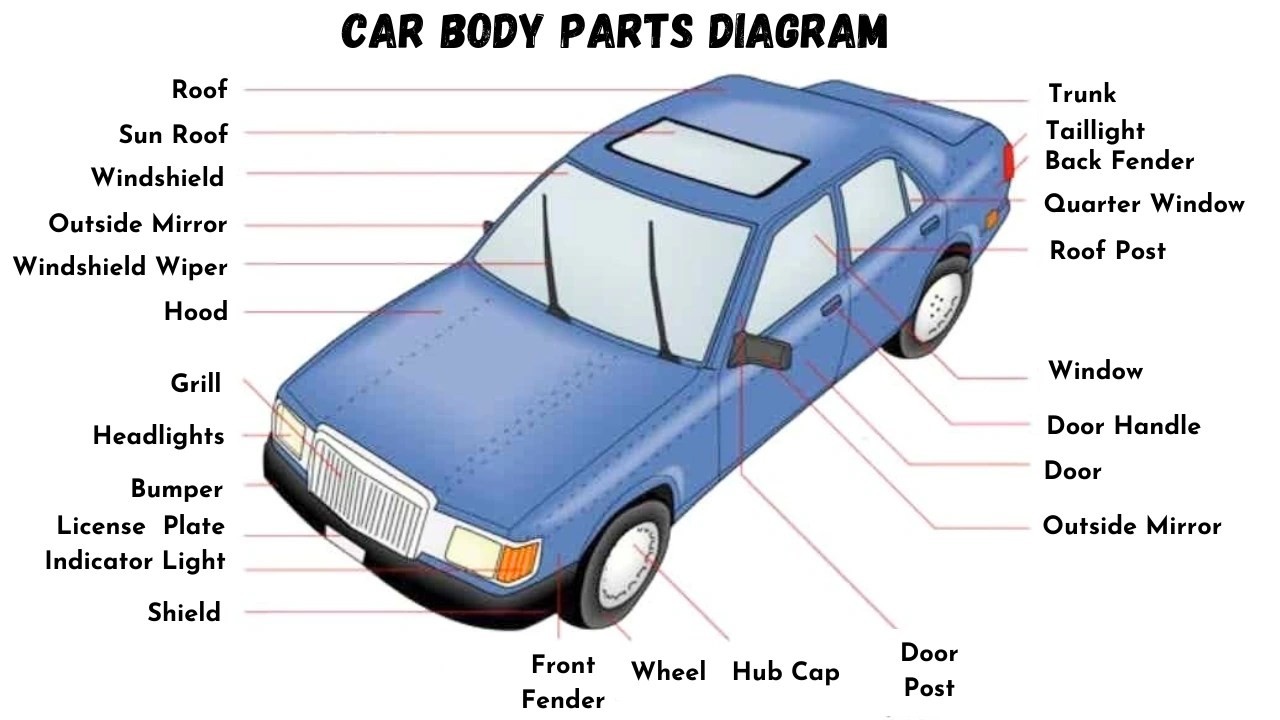
Have you ever wondered about the different components that make up your car’s exterior? Just like the human body, a car is composed of various parts working together. Understanding the names of car body parts is not only fascinating but also practical for maintenance, repairs, and even just appreciating your vehicle. This comprehensive guide will explore the major components of a car’s body, providing you with the names and functions of each part.
Exploring the Anatomy of a Car: Body Parts Names and Functions
The car body is more than just aesthetics; it’s a complex assembly of parts designed for safety, aerodynamics, and structural integrity. Let’s delve into the names of these essential car body parts:
1. Body Shell: The Foundation
 Car Body Shell
Car Body Shell
The body shell is the primary structure of the car. It’s the foundational framework upon which all other body parts, mechanical components, and interior fittings are mounted. Think of it as the skeleton of your car. It’s designed to provide structural rigidity and safety in case of collisions. The body shell typically excludes doors, windows, and detachable panels.
2. Hood or Bonnet: Covering the Engine
The hood (or bonnet in British English) is the hinged cover at the front of the car that protects the engine compartment. It’s crucial for safeguarding the engine and related components from weather elements and road debris. Made usually of steel or aluminum, the hood also allows easy access for maintenance and repairs. Some hoods feature scoops or bulges to accommodate larger engines or improve airflow.
3. Front Bumper: Impact Absorption at the Front
The front bumper is a protective bar at the front of the vehicle, designed to absorb impact during low-speed collisions. It’s engineered to minimize damage to the car’s body in minor accidents and protects crucial components like headlights and the radiator. Modern front bumpers often integrate with the vehicle’s design and may include grilles or fog lights.
4. Rear Bumper: Protecting the Vehicle’s Rear
Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper provides protection to the rear of the car. It’s designed to absorb impacts from the rear and safeguard the trunk, taillights, and exhaust system from damage in minor collisions. Rear bumpers are also crucial for vehicle safety and are often styled to match the overall car design.
5. Bumper Grille: Allowing Airflow
The bumper grille is an opening within the bumper, typically featuring a mesh or slatted design. Its primary function is to allow airflow to the engine and radiator for cooling. Grilles can vary significantly in style and are often a key design element that defines a car’s front appearance. Different types include main grilles, lower grilles, and fog light grilles.
6. Crash Guard or Bullbar: Added Front Protection
Crash guards or bullbars are robust metal bars fitted to the front of a vehicle, primarily for added protection in off-road or rural driving conditions. They are designed to protect the front of the vehicle from impacts with animals or debris. However, their use can be controversial due to pedestrian safety concerns and regulations vary by region.
7. Headlight: Illuminating the Road Ahead
Headlights are essential lighting components mounted at the front of the car. They provide illumination for driving in low-light conditions and at night, ensuring driver visibility and road safety. Modern headlights come in various technologies, including halogen, LED, and xenon, each offering different levels of brightness and efficiency.
8. Fog Lamp: Enhancing Visibility in Poor Weather
Fog lamps are specialized lights designed to improve visibility in foggy, misty, or heavy rain conditions. Typically mounted lower than headlights, fog lamps project a wide, flat beam that cuts through fog and illuminates the road surface, reducing glare and improving safety.
9. Indicator Lights or Signal Lights: Communicating Turns
Indicator lights, also known as signal lights or turn signals, are flashing lights located at the front, sides, and rear of the car. They are used to signal the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes, crucial for communicating with other drivers and ensuring safe maneuvering on the road.
10. Wiper Blade: Clearing the Windshield
Wiper blades are rubber strips attached to wiper arms that sweep across the windshield to remove rain, snow, debris, and washer fluid. They are vital for maintaining clear visibility through the windshield in inclement weather, ensuring driver safety.
11. Radiator: Engine Cooling System Component
The radiator is a critical component of the engine cooling system. Positioned behind the grille, it dissipates heat from the engine coolant, preventing overheating. Airflow through the grille and sometimes an auxiliary fan helps cool the radiator and maintain optimal engine temperature.
12. Radiator Supports: Holding the Radiator in Place
Radiator supports are structural elements that hold the radiator securely in place within the engine bay. They provide mounting points and stability for the radiator, ensuring it functions correctly and is protected from vibrations and impacts.
13. Cowl Panel: Under the Windshield
The cowl panel is the area located at the base of the windshield, often housing the windshield wipers and ventilation inlets for the cabin. It serves as a transition between the hood and the windshield and can also contribute to the car’s aerodynamics.
14. Quarter Panel: Rear Side Body Section
The quarter panel is the body section located between the rear door and the rear bumper, extending to the roof. It forms a significant part of the car’s side structure at the rear and often includes the wheel arch for the rear wheels.
15. Fender: Wheel Arch Panel
The fender (or wing in British English) is the body panel that frames the wheel arch. Its primary function is to prevent road debris, mud, and water from being thrown up by the tires onto the car body or other vehicles. Fenders contribute to the car’s aerodynamics and styling.
16. Fender Liners or Wheel Well Liners: Protecting the Fenders
Fender liners, also known as wheel well liners, are plastic or composite inner panels fitted inside the fenders. They provide an additional layer of protection to the fenders from corrosion, impacts from stones and debris, and help reduce road noise.
17. Roof: The Car’s Top Cover
The roof forms the upper enclosure of the car, providing protection from the elements for the occupants. Car roofs come in various styles, including hardtops, sunroofs, and panoramic roofs, and contribute to the vehicle’s overall structural integrity.
18. Sunroof: Allowing Light and Air
A sunroof is a movable panel in the car roof that can be opened to allow sunlight and fresh air into the cabin. Sunroofs can be manually operated or electrically powered and come in different sizes and designs, enhancing the driving experience.
19. Mirrors: Enhancing Driver Visibility
Mirrors, including side mirrors (or door mirrors) and the rearview mirror, are crucial for driver visibility. They allow the driver to see areas around and behind the vehicle, minimizing blind spots and ensuring safe lane changes and maneuvering.
20. Doors: Entry and Exit Points
Doors are hinged panels that provide access to the car’s interior. They are essential for entry and exit for passengers and driver. Car doors are designed for safety and security and include features like door locks, windows, and interior panels.
21. Door Handle: Opening and Closing Doors
The door handle is the mechanism used to open and close the car doors. Door handles can be exterior handles for outside access and interior handles for opening the door from inside. They come in various designs, from traditional levers to modern electronic or flush handles.
22. Window Glass: Visibility and Protection
Window glass panels are fitted into the door frames and windshield to provide visibility and protect occupants from wind, rain, and debris. Car windows are typically made of tempered or laminated glass for safety and durability.
23. Quarter Window: Small Side Window
The quarter window is a smaller window located behind the rear door or in the rear pillar of some vehicles. It provides additional visibility and can sometimes be a fixed or operable window, depending on the car design.
24. Trunk or Decklid: Rear Storage Access
The trunk (or decklid or boot in British English) is the hinged cover at the rear of the car that provides access to the luggage compartment. Trunks vary in size and design and are essential for cargo storage.
25. Mud Flaps or Splash Guards: Reducing Road Spray
Mud flaps, also known as splash guards, are panels located behind the wheels. They are designed to reduce the amount of water, mud, and road debris sprayed upwards and rearwards by the rotating tires, protecting the vehicle and other road users.
26. Wheels: Enabling Movement
Wheels are circular components that allow the car to move. They consist of a rim and tire assembly. Wheels are connected to the axles and rotate to propel the vehicle. The design and material of wheels can significantly impact the car’s performance and aesthetics.
27. Hubcap or Wheel Cover: Wheel Aesthetics
Hubcaps or wheel covers are decorative covers that fit over the center of the wheel. They primarily serve to enhance the appearance of the wheels and can also protect the wheel nuts from dirt and corrosion.
28. Dashboard or Instrument Panel: Driver Information Center
The dashboard, also known as the instrument panel, is located inside the car, directly in front of the driver. It houses essential instruments and controls, including the speedometer, tachometer, fuel gauge, and warning lights, providing crucial information to the driver.
29. Number Plate or License Plate: Vehicle Identification
The number plate, also known as the license plate, is a metal or plastic plate attached to the front and rear of the vehicle. It displays the vehicle’s registration number, uniquely identifying it.
30. Taillights: Rear Lighting and Signaling
Taillights are lighting assemblies located at the rear of the car. They serve multiple functions, including indicating the vehicle’s presence at night, signaling braking (brake lights), and indicating turns (integrated with indicator lights).
Conclusion: Knowing Your Car Body Parts
Understanding the names and functions of car body parts can be incredibly helpful for car owners. Whether you’re discussing repairs with a mechanic, looking to customize your vehicle, or simply wanting to be more knowledgeable about your car, this guide provides a solid foundation. Familiarizing yourself with these “Car Body Parts Names” will enhance your understanding of automotive anatomy and improve your car ownership experience.