Looking to monitor your car’s performance and diagnostics without the hassle of wires?
This introduction delves into the world of Bluetooth OBD2 data logging, highlighting its key benefits and practical applications. Discover how you can wirelessly access and record valuable data from your vehicle using a Bluetooth Obd2 Data Logger. Unlike standard OBD2 scanners, advanced devices like the CANedge offer a more versatile solution for logging and processing your car’s data. With 100% free software and APIs, including browser-based dashboards, you gain complete control over your vehicle data.
Explore below why a Bluetooth OBD2 data logger, especially the CANedge, is an excellent choice for CAN and OBD2 data logging and telematics applications.
Tip: Watch our brief 4-minute introductory video to quickly understand the basics!
In this article
products contact us
Understanding Bluetooth OBD2 Data Logging
First, let’s recap the fundamentals of OBD2 and how Bluetooth technology enhances data logging:
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) provides a standardized set of parameters, known as OBD2 PIDs, that can be recorded and easily interpreted across a wide range of vehicles. Bluetooth OBD2 data logging simplifies this process by eliminating the need for physical connections.
Logging OBD2 data wirelessly via Bluetooth typically involves these straightforward steps:
- Bluetooth OBD2 Logger Configuration: Set up your Bluetooth OBD2 data logger with the specific OBD2 PIDs you want to monitor.
- Wireless Connection: Plug the Bluetooth OBD2 adapter into your car’s OBD2 port and establish a Bluetooth connection to your recording device (e.g., smartphone, laptop). Start logging wirelessly.
- Data Extraction and Decoding: Depending on the device, you might extract data via SD card or direct download. Use free software/APIs to decode the logged data.
For more detailed instructions, refer to the FAQ section below or our comprehensive documentation:
CLX000 OBD2 guide CANedge OBD2 guide
Top 4 Advantages of Bluetooth OBD2 Data Loggers
Bluetooth OBD2 logging provides a convenient way to gather vehicle data from virtually any car. Here are the primary benefits:
Enhanced Driver and Vehicle Optimization
Bluetooth OBD2 data enables real-time monitoring and optimization of driving habits and vehicle performance. For instance, you can track fuel efficiency, engine performance metrics, and more. OEMs can utilize this data to evaluate the real-world performance of prototype components.
Streamlined Rare Issue Diagnostics
Intermittent car problems can be challenging to diagnose as they may not occur during service appointments. A Bluetooth OBD2 data logger allows you to continuously record data, capturing events leading up to a rare issue. This logged data can be invaluable for pinpointing the root cause of the problem.
Wireless Car Fleet Management
Bluetooth OBD2 telematics, especially when integrated with WiFi or cellular connectivity, revolutionizes fleet management. It facilitates driver behavior analysis, fuel consumption reduction, proactive maintenance, adherence to regulations, and improved incident management. Explore the potential of predictive maintenance through OBD2 data.
Unmatched Data Control and Custom Integration
A Bluetooth OBD2 data logger that offers WiFi connectivity provides complete control over your data. You can record raw time-series data, extract it via SD card, or wirelessly upload it to your own server. Open APIs simplify custom integration with your existing systems and platforms.
Considering which benefits align with your Bluetooth OBD2 logging needs? Contact us for expert guidance!
Contact us
Introducing the CANedge Bluetooth OBD2 Compatible Data Logger
While not directly Bluetooth, the CANedge CAN bus data logger surpasses typical Bluetooth OBD2 loggers in capability and flexibility. It offers optional GPS/IMU, WiFi, and 3G/4G, making it ideal for advanced OBD2 fleet telematics and applications requiring robust data logging.
PLUG & PLAY
Effortless, out-of-the-box data logging. Standalone operation. Seamlessly connect your vehicle to your server.
PRO SPECS
Removable 8-32GB SD card. Dual CAN/LIN channels. CAN FD support. Zero data loss. 50 µs RTC accuracy. Error frame logging. MF4 file format.
COMPACT & RUGGED
Small form factor: 8 x 5 x 2 cm. 100G shock resistance. Durable aluminum enclosure. Multiple LEDs for status indication. Configurable 5V power output (CH2).
WIFI/LTE CONNECTIVITY
Wirelessly push data to your server via WiFi or 3G/4G. End-to-end security. Over-the-air (OTA) updates. E2E security. OTA updates
GNSS + 3D IMU
Integrated GPS/IMU. Enhanced accuracy through sensor fusion. Records position, speed, distance, and more.
OPEN & INTEROPERABLE
Free open-source software/APIs. MF4 to ASC/CSV conversion. DBC support. Python API. Ready-to-use dashboards.
learn more
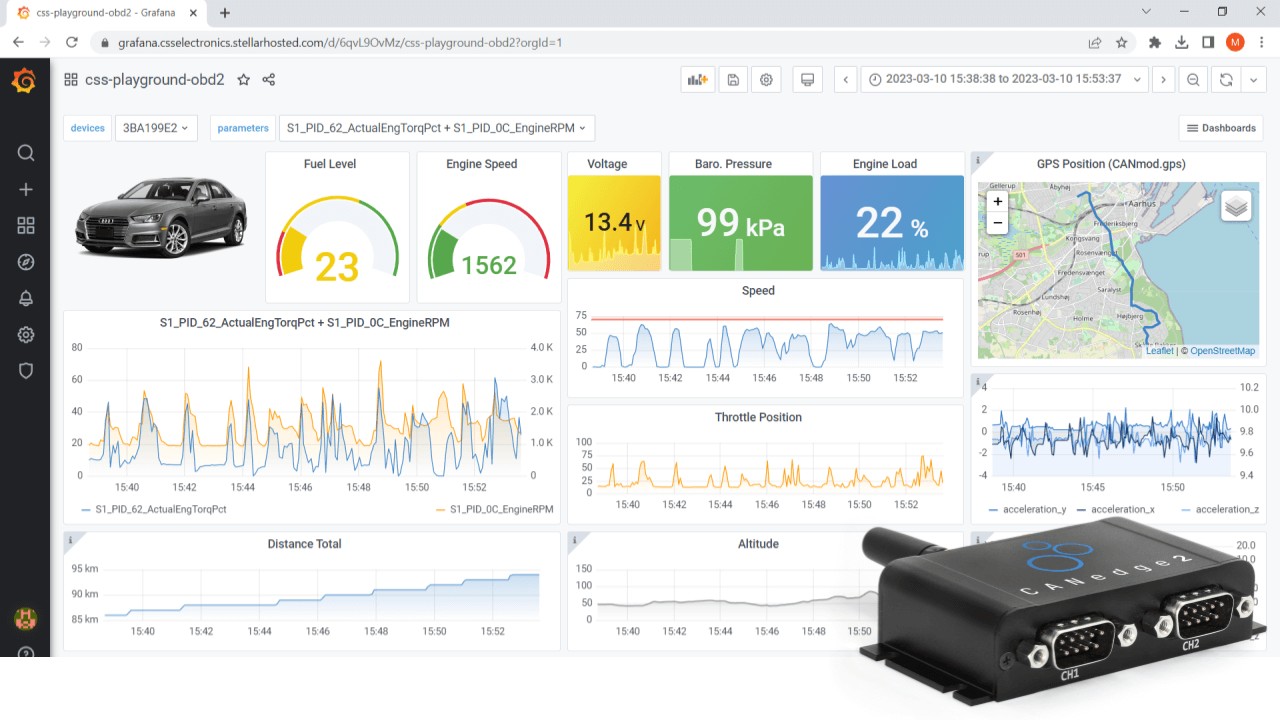
Software Example: Custom OBD2 Dashboards
The CANedge empowers you to create free, personalized browser dashboards to visualize your OBD2 data and set up alerts. Enhance your insights by combining OBD2 data with GPS/IMU data using a CANedge with GNSS/IMU.
Explore our online playground or delve deeper into our dashboard introduction.
playground dashboards intro
Get Your ‘OBD2 Data Pack’
Eager to work with authentic OBD2 data?
Download our comprehensive ‘data pack,’ which includes:
- Our OBD2 DBC file
- 25+ car DBC files (reverse-engineered)
- 100+ MB of data from 10+ vehicles
download now
Practical Use Cases
Below are real-world examples of how the CANedge can be effectively used for OBD2 data logging.
OEM Vehicle Part Field Testing
Do you require robust CAN/OBD2 field data logging from vehicles in operation?
For OEMs conducting late-stage field evaluations of prototype equipment, capturing OBD2 and CAN data from multiple vehicles over extended periods (e.g., months) is often crucial. The CANedge1 is ideally suited for this purpose due to its compact design, plug-and-play simplicity, and ease of pre-configuration. Data can be gathered periodically and analyzed using industry-standard CAN tools or the free asammdf GUI/API.
canedge1
Advanced Vehicle Telematics (OBD2 + GNSS/IMU + 3G/4G)
Looking to implement sophisticated OBD2 telematics for on-road vehicle fleets?
The CANedge3 enables wireless uploading of recorded OBD2 data via 3G/4G using your own SIM card. This facilitates near real-time OBD2 data transfer from vehicles to your private cloud server. OBD2 data can be automatically processed through open APIs (including OBD2 DBC decoding support), and CANedge3 devices support over-the-air updates. Furthermore, the integrated GPS/IMU in the CANedge3 adds valuable data streams like position, speed, trip distance, acceleration, and orientation to your telematics data.
canedge3
Case Study: OBD2/CAN Telematics Implementation
Discover how Volkswagen leverages the CANedge2 to log both OBD2 and raw CAN data to an SD card, and automatically push data to their self-hosted server for in-depth analysis.
“The CANedge2 allowed us to achieve rapid deployment with highly configurable options, and the support was exceptional!“
learn more 100+ case studies
Sample OBD2 Data from an Audi A4
Download OBD2 sample data recorded with the CANedge below.
You can also download our free, open-source OBD2 software to experience the process of decoding raw OBD2 data firsthand.
Raw OBD2 Decoded OBD2 Software
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The OBD2 protocol (SAE J1979) defines a standardized set of vehicle parameters that you can log. However, OBD2 support and the parameters available vary by vehicle make and model, with older vehicles often supporting fewer parameters.
Here are some common OBD2 parameters that are frequently accessible:
-
Fuel system status
-
Engine load
-
Coolant temperature
-
Fuel trim
-
Fuel pressure
-
Intake manifold pressure
-
Engine RPM
-
Vehicle speed
-
Intake air temperature
-
MAF air flow rate
-
Throttle position
-
Air status
-
Oxygen sensor status
-
Runtime since engine start
-
Distance with MIL on
-
Fuel tank level input
-
System vapor pressure
-
Absolute load value
-
Hybrid battery pack life
-
Engine oil temperature
-
Engine fuel rate
-
Torque
-
VIN
-
Various DTCs
For more in-depth information, consult the OBD2 PID Wiki page or the SAE J1979 standard.
To convert raw OBD2 data from a CANedge OBD2 data logger into human-readable values (e.g., km/h, RPM), you need a database of decoding rules and suitable OBD2 software.
We provide a 100% free OBD2 DBC file that includes most standardized Mode 01 (Service 01) OBD2 PID decoding rules, based on sources like the OBD2 PID Wiki page.
The OBD2 DBC file utilizes extended multiplexing for OBD2 decoding. Learn more in our DBC introduction and our OBD2 introduction, where we explain interpreting raw CAN frames with OBD2 responses.
Load your raw OBD2 data and the OBD2 DBC file into our free software tools, such as asammdf or our OBD2 dashboard integrations, to visualize decoded OBD2 parameters like Speed, Engine Speed, MAF, and Fuel Level.
This approach allows for easy modification of the OBD2 DBC to include proprietary OBD2 PIDs and combine it with proprietary CAN DBC files for comprehensive CAN/OBD2 car data logging.
What is UDS?
The Unified Diagnostic Services protocol (UDS, ISO 14229-1) is a communication protocol used within automotive ECU communication. UDS diagnostic tools are used to send request messages on the CAN bus, for tasks like retrieving information from specific ECUs. While OBD2 is designed for on-board diagnostics during vehicle operation, UDS is intended for off-board diagnostics when the vehicle is stationary.
How to Make UDS Requests over ISO-TP (ISO 15765-2)
Requesting OBD2 PIDs is relatively simple, involving single CAN frame requests and responses. UDS requests, however, can require transport protocol requests. For example, using UDS service 0x22 to request data by identifier involves a more complex communication flow:
- A ‘UDS data logger’ sends a request frame specifying the service ID (SID) and data identifier (DID).
- The car responds with a first frame containing SID, DID, total message length, and initial payload bytes.
- The UDS logger acknowledges with a flow control frame.
- The ECU then sends consecutive frames with the remaining message payload.
Logging UDS data requires a tool capable of sending custom CAN frames and flow control frames. Software tools must also reconstruct multi-frame UDS responses to extract and decode the payload.
UDS and OBD2 Extended PIDs for Enhanced Car Data Logging
UDS service IDs (SID) and data identifiers (DID) are sometimes combined into ‘extended OBD2 PIDs,’ like 0x220101. Service 0x22 UDS requests can access car data beyond standard service 01 OBD2 PIDs. For instance, some electric vehicles provide State of Charge (SoC%) data via UDS service 0x22.
Utilizing the CANedge as a Versatile UDS Data Logger
The CANedge can be configured to send UDS requests by sending a request frame followed by a flow control frame within a specified timeframe. This initiates the full UDS response sequence. Log files with UDS responses can be analyzed using tools like CANalyzer (by converting MF4 data to Vector ASC) for decoding. Alternatively, our free Python CAN bus API can process multi-frame UDS responses, enabling data visualization on platforms like Grafana UDS dashboards. Our github API examples include UDS response data and a UDS DBC file for decoding State of Charge (SoC%) from a Hyundai Kona EV. For more information, see our article on EV data loggers or contact us.
Is My Car OBD2 Compatible?
Most likely, yes. OBD2 has been mandatory in the USA since 1996 and in the EU (as EOBD) since 2003 for cars and light trucks.
However, OBD2 support doesn’t guarantee access to all desired data. Vehicle models vary in supported OBD2 parameters, with older cars often having limited real-time parameter support. Some manufacturers are also restricting OBD2 data access. While most cars use CAN for OBD2 communication, older US cars (pre-2008) and some EU brands may use different protocols.
Note: Check your OBD2 connector for “metal pins” in positions 6 (CAN High) and 14 (CAN Low) – see our OBD2 connector illustration (red pins). If unsure, send us a picture for verification.
There are five OBD2 signal protocols:
- ISO 15765 (CAN): Predominant, required in US vehicles since 2008.
- SAE J1850 (PWM): Ford standard.
- SAE J1850 (VPW): General Motors standard.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by Chrysler and some EU/Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230 (KWP2000): Primarily used by EU manufacturers.
The CANedge/CLX000 supports CAN-based OBD2. Contact us if you’re unsure about your car’s compatibility.
For a rough protocol check, use this resource: OBD2 compatibility (cars). See our OBD2 intro for basics.
With an OBD2 logger, you can verify supported Mode 01 OBD2 parameter IDs by requesting ‘Supported PIDs’ parameters (IDs 00, 20, 40, 60, 80, A0, C0) and analyzing the response data bytes (see the Wikipedia OBD2 PID article).
OBD2 vs. J1939 Data Logging
OBD2 data logging is typically for cars and light trucks. For heavy-duty vehicles (trucks, tractors, excavators), J1939 data logging is usually necessary. J1939 is a standardized protocol for heavy-duty vehicles, allowing data decoding across brands, similar to OBD2. A J1939 DBC file is needed to decode J1939 data, and CANedge/CLX000 can also function as J1939 data loggers.
Which OBD2 Data Logger is Right for Me? CANedge vs. CLX000
Both CANedge and CLX000 data loggers are suitable for OBD2 data logging.
For SD card logging, the CANedge series is recommended, being optimized for logging and offering auto-upload capabilities via CANedge2, ideal for OBD2 telematics and OBD2 dashboards.
For real-time OBD2 data streaming via USB to a PC, the CLX000 series, such as the CL2000, is preferable.
Contact us for personalized guidance to find the best fit for your use case.
Can I Stream OBD2 Data in Real-Time?
Yes, the CLX000 series supports real-time streaming of raw CAN and OBD2 data via USB – see our OBD2 streaming intro.
Raw CAN Data vs. OBD2 Data Logging
Connecting a CAN logger like CANedge or CLX000 to your OBD2 port typically starts recording raw CAN bus data by default. This raw CAN data is used for internal vehicle communication.
OEMs may log raw CAN data as they possess the CAN database (DBC file) for decoding. For non-OEMs, decoding raw CAN data often involves car hacking or finding partial databases online (e.g., opendbc).
For most users, OBD2 protocol data is more accessible. Almost all modern cars use CAN bus for OBD2 communication. OBD2 data is “on-request,” unlike raw CAN data. Logging OBD2 data involves sending specific CAN frames to request data, and the vehicle responds if the requested OBD2 PID is supported.
Types of OBD2 Devices
The OBD2 device market offers various types:
OBD2 Scanners: Used by mechanics for diagnostics, identifying diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and often include code-clearing functionality. Bluetooth and WiFi OBD2 scanners provide convenient smartphone access to diagnostic codes.
OBD2 Dongles: Small, affordable, user-friendly consumer Bluetooth OBD2 readers, often based on ELM327 microcontrollers. They offer real-time vehicle data via smartphone apps, suitable for basic consumer use but limited in flexibility.
OBD2 Data Loggers: Record OBD2 time-series data to SD cards in standalone mode. Data is extracted later via USB or SD card for analysis. The CANedge1 is an example of a versatile CAN/OBD2 data logger.
OBD2 WiFi/LTE Loggers: OBD2 data loggers with WiFi or 3G/4G capabilities, such as CANedge2/CANedge3, log to SD cards and auto-transfer data to servers, ideal for OBD2 telematics and creating OBD2 dashboards.
OBD2 Interfaces: CAN interfaces like CLX000 can also function as OBD2 interfaces, enabling real-time USB streaming of OBD2 data to a PC via software like SavvyCAN.
Will the Logger Drain My Car Battery?
In most cases, no.
CANedge typically powers on/off with the ignition as the OBD2 port often uses the IGN power supply. This prevents battery drain when the vehicle is off.
However, some vehicles may have OBD2 ports directly connected to the battery. The CANedge’s power draw is minimal (<2W), but if concerned, check the LEDs 15-20 minutes after turning off the car – if LEDs are off, the CANedge is off.
If the CANedge remains on, disconnect it for extended vehicle-off periods. Alternatively, configure the CANedge to start/stop based on CAN data patterns related to ignition status. Using a DB9-DC splitter cable and cigarette lighter adapter to power the CANedge via the cigarette lighter (ignition-linked) is another solution. See CANedge Docs for details.
Can I Log GPS Data with OBD2 Data?
While your car may have built-in GPS, accessing this data via OBD2 or proprietary CAN is often not feasible. Using a CANedge with GNSS/IMU is recommended. This allows you to record synchronized GNSS/IMU data alongside CAN/OBD2 data via Channel 1.
Ready to start Bluetooth-compatible OBD2 data logging?
Get your CANedge today!
Buy now Contact us
Recommended for you
CANEDGE1 – PRO BLACK BOX LOGGER
CANEDGE2 – PRO CAN IoT LOGGER
[