For car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike, understanding your vehicle’s health is paramount. Modern vehicles are complex machines, and monitoring systems like the transmission temperature can provide crucial insights into their performance and potential issues. OBD2 scanners have become indispensable tools for accessing this data. BlueDriver® is a popular name in the OBD2 scanner market, but when it comes to specific parameters like transmission temperature, can BlueDriver OBD2 reliably deliver? Let’s delve into the capabilities of BlueDriver and explore how it stacks up against alternatives like OBDLink® MX+ in monitoring this vital metric.
BlueDriver® has gained recognition for its user-friendly interface and ability to read generic OBD-II codes. It offers a convenient way to diagnose common engine problems. However, the depth of diagnostic information an OBD2 scanner can provide varies significantly. “Enhanced OEM diagnostics” is a key term in this context, referring to manufacturer-specific data beyond the standard OBD-II parameters. This enhanced data includes things like detailed trouble codes for systems beyond the engine (like ABS, airbag, and HVAC) and, importantly, live parameters such as transmission temperature.
When comparing BlueDriver® and OBDLink® MX+ in terms of enhanced OEM diagnostics, a clear distinction emerges. While BlueDriver® can read some OEM diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), its ability to display OEM live parameters is severely limited – it essentially offers no support for them. This is a significant drawback if you’re looking to monitor critical parameters like transmission temperature. If your goal is to keep an eye on your transmission’s temperature, tire pressure, or other manufacturer-specific live data, BlueDriver® falls short.
In contrast, OBDLink® MX+ excels in accessing enhanced OEM diagnostics. It not only reads generic OBD-II data but also provides access to a vast range of OEM DTCs and, crucially, thousands of OEM live parameters. This includes transmission temperature, making it a superior tool for comprehensive vehicle monitoring. Furthermore, OBDLink® MX+ boasts hardware compatibility that BlueDriver® lacks, specifically the ability to communicate on GM SW-CAN and Ford MS-CAN networks. These manufacturer-specific networks are essential for accessing a broader spectrum of diagnostic information in vehicles from these brands. BlueDriver’s limitations in hardware mean it cannot tap into these networks, leaving a significant portion of potentially valuable data inaccessible.
To illustrate this point, consider a vehicle network diagram, like that of a 2015 Ford Expedition. Modern vehicles utilize networks to connect various electronic control units (ECUs), which manage different vehicle functions. In the Ford Expedition example, ECUs are distributed across networks like HS-CAN and MS-CAN. OBDLink MX+ can communicate with modules on both networks, granting access to a wider range of parameters and DTCs. BlueDriver®, however, is restricted to HS-CAN and cannot access the modules and data residing on the MS-CAN network. This hardware difference directly impacts the amount of diagnostic information accessible to the user, particularly for those interested in parameters like transmission temperature that might be available on these proprietary networks.
Beyond enhanced diagnostics, another critical aspect of OBD2 scanners is app support. Both OBDLink MX+ and BlueDriver® come with their own mobile apps for Android and iOS. OBDLink MX+ further extends its compatibility by including a license for OBDwiz, a Windows-based diagnostic program. However, the openness of their architectures is where they diverge significantly.
OBDLink MX+’s open architecture allows it to be compatible with dozens of third-party automotive apps. This expands its functionality dramatically, enabling users to perform specialized diagnostics, track performance metrics, customize digital dashboards, and even access vehicle-specific features through various apps developed by different vendors. In contrast, BlueDriver® operates on a closed architecture. Users are limited to the BlueDriver® app, restricting their choices and potentially missing out on specialized functionalities offered by third-party applications.
| Feature | MX+® | BlueDriver® |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced OEM Diagnostics | DTCs & thousands of OEM parameters, GM & Ford network access | DTCs only, no OEM parameters, limited network access |
| Third-party App Support | Dozens of popular apps | BlueDriver® app only |
| iOS Support | Yes | Yes |
| Android Support | Yes | Yes |
| Windows Support | Yes | No |
| Sampling Rate | Up to 100 samples/second | Up to 10 samples/second |
| Battery Drain Protection | Excellent | Inadequate |
| Overvoltage Protection | Survives 90V continuous | Fails at 19V |
| Warranty | 3 years | 1 year |


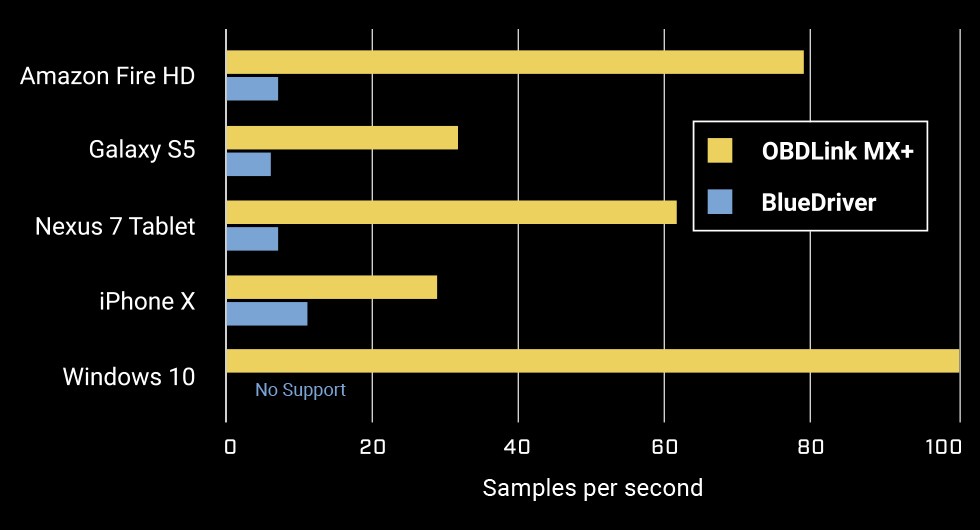


Sampling rate is another important technical specification. It determines how many data points an OBD2 device captures per second. A higher sampling rate is crucial for accurately monitoring rapidly changing signals and multiple parameters simultaneously. This is especially relevant for smooth data visualization in graphs and digital dashboards, essential for real-time monitoring of parameters like transmission temperature during driving. Benchmark tests have shown OBDLink MX+ to be significantly faster, with sampling rates up to ten times higher than BlueDriver®, providing a much more responsive and detailed data stream.
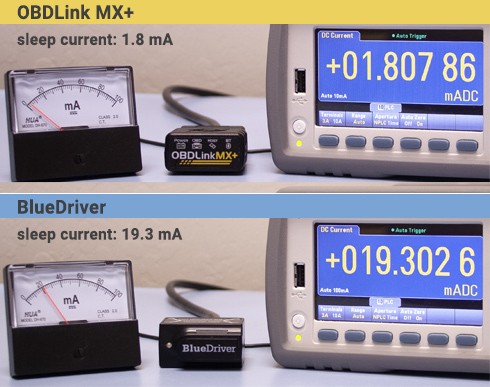
For users who prefer to leave their OBD2 scanner plugged in continuously, battery drain protection is a vital consideration. A well-designed OBD2 adapter should enter a low-power “sleep” mode when the engine is off to minimize battery drain. Tests have revealed significant differences in power consumption between OBDLink MX+ and BlueDriver®. BlueDriver® takes considerably longer to enter sleep mode and, more alarmingly, consumes significantly more energy in sleep mode – up to ten times more than OBDLink MX+. This excessive current draw of BlueDriver® can potentially lead to battery drain issues, a concern echoed by user reports.
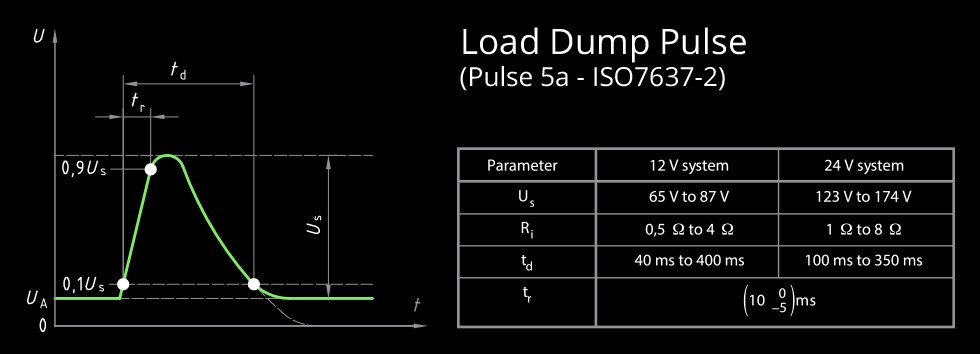
Electrical robustness is also paramount for OBD2 devices due to the harsh electrical environment in vehicles. Overvoltage protection is crucial to safeguard the device from voltage spikes, such as “load dump” pulses, which can occur when the battery is abruptly disconnected while the alternator is charging. Tests simulating load dump conditions and continuous overvoltage scenarios have demonstrated the superior overvoltage protection of OBDLink MX+. While OBDLink MX+ survived 90-volt pulses and continuous 90-volt exposure without damage, BlueDriver® failed catastrophically, suffering permanent damage at just 19 volts in ramp-up tests and under pulse testing. This difference in overvoltage protection highlights a significant disparity in the robustness and reliability of these two OBD2 adapters.
Finally, warranty coverage provides an indication of manufacturer confidence in product quality. OBDLink MX+ offers a 3-year warranty, triple the 1-year warranty provided with BlueDriver®, further emphasizing the greater durability and reliability of OBDLink MX+.
In Conclusion:
While BlueDriver® offers a user-friendly OBD2 scanning experience for basic diagnostics and reading some OEM DTCs, it falls short when it comes to accessing crucial live parameters like transmission temperature. For users who require comprehensive vehicle monitoring, including transmission temperature, and demand access to a wider range of OEM data, superior performance, robust protection, and broader app compatibility, OBDLink® MX+ emerges as the clear winner. Its enhanced OEM diagnostic capabilities, faster sampling rate, better battery drain protection, superior overvoltage protection, and longer warranty make it a more reliable and feature-rich choice for serious car enthusiasts and professionals alike. If monitoring Blue Driver Obd2 Transmission Temperature is your goal, understanding the limitations of BlueDriver® and the capabilities of alternatives like OBDLink MX+ is essential for making an informed decision.