Just like the human heart is essential for life, the engine is the powerhouse of your car. It’s responsible for converting fuel into the energy that moves your vehicle. While often considered a single unit, a car engine is actually a complex assembly of numerous components working in perfect harmony. Understanding the names and functions of these car engine parts is crucial for every car owner, whether you’re performing basic maintenance or simply want to be more informed about your vehicle.
Essential Car Engine Parts Explained
Modern car engines are built around sturdy metal cylinders, designed to withstand intense pressure and heat. Most cars today utilize engines with four to eight cylinders, although some high-performance vehicles can have as many as sixteen. These cylinders operate with precise timing, managing the intake of fuel and air for combustion and the expulsion of exhaust gases. Let’s explore some of the most vital car engine parts and their roles, referring to the diagram below to visualize their placement within the engine.
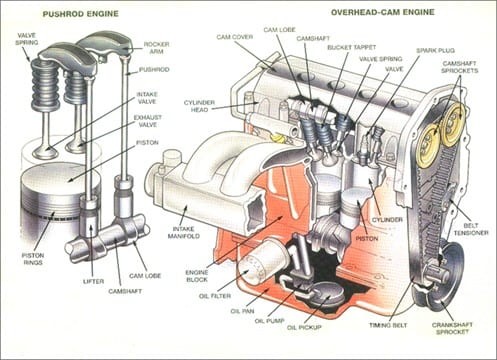 Diagram illustrating the major car engine parts and their locations within the engine block.
Diagram illustrating the major car engine parts and their locations within the engine block.
-
Engine Block: Consider the engine block as the foundational structure of your engine. Typically constructed from aluminum or iron, it’s a robust casting with precisely machined bores that form the cylinders. The engine block not only houses the cylinders but also incorporates passageways for coolant and oil, essential for engine temperature regulation and lubrication. Oil pathways are specifically designed to be narrower than coolant passages. Furthermore, the engine block serves as the primary housing for key internal components such as the pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft. Depending on the vehicle, it can contain anywhere from four to twelve cylinders, arranged in configurations like inline, flat, or V-shaped.
-
Pistons: Pistons are cylindrical components with a flat top surface that move vertically within the cylinders. Their primary function is to capture the energy released from the combustion of fuel and air, converting this force into motion that is transferred to the crankshaft, ultimately propelling the vehicle. During each crankshaft rotation, a piston travels up and down within the cylinder twice. In an engine operating at 1250 RPM, each piston will complete this up-and-down cycle an astonishing 2500 times per minute. Fitted around each piston are piston rings. These rings are crucial for maintaining compression within the combustion chamber and minimizing friction as the piston moves within the cylinder walls.
-
Crankshaft: Positioned in the lower section of the engine block, the crankshaft resides within crankshaft journals, areas specifically designed to support the shaft on bearings. This carefully engineered and balanced component is connected to the pistons via connecting rods. Much like a jack-in-the-box mechanism, the crankshaft transforms the linear, up-and-down motion of the pistons into a rotational motion, operating at engine speed. This rotational force is then used to power the vehicle’s drivetrain.
-
Camshaft: The camshaft’s location can vary depending on the vehicle design; it may be situated within the engine block or in the cylinder heads. Many modern vehicles feature camshafts in the cylinder heads, known as Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC) or Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) configurations. Supported by a series of oil-lubricated bearings for durability, the camshaft is responsible for precisely regulating the timing of valve opening and closing. It converts the rotary motion from the crankshaft into an up-and-down motion, which is then used to control the movement of lifters, pushrods, rockers, and ultimately, the valves.
-
Cylinder Head: The cylinder head is affixed to the engine block using cylinder bolts and sealed with a head gasket to prevent leaks. This component is integral as it houses numerous parts including valve springs, valves, lifters, pushrods, rockers, and camshafts. The cylinder head manages the critical passageways that facilitate the flow of intake air into the cylinders during the intake stroke and the removal of exhaust gases during the exhaust stroke.
-
Valves (Intake and Exhaust): Valves are essential components that control the flow of gases into and out of the combustion chamber. Intake valves open to allow the air-fuel mixture to enter the cylinder, while exhaust valves open to release the burnt gases after combustion. The precise timing of valve opening and closing is critical for engine efficiency and performance, orchestrated by the camshaft.
-
Timing Belt/Chain: To ensure the engine runs smoothly and efficiently, the camshaft and crankshaft must be synchronized. This synchronization is achieved by either a timing belt or a timing chain. A timing belt is typically made from durable rubber reinforced with cogs that interlock with pulleys on the camshaft and crankshaft. A timing chain, similar to a bicycle chain, wraps around toothed pulleys. Both systems ensure that the valves open and close at the correct moments in relation to the piston movement.
Recognizing Common Car Engine Problems
Given the intricate nature of an engine, with its numerous parts operating at high speeds, wear and tear over time is inevitable. This wear can lead to various engine problems, often signaled by changes in your car’s behavior. Here are some common engine issues and their associated symptoms:
-
Poor Compression: This issue often results in a noticeable loss of engine power, misfires, or even the inability to start the engine.
-
Cracked Engine Block: A crack in the engine block can lead to serious problems, including engine overheating, smoke emanating from the exhaust, or coolant leaks, often visible on the engine’s exterior.
-
Damaged Pistons, Rings, and/or Cylinders: Damage to these components can manifest as unusual rattling sounds, blue-tinted smoke from the exhaust, a rough engine idle, or failure to pass emissions tests.
-
Broken or Worn Rods, Bearings, & Pins: Problems with these parts may produce tapping or ticking noises, a drop in oil pressure, the presence of metal shavings in the engine oil, or rattling sounds particularly noticeable during acceleration.
Car engines, while complex in their construction, serve a fundamental purpose: to propel your vehicle forward. With so many components working in concert to generate this motion, consistent and proper vehicle maintenance is paramount for ensuring engine longevity. Regular oil changes, fluid flushes, and timely replacement of belts and hoses are vital preventative measures that can help avoid major engine failures.
For expert engine maintenance and repair, Sun Auto Service is a trusted name. When seeking a reliable service center to care for your vehicle, you need assurance of honest and high-quality work. Sun Auto Service is committed to providing trustworthy, quality service at affordable prices. We are proud to be recognized as an A+ rated business by the Better Business Bureau, employ ASE Certified Technicians, and offer a comprehensive nationwide warranty, ensuring your satisfaction long after you leave our service center. Dealership-level service that respects your budget? That’s the Sun Auto Service commitment.