Car air conditioning (aircon) systems are marvels of automotive engineering, providing crucial comfort, especially in sweltering climates. Understanding how these systems work, and more specifically, identifying the individual components through a Car Aircon Parts Diagram, can be incredibly beneficial for both car enthusiasts and those looking to troubleshoot issues. As a seasoned car repair expert at carparteu.com, I’ve seen firsthand how a little knowledge of your car’s aircon system can go a long way. Today, we’re going beyond the basics and dissecting the heart of the system – the compressor – while exploring the broader car aircon parts diagram to give you a comprehensive understanding.
To truly grasp the intricacies, let’s embark on a journey similar to one I recently undertook, dismantling a car AC compressor to understand its inner workings. Inspired by a desire to create a “cut-away” display model, this exploration delves into the mechanics of a clutch-variable compressor, a common type in modern vehicles. While this article won’t turn you into an AC repair specialist overnight, it will equip you with valuable insights into the components detailed in a car aircon parts diagram and how they function together.
Before we dive into the compressor teardown, let’s establish a fundamental understanding of the car air conditioning system. A car aircon parts diagram typically illustrates a closed-loop system where refrigerant circulates, undergoing phase changes to cool the air entering your vehicle’s cabin. Here’s a simplified overview:
The system’s core components, clearly identifiable on any car aircon parts diagram, include:
- Compressor: The powerhouse of the system. It compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature and pressure. We’ll be dissecting this in detail.
- Condenser: Usually located at the front of the car, the condenser dissipates heat from the high-pressure refrigerant gas, causing it to condense into a liquid.
- Evaporator: Positioned inside the vehicle’s dashboard, the evaporator is where the liquid refrigerant expands and evaporates, absorbing heat from the cabin air and cooling it down.
- Expansion Valve or Orifice Tube: This component regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, controlling the cooling process.
- Receiver Drier or Accumulator: These components filter out moisture and contaminants from the refrigerant, ensuring system longevity and efficiency.
- Refrigerant: The lifeblood of the system, circulating and undergoing phase changes to transfer heat. R134a is a common type, though newer systems may use R1234yf.
For a more visual and detailed explanation of how these parts work in concert, numerous resources are available online. A video explanation can further solidify your understanding of the car aircon parts diagram in action.
Modern car aircon systems are sophisticated, incorporating sensors and electronic controls for optimal performance and efficiency. A functional diagram, like the one below for a Ford Fiesta, showcases the interconnectedness of these components and the role of electronic control units (ECUs). Analyzing such diagrams is crucial for advanced diagnostics and repairs.
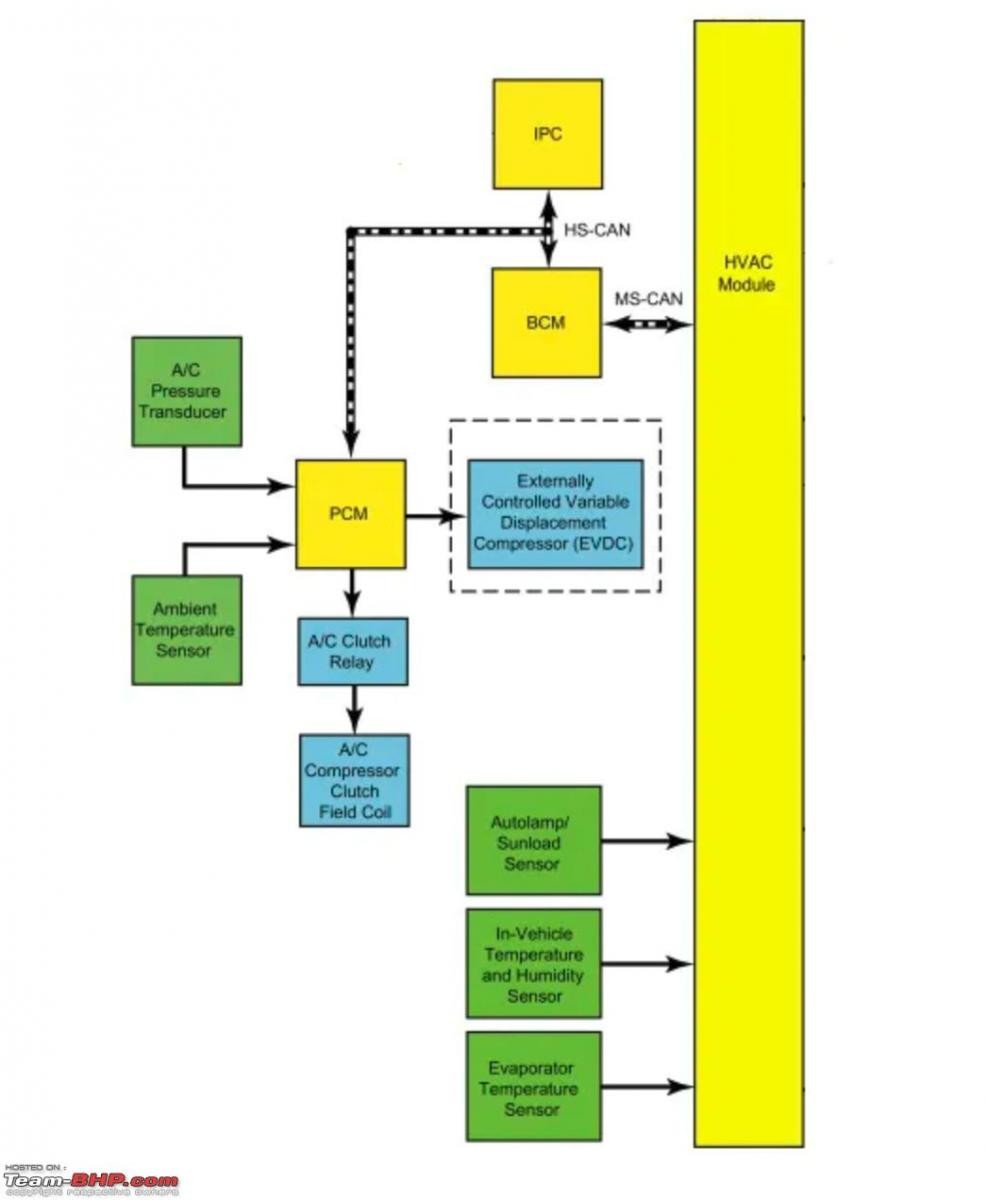 Ford Fiesta AC system functional diagram showcasing various sensors and control units
Ford Fiesta AC system functional diagram showcasing various sensors and control units
Now, let’s shift our focus back to the compressor, the component we’re taking apart. As indicated on a car aircon parts diagram, the compressor is responsible for circulating the refrigerant. However, not all compressors are created equal. They can be broadly categorized based on their operation:
- Clutch Compressors: Found in older vehicles, these compressors engage and disengage using an electromagnetic clutch. You’ll typically hear a distinct “click” when the clutch engages, and the compressor operates in an on/off manner.
- Variable Compressors: These compressors run continuously once the engine is started, but they regulate the refrigerant flow volume to match cooling demand. While efficient, early variable compressors faced durability concerns when not in constant use, particularly regarding lubrication.
- Clutch-Variable Compressors: The most common type in modern cars, these compressors combine the benefits of both systems. They offer variable refrigerant flow for efficiency and can disengage completely via a clutch when air conditioning is not needed, reducing wear and engine load. The compressor we’re examining is of this clutch-variable type.
The image below shows a side-by-side comparison of a new and an old compressor. The old unit, slated for dissection, clearly displays the clutch mechanism at the front. The electrical connector for the clutch is also visible.
When replacing a compressor, it’s crucial to know if it comes pre-filled with oil. Car AC systems require a precise amount of lubricant. Overfilling or underfilling can lead to system damage. Refrigerant recharging involves adding the correct amount of refrigerant, lubricant, and often a UV dye for leak detection. Always consult your vehicle’s workshop manual for specific oil and refrigerant capacities. Checking the compressor’s model plate, as shown below, reveals important information like the refrigerant type (R134a in this case).
Let’s begin the teardown process, starting with the clutch. A closer look at the clutch mechanism reveals the electrical lead that powers the electromagnet.
To remove the pulley and clutch, a small bolt on the compressor shaft needs to be detached. Securing the pulley in a vise allows for easy removal of this bolt.
The inner side of the clutch plate reveals its engagement mechanism. When the electromagnet is energized, it pulls the clutch plate towards the pulley, engaging the compressor shaft. The pulley itself houses a bearing, allowing it to freewheel when the clutch is disengaged. Splines on the clutch plate center match corresponding splines on the compressor shaft, creating a direct connection when engaged.
From a top view, the clutch plate assembly shows the spring mechanism that disengages the clutch when the electromagnet is de-energized. The gap between the clutch plate and pulley can indicate clutch wear.
With the components laid out in order of removal, we can see the clutch plate, circlip, pulley with bearing, and the exposed electromagnet. Wear in these compressors often manifests in the bearing or clutch. Replacing these components is often possible without removing the compressor from the car, saving time and the need to evacuate the refrigerant.
A close-up of the electromagnet reveals a felt seal, likely designed to protect against dirt and debris ingress from the clutch.
Removing the electromagnet exposes the front assembly of the compressor. Notice the green dye – a telltale sign of a refrigerant leak, and in this case, the reason for compressor replacement. Leaks often occur at pipe connections or, more commonly, at the compressor shaft’s front seal. This front seal leak was identified as the issue in this Fiesta’s AC system.
The splined compressor shaft is now clearly visible. It directly connects to the clutch plate, initiating compressor rotation upon clutch engagement. Another bearing and circlip are located deeper within the front recess. While component replacement is theoretically possible, specialized tools and expertise are often required, making full compressor replacement a more practical solution in many cases.
Further disassembly involves separating the compressor body. This particular compressor has three main sections: the front assembly, the middle section containing the cylinders, and the rear section housing the control solenoid and valve plates.
Exploring the anatomy of a car AC compressor provides valuable insight into the complex workings of your vehicle’s climate control system. While this teardown focuses on the compressor, remember that it’s just one piece of the puzzle, as illustrated by a comprehensive car aircon parts diagram. Understanding the function of each component, from the condenser to the evaporator and expansion valve, is key to diagnosing and maintaining your car’s AC system. For more in-depth information and discussions on car AC compressors and related topics, you can explore online automotive enthusiast forums and communities.
