If you’re managing a fleet of vehicles, or simply keen on understanding your car’s health, you’ve likely encountered the term “OBD-II codes.” Often associated with the “Check Engine” light, these codes are essentially your vehicle’s way of communicating potential issues. But delving deeper, modern vehicles utilize a sophisticated communication network called Controller Area Network (CAN) to transmit these diagnostic messages. Understanding C.a.n. Obd2 Codes is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and ensuring your fleet operates smoothly.
This guide will break down the intricacies of CAN OBD2 codes, explaining what they are, how they function within your vehicle’s network, and why they are indispensable for managing your vehicles. We’ll explore how to interpret these codes, their different types, and how to leverage this information for optimal vehicle care and fleet management.
Understanding OBD-II and CAN: The Communication Backbone
On-board diagnostics (OBD-II) is a standardized system implemented in vehicles to monitor and report on their performance and health. Think of it as your car’s internal monitoring system, constantly checking various components and systems. When an issue arises, the OBD-II system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), signaling that something needs attention.
However, the language spoken within your vehicle’s systems is often through the Controller Area Network (CAN). CAN bus is a robust communication protocol that allows different electronic control units (ECUs) within your vehicle – such as the engine control module, transmission control module, anti-lock braking system, and more – to communicate with each other without a central host computer. OBD-II systems commonly utilize CAN bus to transmit diagnostic data, making c.a.n. obd2 codes a more precise way to refer to these diagnostic messages in modern vehicles.
Essentially, when your vehicle’s computer detects a problem—say, in the engine, transmission, or emissions system—it generates an OBD-II code. This code is then transmitted through the CAN bus network, and can be accessed via the OBD-II port, typically found under your dashboard.
This code is a valuable clue, guiding you or a mechanic to pinpoint the exact source of the problem. It empowers you to troubleshoot effectively and make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and fleet operations.
Decoding the Types of CAN OBD2 Codes
When a warning light illuminates on your dashboard and a CAN OBD2 code is triggered, understanding the category of the code is the first step towards diagnosis. These codes are broadly classified into four main types, each relating to different vehicle systems.
Powertrain Codes: Engine and Transmission Issues
Powertrain codes, starting with the letter ‘P’, are the most common type of CAN OBD2 codes. They indicate problems within the powertrain, which encompasses the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. These codes are crucial for diagnosing issues affecting your vehicle’s power delivery and overall performance.
For example, the code P0301 indicates a cylinder 1 misfire. This means that cylinder number one in your engine is not firing correctly. This could be due to various reasons, such as faulty spark plugs, fuel injectors, or ignition coils. A powertrain code like P0301 provides critical information for mechanics to start investigating the engine’s ignition or fuel systems to resolve issues that can lead to reduced fuel efficiency and engine damage if left unaddressed.
Body Codes: Comfort and Convenience Systems
Body codes, identified by the letter ‘B’, signal issues within the vehicle’s body systems. This category includes systems related to passenger comfort, convenience, and safety, such as lighting, airbags, power windows, and climate control.
For instance, a B0010 code might indicate a problem with the passenger-side front airbag deployment loop. This is a serious safety concern, as it suggests that the airbag system may not function correctly in a collision. Body codes like B0010 highlight problems that, while not directly related to engine performance, are crucial for vehicle safety and occupant protection.
Chassis Codes: Handling and Braking Systems
Chassis codes, beginning with the letter ‘C’, point to problems within the vehicle’s chassis systems. This includes components related to ride control, handling, and braking, such as the suspension, steering, and anti-lock braking system (ABS).
Consider the chassis code C0040, which can indicate a fault in the front right wheel speed sensor circuit. Wheel speed sensors are vital for systems like ABS and traction control. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to ABS failure, compromised stability control, and inaccurate speedometer readings. Chassis codes like C0040 are essential for diagnosing issues that affect vehicle safety and handling dynamics.
Network Communication Codes: Communication Network Issues
Network communication codes, starting with the letter ‘U’, are related to problems within the vehicle’s communication network, specifically the CAN bus system itself or the communication between different modules. These codes indicate disruptions in data flow between the various ECUs in the vehicle.
A common network communication code is U0100, which signifies “Lost Communication With ECM/PCM.” This means that there is a communication breakdown between the vehicle’s Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM) and other modules on the CAN bus network. This type of issue can arise from various causes, including wiring problems, faulty modules, or even a low battery. U-codes like U0100 can manifest in a range of symptoms, from engine performance issues to complete system failures, because effective communication is essential for the integrated operation of modern vehicles.
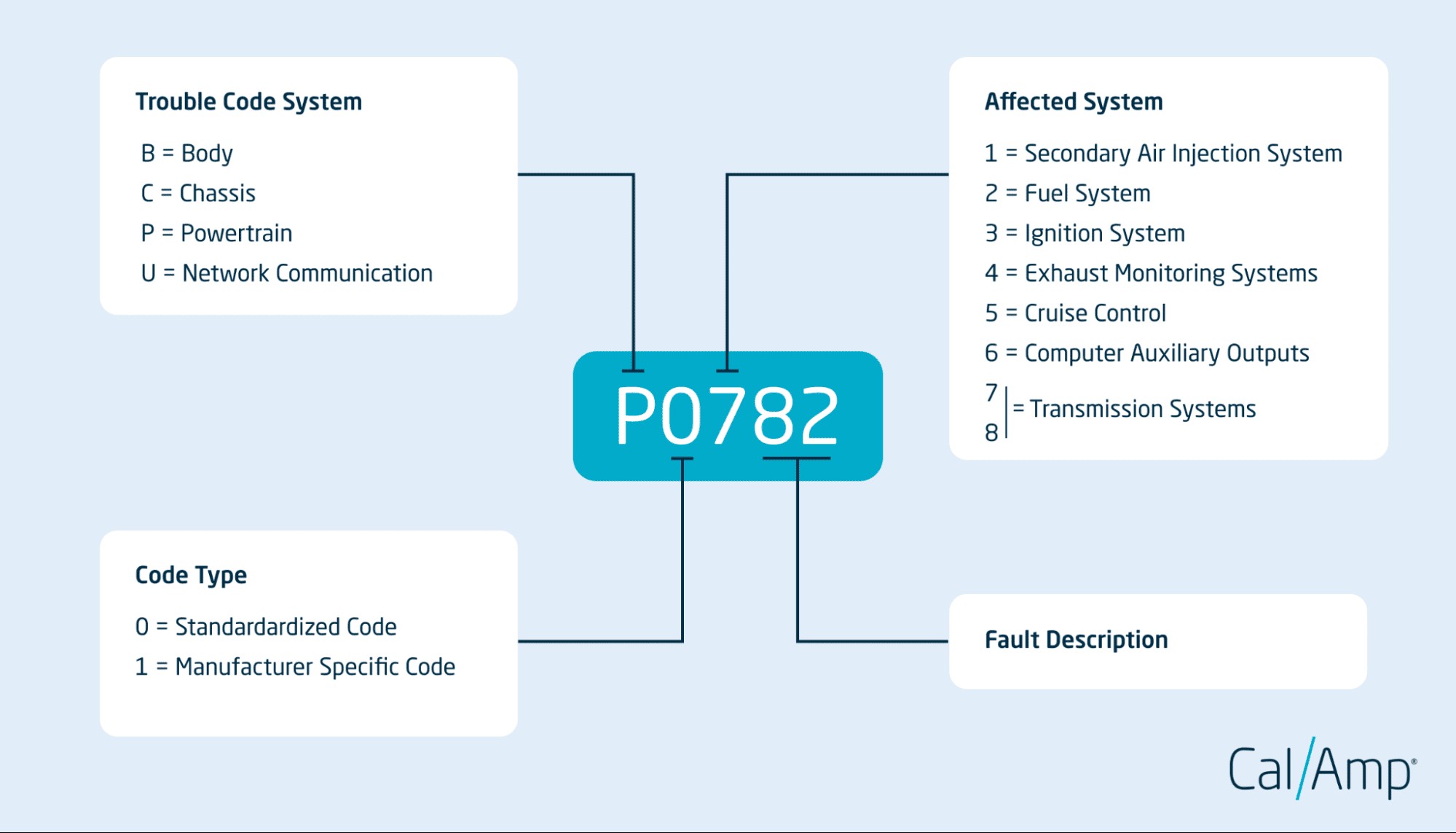
Reading and Interpreting CAN OBD2 Codes: A Step-by-Step Guide
CAN OBD2 codes are structured in a five-character format, with each position providing specific information about the detected issue.
Breaking down each character will help you understand the nature and location of the problem.
First Character: Trouble Code System
The first character is always a letter, indicating the primary system affected:
- P: Powertrain (Engine, Transmission, Drivetrain)
- B: Body (Comfort, Convenience, Safety Systems)
- C: Chassis (Suspension, Steering, Brakes)
- U: Network Communication (CAN Bus and Module Communication)
Second Character: Code Type
The second character is a digit, indicating whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
-
0: Generic or Standardized Code (SAE standardized codes common across all makes and models)
-
1: Manufacturer-Specific Code (Enhanced codes specific to a particular vehicle manufacturer)
- Standardized Code (0): A P0XXX code, for example, is a generic powertrain code defined by SAE standards. P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1) is a common generic code seen across many vehicle brands.
- Manufacturer-Specific Code (1): A P1XXX code, such as P1450 (Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Circuit Malfunction – Ford Specific), indicates a powertrain issue but is defined specifically by the vehicle manufacturer, offering more granular detail for diagnosis.
Third Character: Affected Sub-System
The third character is a digit indicating the specific sub-system within the broader system identified by the first character. While the exact meaning can vary slightly, common categories include:
-
1: Fuel and Air Metering
-
2: Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
-
3: Ignition System or Misfire
-
4: Auxiliary Emission Controls
-
5: Vehicle Speed Controls & Idle Control System
-
6: Computer Output Circuit
-
7, 8: Transmission
- For example, in a P03XX code range, the ‘3’ signifies the Ignition System or Misfire sub-system within the Powertrain.
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Code Identifier
The fourth and fifth characters are digits that provide a precise identifier for the specific fault within the identified system and sub-system. These digits pinpoint the exact nature of the problem.
- For example, P0420, where ‘4’ indicates Exhaust Monitoring Systems and ’20’ specifies “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)”. The ’20’ narrows down the problem to catalytic converter efficiency.
Clearing CAN OBD2 Codes: Methods and Precautions
While clearing CAN OBD2 codes might seem like a quick fix, it’s generally advised to address the underlying issue first. However, there are situations where clearing codes is necessary, such as after repairs have been made or in specific diagnostic procedures.
Using an OBD-II Scanner for Code Clearing
OBD-II scanners are not only useful for reading codes but also for clearing them. These devices connect to your vehicle’s OBD-II port and allow you to command the vehicle’s computer to erase stored codes and turn off the “Check Engine” light.
Using a scanner to clear codes can be beneficial for:
- Post-Repair Verification: After completing repairs, clearing the code allows you to confirm if the issue is truly resolved and if the code returns.
- Diagnostic Steps: In some diagnostic procedures, clearing codes and then re-scanning after a test drive helps isolate intermittent faults.
- Minor, Non-Recurring Issues: Occasionally, a transient issue might trigger a code that doesn’t represent a persistent problem. Clearing the code and monitoring if it reappears can be a reasonable approach in such cases.
However, it’s crucial to remember that simply clearing a code without fixing the root cause is only masking the symptom, not resolving the problem. The code and the underlying issue are likely to return.
Drive Cycle Method for Code Clearing
Some CAN OBD2 codes, especially those related to emissions monitoring, might clear themselves after a series of successful “drive cycles.” A drive cycle is a specific sequence of driving conditions that allows the vehicle’s computer to run self-tests on various systems.
Completing a drive cycle involves:
- Cold Start: Starting the vehicle after it has been sitting for several hours.
- Idling: Letting the engine idle for a specific period.
- Acceleration and Deceleration: Driving at various speeds and throttle positions.
- Cruising: Maintaining a steady speed for a set duration.
The exact drive cycle procedure varies between vehicle manufacturers and models. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or online resources for the specific drive cycle for your vehicle.
While drive cycles can clear certain codes automatically, they are not a guaranteed method for all types of CAN OBD2 codes and are not a substitute for proper diagnosis and repair.
Professional Mechanic Assistance for Code Clearing and Diagnosis
If you are unsure about the meaning of a CAN OBD2 code, how to properly diagnose the underlying problem, or how to clear codes effectively, seeking assistance from a qualified mechanic is always recommended.
Mechanics possess:
- Expertise and Training: Mechanics are trained to accurately diagnose vehicle problems based on CAN OBD2 codes and other diagnostic information.
- Specialized Tools: They have access to advanced diagnostic tools beyond basic OBD-II scanners, enabling them to perform in-depth analysis.
- Comprehensive Repair Capabilities: Mechanics can not only diagnose but also perform the necessary repairs to address the root cause of the codes.
Consulting a mechanic ensures that the problem is not just temporarily cleared but properly fixed, preventing potential further damage and ensuring vehicle safety and reliability.
Preventing CAN OBD2 Codes: Proactive Vehicle Maintenance
Preventing CAN OBD2 codes from appearing in the first place is always the best approach, saving you time, money, and potential vehicle downtime. Proactive vehicle maintenance is key to minimizing the occurrence of diagnostic trouble codes.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance Schedule
Adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is the cornerstone of preventing CAN OBD2 codes. Routine maintenance tasks help identify and address minor issues before they escalate into problems that trigger diagnostic codes.
Key maintenance tasks include:
- Regular Oil Changes: Fresh, high-quality engine oil lubricates engine components, reducing wear and preventing engine-related codes. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals.
- Air and Fluid Filter Replacements: Replacing air filters, fuel filters, and cabin air filters at recommended intervals ensures proper engine airflow, fuel delivery, and prevents contamination that can lead to codes.
- Spark Plug Inspection and Replacement: Faulty spark plugs can cause engine misfires, triggering powertrain codes. Inspect and replace spark plugs as per the maintenance schedule.
- Brake System Checks: Regular brake inspections ensure brake components are in good condition, preventing brake-related chassis codes.
- Tire Rotations and Inspections: Proper tire maintenance contributes to vehicle handling and safety, and regular checks can prevent issues that might indirectly trigger codes.
- Fluid Level Checks: Regularly check and top off essential fluids like coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid. Low fluid levels can lead to system malfunctions and codes.
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and adhere to it diligently.
Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
The quality of fuel and fluids used in your vehicles directly impacts their performance and longevity. Using substandard fuel or fluids can contribute to the occurrence of CAN OBD2 codes.
- High-Quality Fuel: Use fuel from reputable gas stations and choose the correct octane rating recommended for your vehicle. High-quality fuel ensures cleaner combustion and reduces the risk of fuel system and emission-related codes.
- Manufacturer-Recommended Fluids: Always use fluids that meet or exceed the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications for engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, brake fluid, and other essential fluids. These fluids are formulated to provide optimal performance and protection for your vehicle’s systems.
- Regular Fluid Checks and Top-offs: Periodically check fluid levels and top them off as needed. Pay particular attention to engine oil and coolant levels.
Using quality fuel and fluids and maintaining proper fluid levels is a proactive step in preventing component wear and tear and reducing the likelihood of CAN OBD2 codes.
Managing CAN OBD2 Codes for Fleets: Efficiency and Automation
For fleet managers, dealing with CAN OBD2 codes across multiple vehicles can be a complex task. Streamlining the process through centralization and automation is essential for efficient fleet management and minimizing vehicle downtime.
Centralized CAN OBD2 Code Tracking Systems
Implementing a centralized system for tracking CAN OBD2 codes across your fleet provides significant advantages. Instead of manually checking each vehicle, a centralized system gathers diagnostic data from all vehicles in one place, simplifying data access and analysis.
Fleet management solutions, like the CalAmp iOn, offer real-time CAN OBD2 code tracking capabilities. These systems:
- Collect Real-Time Data: Telematics systems integrated with vehicles automatically collect CAN OBD2 code data as soon as codes are generated.
- Centralized Dashboard: Provide a central dashboard where fleet managers can view all active and historical codes for all vehicles in the fleet.
- Alert Notifications: Generate alerts when new codes appear, enabling prompt responses to potential issues.
- Reporting and Analytics: Offer reporting and analytics tools to identify trends, recurring issues, and potential problem vehicles within the fleet.
- Integration with Maintenance Scheduling: Can integrate with maintenance scheduling systems to automatically trigger maintenance tasks based on detected codes.
Centralized CAN OBD2 code tracking significantly improves fleet maintenance efficiency, enabling proactive issue resolution and reducing vehicle downtime.
Continuous Fleet Monitoring with Telematics
Continuous fleet monitoring using telematics systems takes CAN OBD2 code management a step further. Telematics provides a constant stream of vehicle data, including location, performance metrics, driver behavior, and CAN OBD2 codes.
Benefits of continuous monitoring include:
- Early Code Detection: Issues are detected as soon as they occur, enabling rapid response and preventing minor problems from escalating.
- Proactive Maintenance: Allows for proactive maintenance scheduling based on real-time vehicle health data, reducing the risk of breakdowns.
- Performance Optimization: By monitoring vehicle performance data alongside CAN OBD2 codes, fleet managers can identify vehicles with reduced efficiency or potential mechanical issues impacting fuel economy and operational costs.
- Reduced Downtime: Faster detection and response to issues minimize vehicle downtime and keep the fleet operational.
Telematics systems provide a comprehensive solution for managing CAN OBD2 codes and overall fleet health, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Prioritizing Repairs Based on Code Severity
Not all CAN OBD2 codes are equally critical. Fleet managers should implement a system for prioritizing repairs based on the severity and potential impact of each code.
Prioritization involves:
- Code Severity Classification: Categorizing codes based on their potential impact on vehicle safety, performance, and operational capability.
- Immediate Action for High-Severity Codes: Codes indicating serious safety concerns or potential for major damage should be addressed immediately to prevent breakdowns and ensure driver safety.
- Scheduled Maintenance for Lower-Severity Codes: Less critical codes can be scheduled for repair during routine maintenance intervals, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing disruption to fleet operations.
- Clear Communication with Maintenance Teams: Ensuring clear communication of code severity and repair priorities to maintenance teams for efficient workflow management.
Prioritizing repairs based on code severity ensures that critical issues are addressed promptly while optimizing maintenance schedules for less urgent repairs, maximizing fleet uptime and minimizing repair costs.
In Conclusion: Leveraging CAN OBD2 Codes for Vehicle Health
CAN OBD2 codes are more than just error messages; they are valuable insights into your vehicle’s health and performance. Understanding c.a.n. obd2 codes empowers you to proactively manage vehicle maintenance, diagnose issues efficiently, and ensure your fleet operates reliably.
From deciphering code types and structures to utilizing scanners and telematics systems, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to effectively navigate the world of CAN OBD2 diagnostics. By embracing proactive maintenance and leveraging the power of CAN OBD2 data, you can keep your vehicles running smoothly, minimize downtime, and optimize your fleet operations.
For fleet management, solutions like CalAmp iOn take CAN OBD2 code management to the next level, providing real-time visibility, automated tracking, and comprehensive fleet health insights.
Request a demo today to discover how CalAmp iOn can revolutionize your fleet maintenance strategy and enhance your operational efficiency.