oil Pump and Oil Filter
The oil pump circulates engine oil to lubricate engine components, reducing friction and wear for smooth operation. Simultaneously, the oil filter removes contaminants from the oil, maintaining its cleanliness and effectiveness. Together, they significantly extend the engine’s lifespan and reliability.
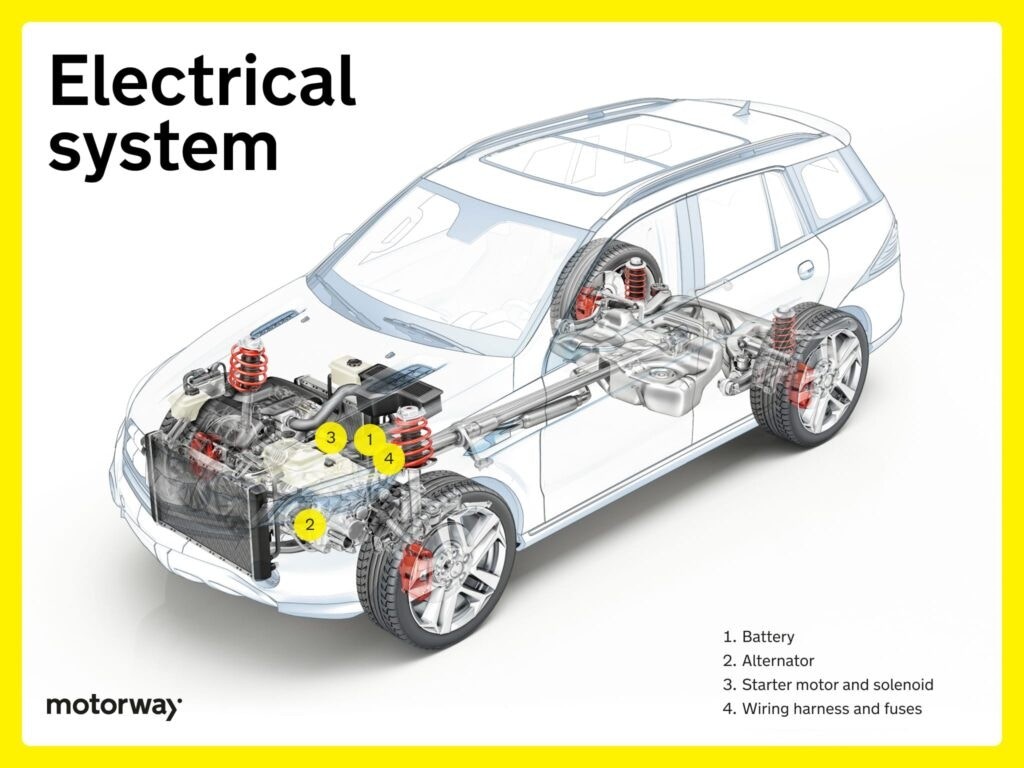
Electrical System
Your car’s electrical system is central to all its functions, from the engine to interior accessories.
Battery
The car battery provides the initial electrical energy to start the engine and power electrical functions. All cars, including EVs (which also have auxiliary 12V batteries), rely on batteries. Battery issues or reduced capacity will require replacement.
Alternator
The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine’s rotation into electrical energy. This energy recharges the battery and powers the car’s electrical system while the engine is running.
Crucially, the alternator regulates voltage to maintain a consistent electrical supply, preventing battery overcharging and ensuring electrical components receive the correct power levels.
Starter Motor and Solenoid
The starter motor and solenoid work together to initiate engine start-up. The solenoid activates the starter motor, which then turns the engine crankshaft to begin the combustion process. This coordinated action converts electrical energy into the mechanical motion required to start the engine.
Wiring Harness and Fuses
The wiring harness distributes electricity throughout the vehicle, connecting various electrical components. Fuses, strategically placed within the harness, protect the electrical system from overloads by breaking circuits when excessive current is detected. Together, they ensure a safe and organized electrical power flow, preventing damage and safeguarding the entire electrical network.
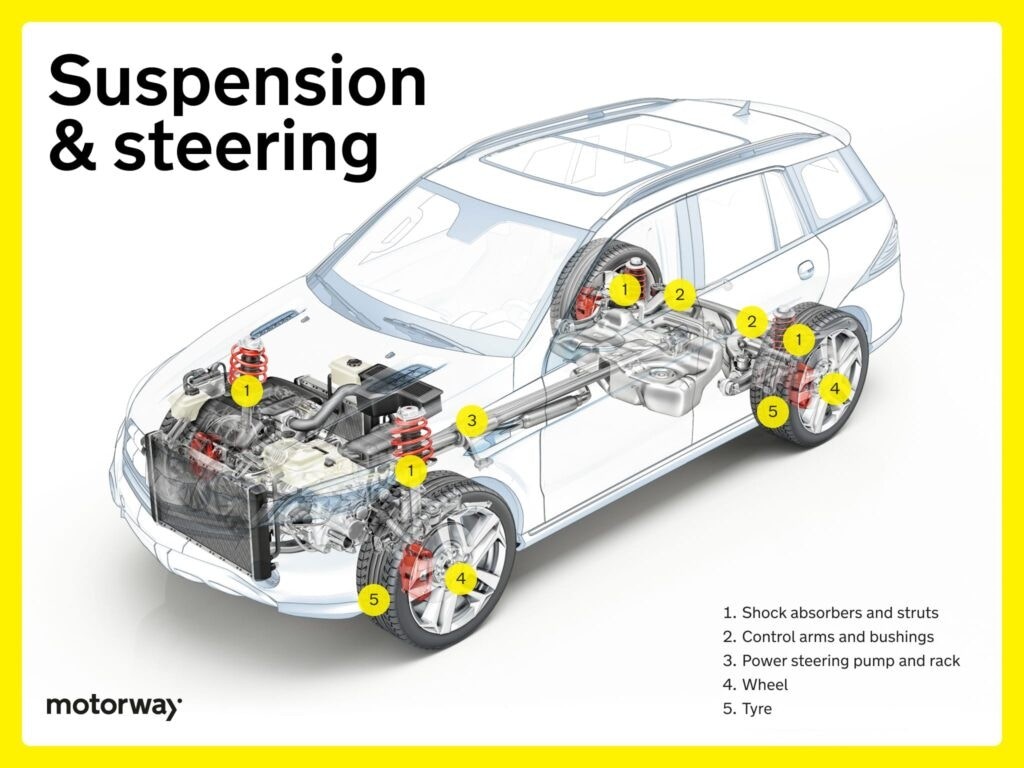
Suspension and Steering Systems
Smooth handling and maneuverability rely heavily on complex power steering and suspension systems.
Shock Absorbers and Struts
Shock absorbers and struts are vital for a car’s suspension. Typically, a car has four shock absorbers designed to dampen shocks and vibrations, improving ride comfort by controlling wheel movement.
Struts, often at the front and sometimes rear, combine structural support with shock absorption, enhancing vehicle stability and handling. Together, they minimize the impact of road imperfections, ensuring a smoother and more enjoyable ride.
Control Arms and Bushings
Control arms and bushings in the chassis contribute to stability and smooth handling. Control arms link the suspension system to the vehicle’s frame, while bushings provide flexibility and cushioning at these connection points. This combination absorbs road irregularities, maintains proper wheel alignment, and ensures a balanced and controlled ride.
Power Steering Pump and Rack
The power steering pump and rack are crucial for responsive steering. The pump generates hydraulic pressure, which the rack then uses to convert into controlled steering motion, making steering easier and more precise. Together, they provide smooth and effortless maneuverability, enhancing driving ease and control.
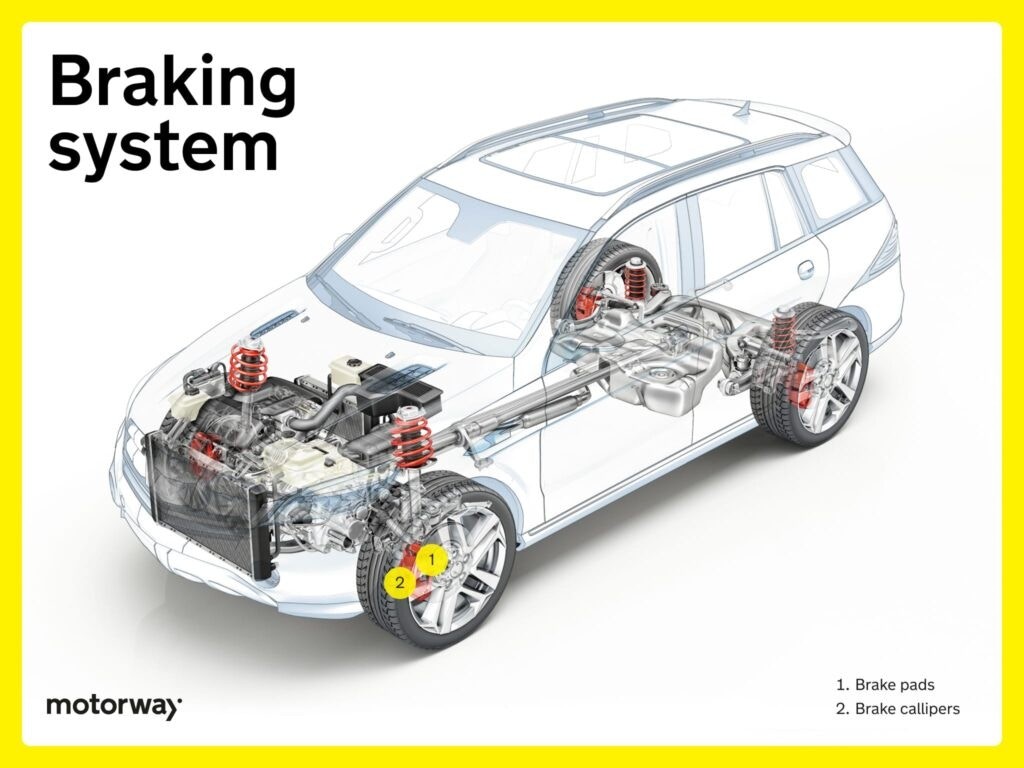
Braking System
The braking system is a meticulously engineered part of your vehicle, rigorously tested to ensure road safety.
Brake Pads
Brake pads are friction components, often made of composite materials, that press against the brake rotors. This action converts kinetic energy into heat, causing the vehicle to slow down or stop. Their robust design ensures reliable braking performance when the brake pedal is used, contributing to both safety and the longevity of the braking system. Brake pads are subject to wear and tear over time, particularly with frequent or aggressive braking.
Brake Calipers
Brake calipers are positioned around the brake rotors and contain pistons. When hydraulic pressure is applied (by pressing the brake pedal), these pistons clamp the brake pads against the rotor. This generates the friction needed for controlled deceleration. Their precise function ensures responsive and reliable braking, which is fundamental for driving safety.
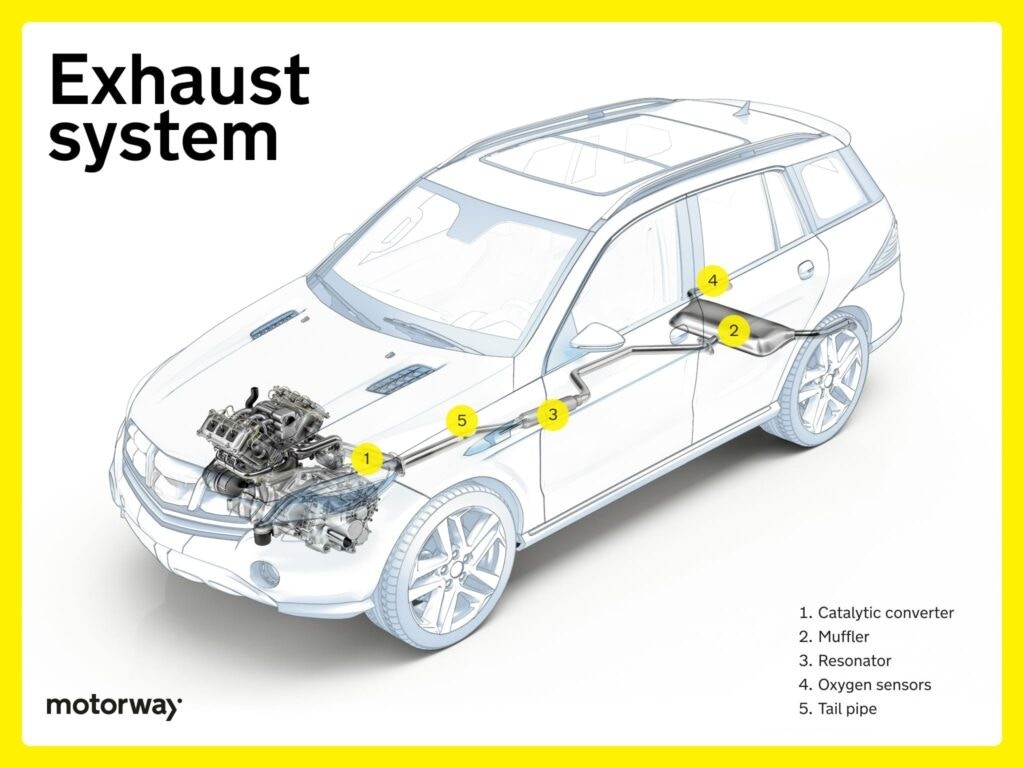
Exhaust System
Maintaining your exhaust system is crucial for ensuring your car runs cleanly and minimizes pollutant emissions.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter, in vehicles with internal combustion engines, reduces harmful emissions. It converts pollutants like carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances through chemical catalysis. This device plays a vital role in reducing vehicle emissions, contributing to cleaner air and environmental protection, and is a key component for meeting emission standards.
Muffler and Resonator
The muffler and resonator work together in the exhaust system to manage and reduce noise. The muffler is primarily responsible for reducing exhaust noise, while the resonator fine-tunes sound frequencies to control the exhaust note. This system ensures the vehicle operates at acceptable noise levels while also allowing drivers to hear engine feedback, which can be helpful for driving adaptively.
Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. This data is crucial for the engine control unit (ECU) to precisely adjust the fuel-air mixture. This optimization improves combustion efficiency and reduces emissions by ensuring the engine operates at its most effective air-fuel ratio.
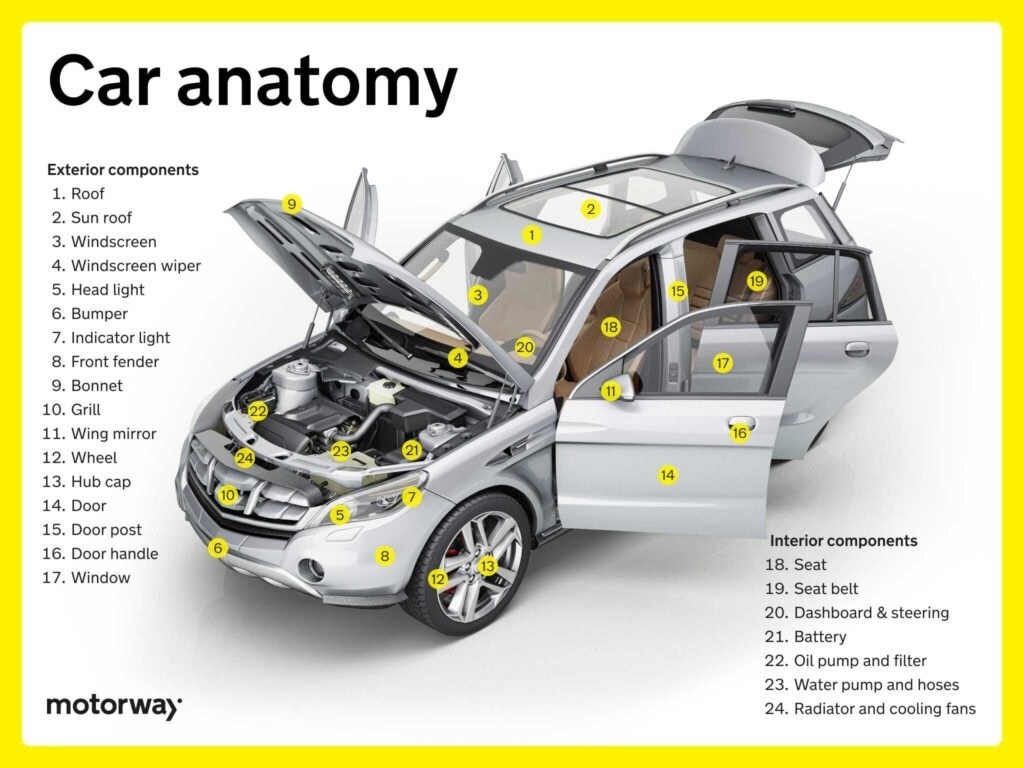
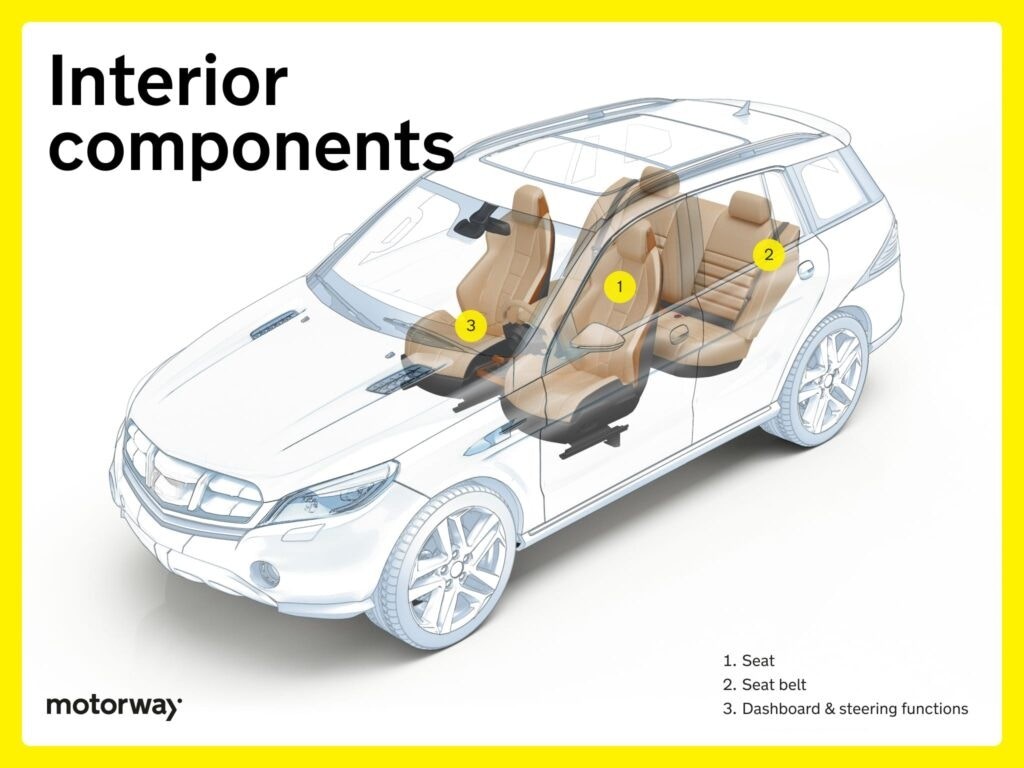
Interior Components
Maintaining your car’s interior is relatively inexpensive and can significantly impact its resale value.
Seats & Seat Belts
Car seats are designed for comfort and support, available in various materials and configurations. Seat belts are essential safety features that secure occupants during travel. Modern seat belts often include pretensioners, which tighten the belt in a collision, and force limiters, which reduce the force exerted on the occupant’s chest.
Dashboard & Steering Functions
The dashboard acts as the driver’s command center, displaying critical information such as speed, fuel level, and engine status. It provides a comprehensive overview of the vehicle’s operational status. The steering wheel integrates power-assisted steering and controls for indicators, wipers, and multimedia systems, putting essential functions within easy reach of the driver.
Exterior Components
Addressing exterior imperfections like scratches can enhance your car’s appearance and resale value.
Features & Controls on Doors
Door features and controls enhance both convenience and safety. Standard features include electric window controls, door locks, and mirror adjustments. Some vehicles also offer advanced features like keyless entry systems and power-operated doors, contributing to a more convenient and user-friendly driving experience.
Wheels and Tyres
Types of Tyres and Their Functions
| Type of Tyre | Function |
|---|---|
| Summer tyres | Designed for warm weather, providing excellent grip and handling in both dry and wet conditions. |
| Winter tyres | Engineered for cold temperatures, featuring special treads for superior traction on snow and ice. |
| All-season tyres | Versatile tyres that offer a balance of traction and durability in various weather conditions, suitable for both wet and dry roads. |
| Performance tyres | Designed for sporty driving, prioritizing enhanced handling, grip, and responsiveness at high speeds. |
| Off-Road tyres | Built for challenging terrains, featuring rugged treads and reinforced sidewalls for increased traction and durability on uneven surfaces. |
| Run-flat tyres | Equipped with reinforced sidewalls, allowing continued driving at reduced speeds for a limited distance after a puncture. |
| Touring tyres | Focused on providing a smooth and comfortable ride, ideal for long journeys with low noise and good handling. |


Wheel Construction Guide: Alloy vs. Steel Wheels
Wheel construction varies, offering different benefits:
- One-piece construction: The wheel is made from a single piece of material, commonly alloy or steel. This is a standard design for both alloy and steel wheels due to its simplicity and strength.
- Two-piece construction: The wheel consists of two parts: the center and the outer rim, joined by bolts or welding. This construction is often found in performance or custom wheels, offering a balance of strength and design flexibility.
- Three-piece construction: The wheel has three components: the center, outer rim, and inner hoop. This modular design allows for extensive customization and is popular in aftermarket wheels, offering high levels of adjustability and style.
- Forged construction: Forged wheels are made from a solid block of metal compressed under high pressure. This process results in wheels that are significantly stronger and lighter than cast wheels, making them ideal for high-performance and racing applications.
- Multi-piece construction: This design combines multiple components, including a center section, outer rim, and bolts, offering versatility in sizing and customization. Multi-piece wheels are favored for their aesthetic appeal and customization options.
Material choices also impact wheel characteristics:
- Alloy wheels: Made from a mixture of metals, typically aluminum or magnesium. They are lightweight, improving heat dissipation and enhancing vehicle aesthetics. Alloy wheels are often preferred for their performance and appearance benefits.
- Steel wheels: Constructed from steel, making them highly durable. Although heavier than alloy wheels, steel wheels are robust, cost-effective, and well-suited for demanding driving conditions where durability is key.
Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
The TPMS is a crucial safety feature that continuously monitors tyre pressure. Sensors in each tyre transmit real-time pressure data to the vehicle’s computer. If tyre pressure deviates from the optimal level, the system alerts the driver. This system enhances safety, improves fuel efficiency, and extends tyre life by ensuring proper inflation is maintained.
FAQs
What parts are under a car?
Beneath a car, you’ll find essential systems including the engine, transmission, suspension, exhaust system, and fuel system. These components work together to ensure the vehicle operates correctly and delivers expected performance. These “Bottom Of Car Parts” are critical for the vehicle’s fundamental operation.
How many car parts are on a car?
The number of parts in a car can vary significantly, but modern vehicles can contain over 30,000 individual components. This includes parts across various systems, highlighting the complex engineering of modern car design. Electric vehicles generally have fewer parts due to simpler powertrains that rely on batteries and electric motors rather than complex mechanical systems.
What are the important parts of a vehicle?
Key vehicle parts include the engine, transmission, braking system, steering system, suspension, and electrical components. Each of these systems plays a vital role in ensuring vehicle safety, performance, and reliability.
What parts of a car can be sold separately?
Individual car components like engines, transmissions, body panels, and certain electrical parts can be sold separately. The feasibility of selling parts depends on market demand and part availability, offering options for repairs, replacements, or upgrades.
Why is there a shortage of car parts?
Car part shortages can arise from various factors, including supply chain disruptions, increased demand for specific components, manufacturing challenges, and global events that impact production and distribution networks.
Need to Sell Your Car?
Want to discover more about car ownership, maintenance, and selling your car? Explore our guides here, covering topics from Clean Air Zones to car tax, and plate changes to part exchange.
