Have you ever been driving at night and marveled at how your car headlights illuminate the road ahead? It’s a critical safety feature we often take for granted. But behind that beam of light is a complex system of components working in harmony. Understanding these Car Headlight Parts is essential for maintenance, repair, and even upgrades to ensure your safety and visibility on the road.
In this guide, we will delve deep into the anatomy of a headlight assembly, exploring each part and its role in producing that crucial beam of light. From the bulbs that generate the light to the lenses that focus it and the housings that protect it all, we’ll break down every essential component of your car’s headlights. Let’s illuminate the world of car headlight parts and understand how they contribute to safer nighttime driving.
Understanding the Headlight Assembly
Definition and Why It Matters
The headlight assembly, also known as a headlamp, is more than just a light on the front of your car. It’s a carefully engineered system designed to provide optimal illumination for drivers. Positioned at the front of the vehicle, these assemblies are indispensable for lighting the road ahead, especially when visibility is compromised by darkness or adverse weather conditions like fog, rain, or snow.
While often used interchangeably, it’s important to distinguish between the “headlamp” – the physical unit attached to the car – and the “headlight” – the beam of light it projects. The effectiveness of the headlight, and thus your safety, is directly dependent on the design and functionality of the car headlight parts within the assembly.
Headlights are a cornerstone of vehicle safety for several critical reasons:
- Road Illumination: The primary function is to light up the road, enabling drivers to see obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles in low-light conditions.
- Enhanced Visibility: Headlights ensure your vehicle is visible to other road users, significantly reducing the risk of accidents, especially at night or in poor weather.
- Navigational Assistance: They play a crucial role in navigating various road conditions, highlighting curves, dips, and uneven surfaces, ensuring you can anticipate and react to the road ahead.
- Signaling Capability: High beam headlights and fog lights serve as essential signaling tools, alerting other drivers to your presence or communicating intentions in challenging conditions.
Without properly functioning headlights, driving at night or in inclement weather would be extremely hazardous. They are meticulously designed to deliver the right amount of light at the correct angle, prioritizing the safety of both the driver and other road users. Regular maintenance and proper alignment of your car headlight parts are therefore paramount for safe driving.
Key Components of a Headlight Assembly
A headlight assembly is a sophisticated unit composed of several car headlight parts, each playing a vital role in delivering effective illumination. Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental components:
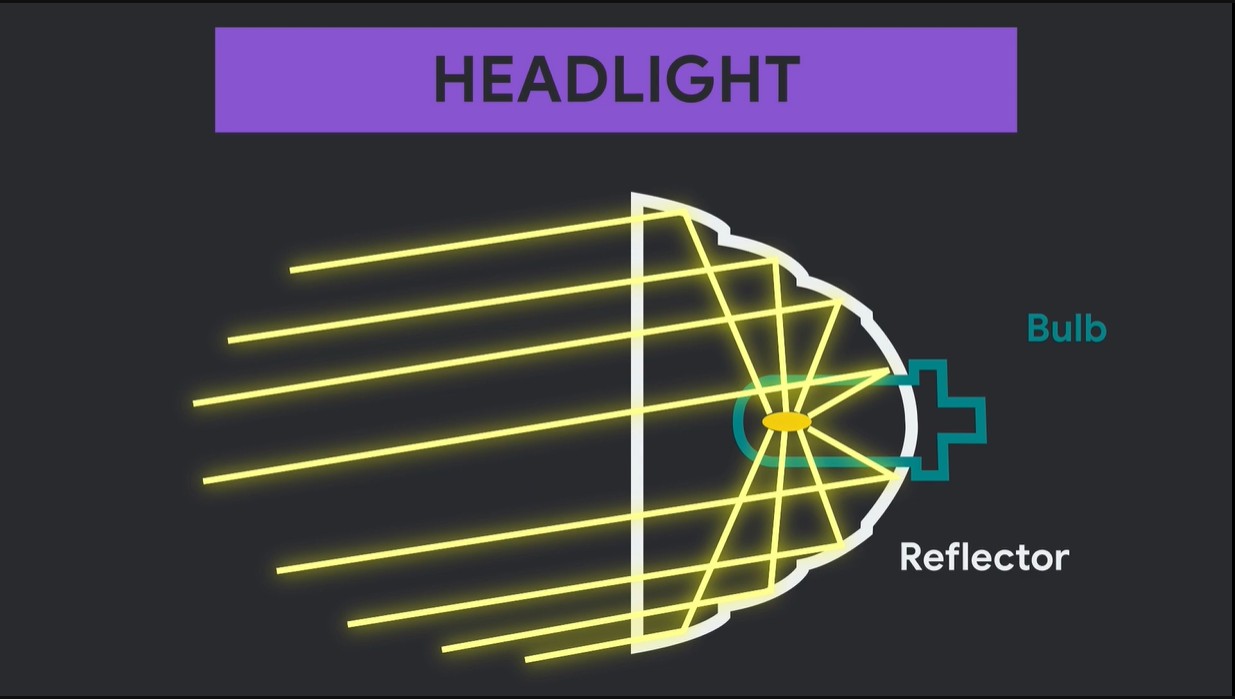
1. Light Bulb: The heart of the headlight, the bulb is the source of light. It generates the beam that illuminates the road. Different types of bulbs, including halogen, LED, and HID, offer varying levels of brightness, color temperature, and energy efficiency.
2. Electric Wires: These are the veins of the headlight system, carrying electrical current from the car’s power source to the bulb. They ensure the bulb receives the necessary power to produce light. In modern vehicles, wiring may also extend to motors, sensors, and adaptive lighting components.
3. Reflector: Positioned behind the bulb, the reflector is designed to capture and direct the light emitted by the bulb. It focuses the scattered light rays into a concentrated beam, enhancing the intensity and reach of the headlight.
4. Lens (Shielding Cover): The outer transparent layer of the headlight assembly, the lens, serves multiple purposes. It protects the internal car headlight parts from external elements like dust, debris, moisture, and weather. It also plays a role in shaping and projecting the light beam accurately, ensuring it is directed onto the road and not scattered aimlessly.
Exploring Headlight Housing
Types of Headlight Housing: Reflector vs. Projector
The headlight housing is the structure that encases and protects the internal car headlight parts, including the bulb, reflector, and wiring. It also determines the style and mounting of the headlight on the vehicle. There are two primary types of headlight housings: reflector and projector.
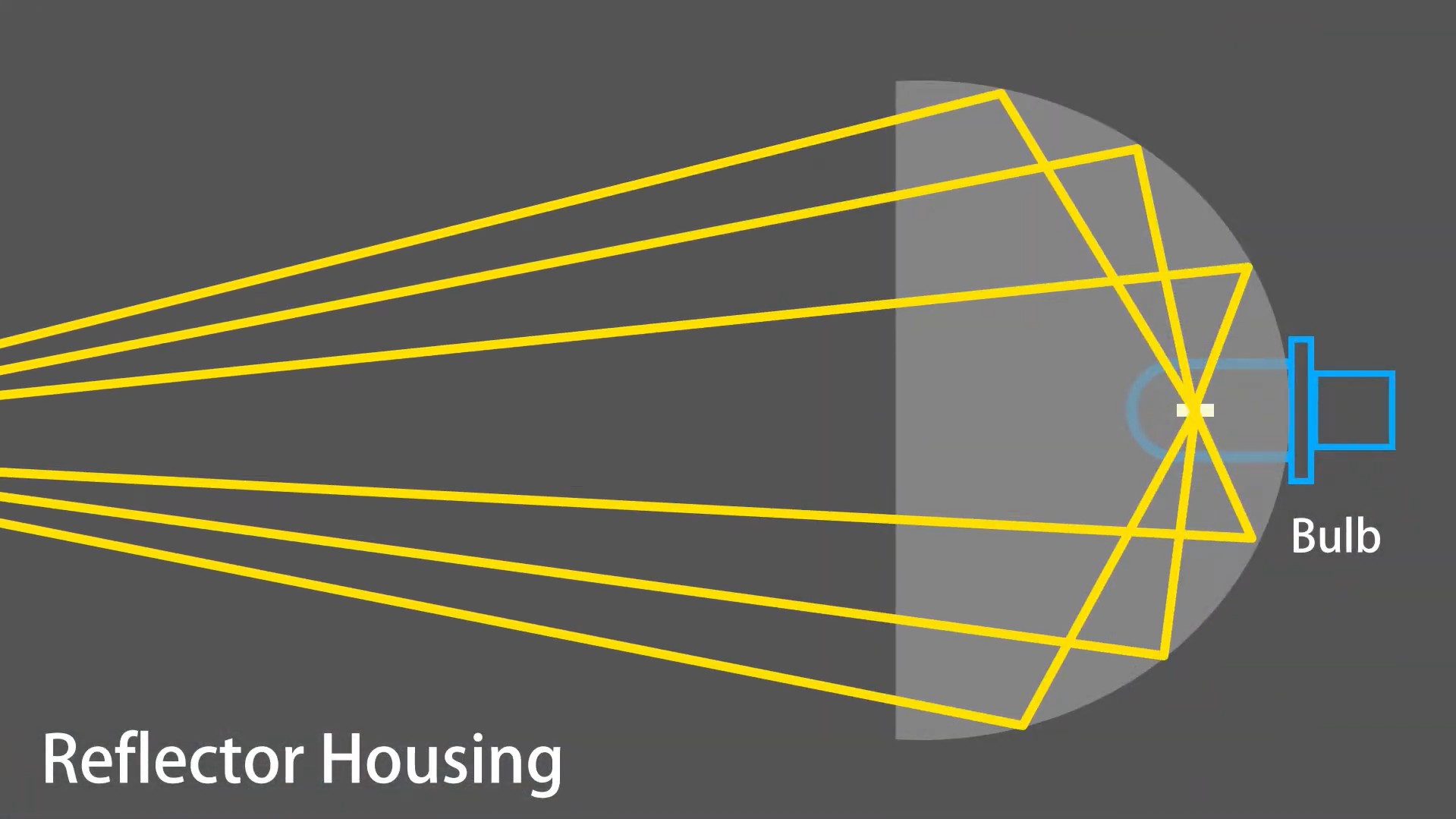
Reflector Housing:
Prior to the mid-1980s, reflector housings were the standard design for vehicle headlights. This design relies on a reflective surface, precisely shaped and positioned behind the bulb, to direct and distribute the light.
Functionality: The reflector’s curved surface is engineered to capture the omnidirectional light emitted by the bulb and redirect it forward, creating a focused beam. Without the reflector, a standard bulb would illuminate in all directions, resulting in weak and scattered light. The reflector concentrates the light, making it brighter and more practical for road illumination. While effective for their time, reflector housings are now largely superseded by more advanced technologies.
- Advantages:
- Simple and cost-effective to manufacture.
- Provides wide light coverage, suitable for general illumination.
- Limitations:
- Less precise light control compared to projector housings, potentially leading to light scatter.
- Can produce glare for oncoming drivers if not carefully designed and aimed.
- Common Applications: Typically found in older vehicles and budget-friendly car models.
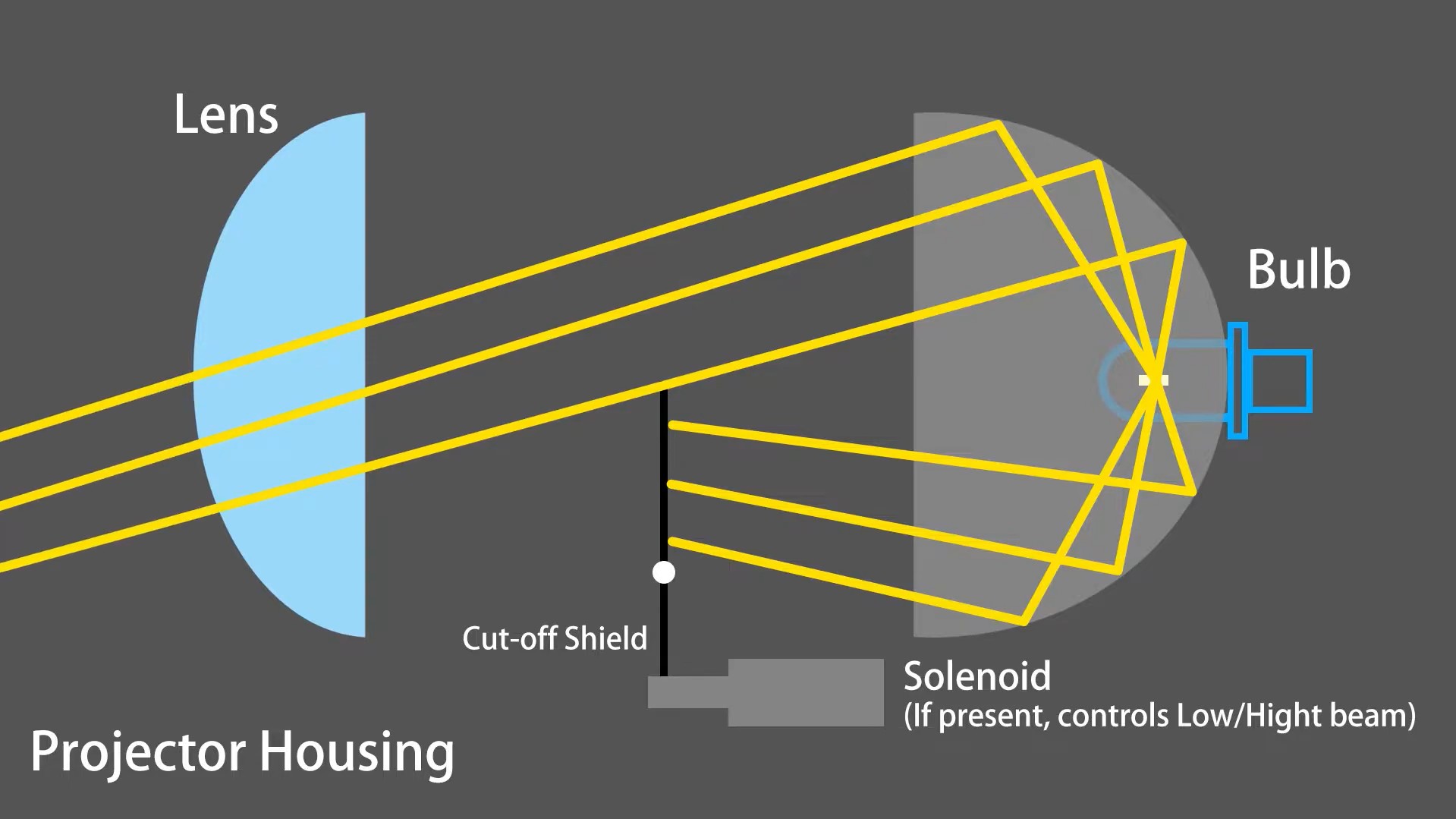
Projector Housing:
Introduced in the 1980s and becoming increasingly prevalent, projector housings are now the standard in most modern vehicles. This design incorporates a projector lens system to create a sharper, more defined beam of light.
Functionality: Projector housings utilize a lens to focus and magnify the light emitted by the bulb. This results in a highly controlled and precise beam pattern, offering superior light distribution and reduced glare compared to reflector designs. The lens concentrates the light more efficiently, leading to more effective illumination and enhanced driving safety. Projector headlights are known for their distinct appearance and performance advantages.
- Advantages:
- Highly precise light output with minimal light scatter, maximizing road illumination.
- Significantly reduced glare for oncoming traffic due to the focused beam.
- Often considered more aesthetically appealing, contributing to modern vehicle styling.
- Limitations:
- Generally more expensive to manufacture than reflector housings.
- Common Applications: Standard in newer cars, luxury vehicles, and performance-oriented models.
Material Choices for Headlight Housing
The materials used for headlight housings must be durable, weather-resistant, and capable of withstanding the heat generated by the bulbs. Material selection impacts both the functionality and aesthetics of the headlight assembly.
Common Materials:
- Plastic (Polycarbonate): Polycarbonate is the most widely used material for modern headlight housings. It’s favored for its exceptional impact resistance, lightweight nature, and moldability, allowing for complex and aerodynamic designs. Polycarbonate is also cost-effective and offers good thermal resistance.
- Glass: Historically, glass was used for headlight housings due to its clarity and scratch resistance. However, it is less common today because of its weight, fragility, and higher manufacturing cost compared to plastic.
- Composite Materials: High-performance and luxury vehicles may utilize composite materials like carbon fiber-reinforced polymers for headlight housings. These materials offer superior strength and lightweight properties, contributing to overall vehicle performance and aesthetics.
Design Considerations:
- Aesthetics: While clear lenses are standard, some designs incorporate textured or patterned lenses for stylistic purposes, enhancing the vehicle’s visual appeal.
- Sealing: Effective sealing is crucial to prevent moisture, dust, and contaminants from entering the housing. Contamination can cloud the lens, corrode reflectors, and damage bulbs, significantly reducing headlight performance.
- Alignment Adjustments: Most headlight housings include mechanisms for minor beam alignment adjustments. These adjustments allow for precise aiming of the headlights to ensure optimal road illumination and prevent glare for other drivers.
Headlight Bulbs: The Source of Illumination
Headlight bulbs are the core car headlight parts responsible for generating the light. Over the years, automotive lighting technology has evolved significantly, leading to various types of headlight bulbs, each with its own characteristics and performance attributes.
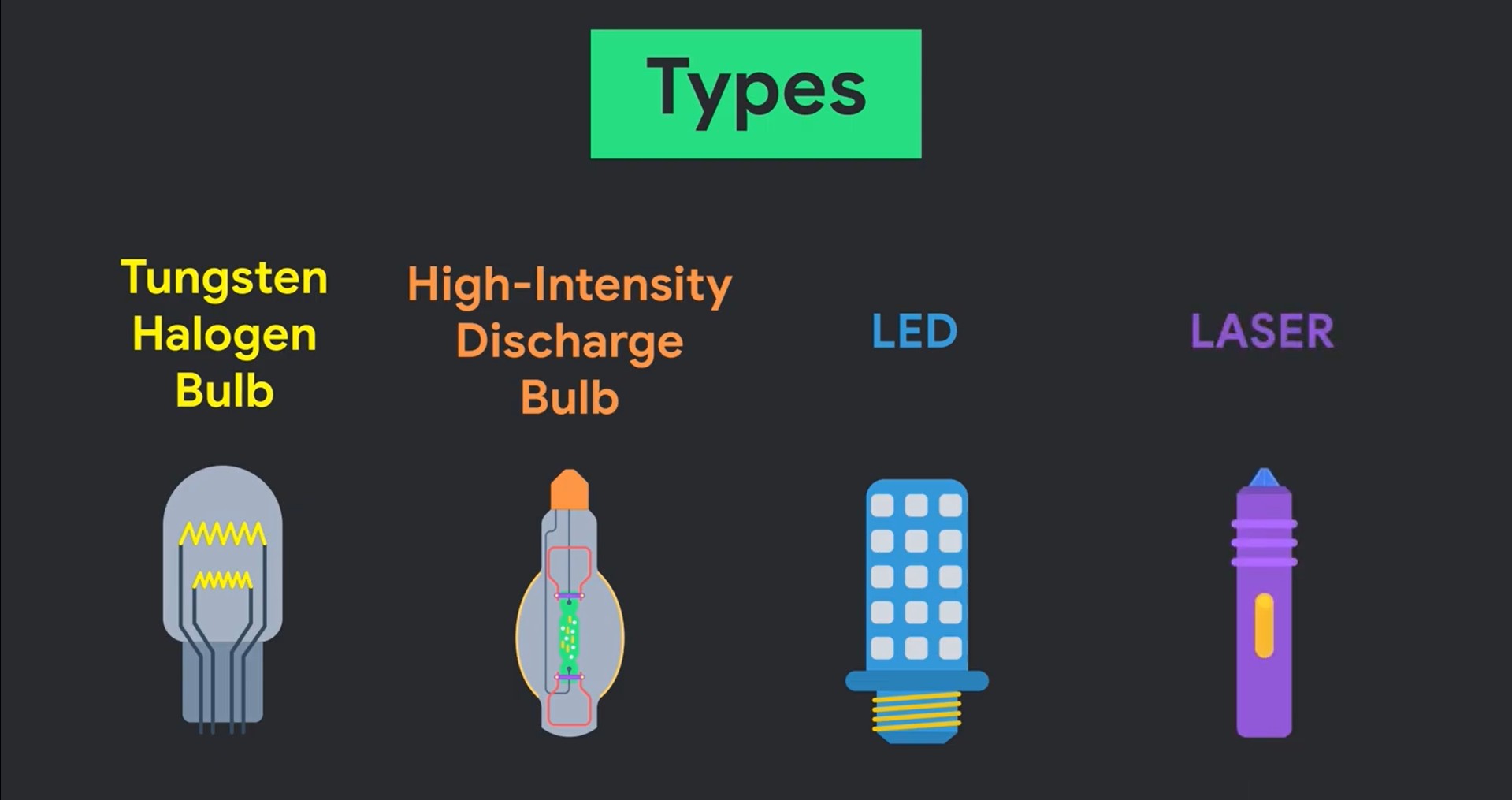
Types of Headlight Bulbs: Halogen, HID, and LED
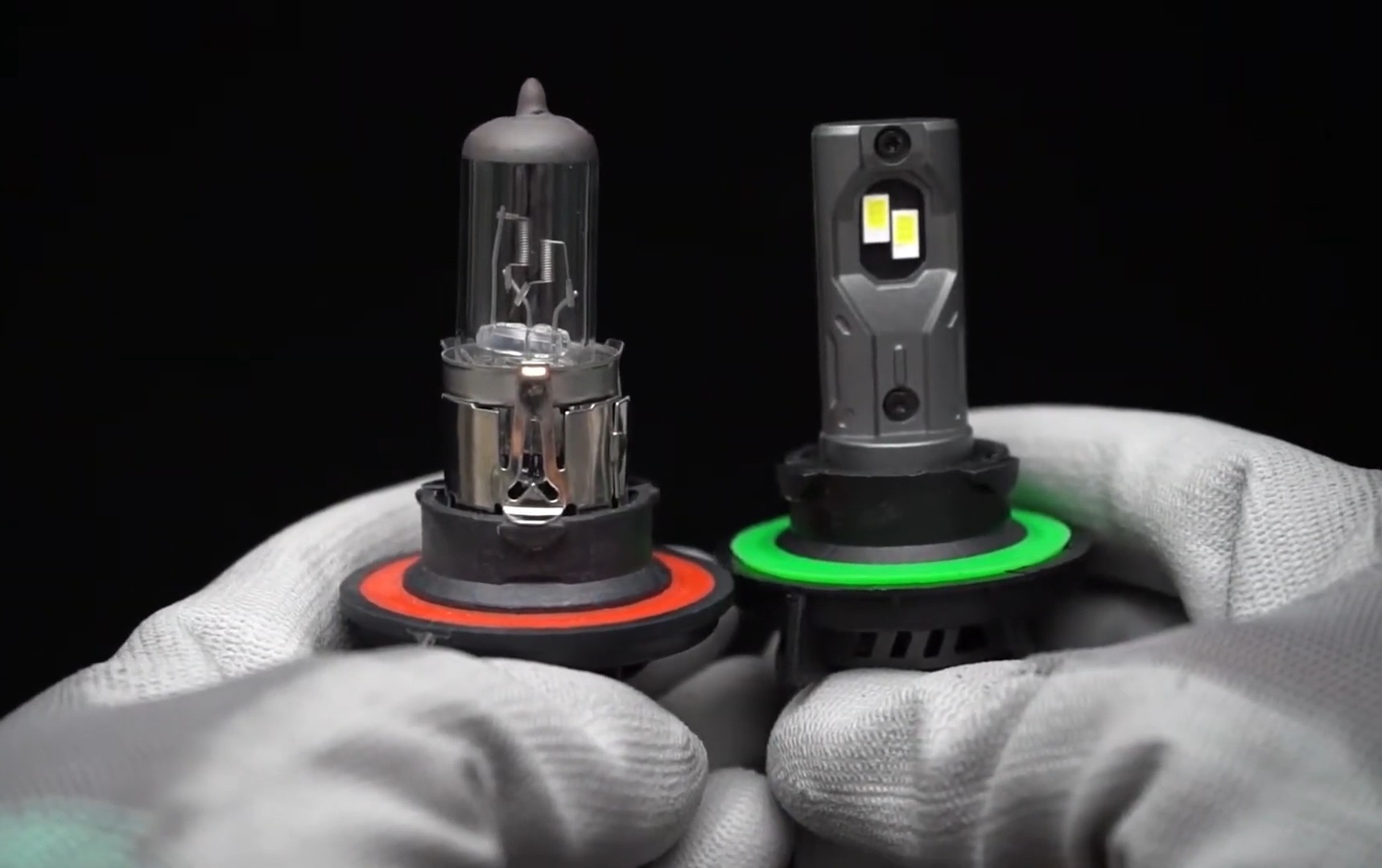
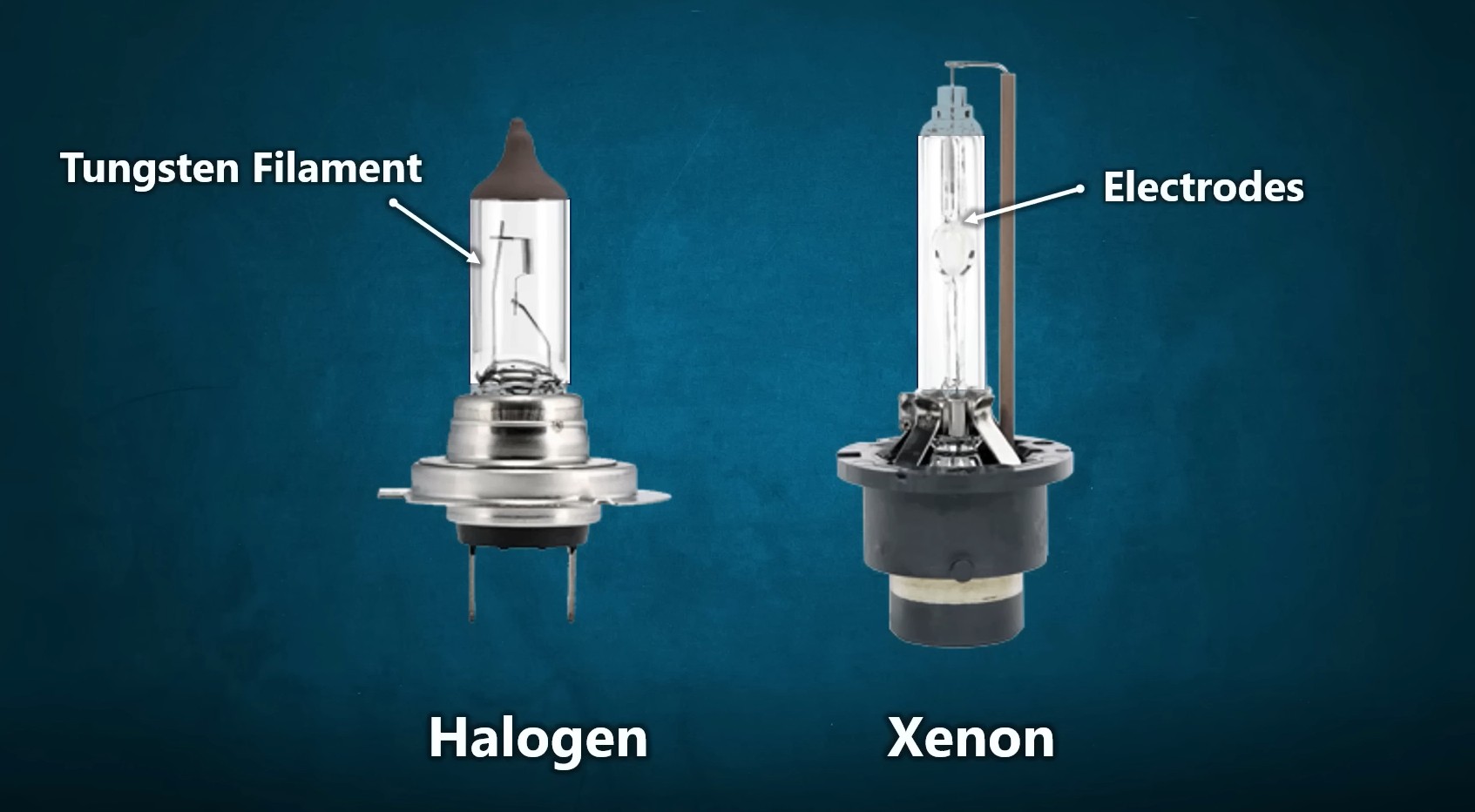
1. Halogen Headlights: Halogen bulbs are the most common and traditional type of headlight bulb. They operate on the principle of heating a tungsten filament inside a glass capsule filled with halogen gas. The heated filament emits light, producing a warm, yellowish beam.
- Mechanism: Electric current heats the tungsten filament, causing it to glow and emit light. Halogen gas increases efficiency and prevents the filament from burning out quickly.
- Lifespan: Typically last between 500 and 1,000 hours.
- Color Temperature: Produce a warm, yellowish light with a Kelvin rating of around 3,200K to 3,500K.
- Brightness (Lumens): Output ranges from 700 to 1,200 lumens, depending on the specific bulb type.
2. HID (High-Intensity Discharge) Bulbs: HID bulbs, also known as Xenon bulbs, generate light through a different process than halogen bulbs. They create an electric arc between two electrodes within a chamber filled with xenon gas. This process produces a much brighter light with a bluish-white hue.
- Mechanism: An electric arc excites xenon gas, causing it to emit intense light. Requires a ballast to regulate voltage and current.
- Lifespan: Last significantly longer than halogen bulbs, typically 2,000 to 3,000 hours.
- Color Temperature: Produce a brighter, bluish-white light with a Kelvin range of 4,300K to 6,000K.
- Brightness (Lumens): Offer superior illumination, producing between 3,000 and 5,000 lumens.
3. LED (Light Emitting Diode) Headlights: LED headlights are the most energy-efficient and longest-lasting type of headlight bulb. They utilize semiconductors that emit light when an electric current passes through them. LEDs are known for their bright white light, low heat generation, and exceptional lifespan.
- Mechanism: Semiconductor diodes emit light when electricity flows through them. Highly efficient and generate very little heat.
- Lifespan: Offer the longest lifespan, ranging from 30,000 to 50,000 hours.
- Color Temperature: Produce a bright white light with a Kelvin range of 5,000K to 6,500K.
- Brightness (Lumens): Output ranges from 2,000 to 4,000 lumens, providing excellent visibility with lower energy consumption compared to HID.
4. Laser Headlights (Emerging Technology): While still relatively new and primarily found in high-end vehicles, laser headlights represent the cutting edge of automotive lighting. They offer even greater efficiency and potential for increased brightness compared to LEDs.
| Feature | Halogen Bulbs | HID (High-Intensity Discharge) Bulbs | LED (Light Emitting Diode) Headlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Tungsten filament heated by electric current | Electric arc between electrodes in xenon gas | Semiconductor emits light when current passes |
| Lifespan | 500 – 1,000 hours | 2,000 – 3,000 hours | 30,000 – 50,000 hours |
| Kelvin (Color Temperature) | 3,200K – 3,500K | 4,300K – 6,000K | 5,000K – 6,500K |
| Lumens (Brightness) | 700 – 1,200 lumens | 3,000 – 5,000 lumens | 2,000 – 4,000 lumens |
| Light Color | Warm yellowish light | Bluish-white light | Bright white light |


The Importance of Bulb Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your car headlight parts, especially the bulbs, is crucial for safe driving. Failing headlights can significantly reduce visibility and increase the risk of accidents. Regularly inspect your headlights to ensure they are functioning correctly and replace bulbs as needed. This proactive approach prevents issues like dimming lights, flickering beams, or complete bulb failure, all of which compromise your safety on the road.
Headlight Lens: Ensuring Clarity and Protection
Material Selection for Cover Lenses: Glass vs. Plastic
The headlight lens, the transparent outer cover, is a critical car headlight part that protects the internal components and shapes the light beam. The choice of lens material significantly impacts durability, clarity, and overall headlight performance.
Historically, glass was the primary material for headlight lenses. Glass offers exceptional optical clarity and is highly resistant to scratches, ensuring a streak-free and bubble-free surface for optimal light transmission. However, glass lenses are heavier and more prone to shattering upon impact, making them less durable in automotive applications. They are also more challenging to mold into complex shapes.
Modern headlight lenses are predominantly made of plastics, specifically polycarbonate (PC). Polycarbonate has become the industry standard due to its superior impact resistance, lightweight nature, and moldability. Polycarbonate lenses are significantly lighter than glass, reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. They also allow for tighter manufacturing tolerances, enabling more precise and complex lens designs. While polycarbonate is more susceptible to scratching than glass, protective coatings are typically applied to enhance scratch resistance and UV protection.
Why Lens Clarity is Essential
Maintaining clear headlight lenses is paramount for optimal illumination and driving safety. Over time, headlight lenses can become cloudy or hazy due to UV radiation exposure, road debris, and environmental pollutants. This hazing effect significantly reduces light output and visibility, even if the bulbs are functioning correctly.
A hazy lens scatters the light, diminishing the intensity and reach of the headlight beam. This not only impairs the driver’s ability to see the road ahead but also reduces the vehicle’s visibility to other drivers, especially at night or in poor weather conditions, increasing the risk of accidents. Regular cleaning and restoration of hazy lenses are essential maintenance steps to ensure your car headlight parts function effectively and maintain driving safety.
Reflector and Projection Modules: Shaping the Beam
Materials for Reflectors: Precision and Durability
Reflectors, crucial car headlight parts in reflector-style headlights, are responsible for directing and focusing the light emitted by the bulb. The materials used for reflectors must be highly reflective, durable, and capable of maintaining their shape and reflectivity over time and under operating temperatures.
Thermoplastics are the most common materials for reflectors due to their precise mold reproducibility and cost-effectiveness. Common thermoplastic materials include:
- Polycarbonate (PC): Favored for its excellent impact resistance, optical clarity, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand high temperatures generated by headlight bulbs.
- Acrylic (PMMA): Known for its high optical clarity and UV resistance, suitable for applications where maximum light transmission and aesthetic appearance are prioritized.
In high-performance applications or areas subject to extreme thermal stress, materials like aluminum or magnesium may be used for reflectors due to their superior heat dissipation properties. Silicone is also utilized in advanced LED headlight systems for its flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures.
The Role of Projection Modules
Projection modules, integral car headlight parts in projector-style headlights, are sophisticated units designed to achieve precise beam patterns and maximize luminous flux. These modules incorporate lenses and reflectors to tightly control and focus the light output.
Projection modules offer several advantages:
- Focused Light Distribution: They enable more concentrated and directed light beams, minimizing light scatter and maximizing illumination on the road.
- Reduced Glare: By precisely controlling the beam pattern, projection modules significantly reduce glare for oncoming traffic, enhancing safety for all drivers.
- Versatility in Design: Projection modules allow for greater flexibility in headlight design, supporting a wide range of shapes and styles, and enabling the implementation of advanced lighting technologies like adaptive headlights and LED systems.
Turn Signals and Other Essential Components
Turn Signal Bulbs: Communication and Safety
Turn signal bulbs are indispensable car headlight parts integrated within the headlight assembly. They are crucial for signaling lane changes and turns, ensuring clear communication with other drivers and pedestrians. Functioning turn signals are essential for preventing accidents and maintaining traffic safety.
In addition to the primary lighting components and turn signals, a complete headlight assembly also includes:
- Housing: The protective outer shell that encases all internal car headlight parts, shielding them from damage and environmental elements.
- Mounting Brackets: Secure the headlight assembly to the vehicle’s body, ensuring stable and precise positioning.
- Adjustment Mechanisms: Allow for fine-tuning of headlight alignment, ensuring proper beam direction and preventing glare.
Each of these components, working in concert, contributes to the overall functionality, performance, and safety provided by the headlight assembly.
Headlight Assembly Replacement: When and How
Cost Considerations and Replacement Process
Replacing a headlight assembly can become necessary due to damage from accidents, wear and tear, or the desire to upgrade to newer lighting technologies. The cost of replacement can vary significantly depending on the vehicle make and model, the type of headlight assembly, and whether you choose OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or aftermarket parts.
Generally, the cost to replace a headlight assembly ranges from $250 to $700, and in some cases, higher for luxury vehicles or complex lighting systems. This cost typically includes both the car headlight parts (the assembly itself) and labor if you opt for professional installation at an auto repair shop. Labor costs can vary, but are usually included in the overall price. The specific cost will depend on the components needing replacement, such as the entire assembly, or just individual parts within it.
DIY vs. Professional Installation
For mechanically inclined individuals with the right tools and knowledge, replacing a headlight assembly can be a DIY project. However, it’s important to assess your skill level and the complexity of your vehicle’s headlight system. While changing a headlight bulb might be straightforward, replacing the entire assembly is more involved due to the integration of various car headlight parts like reflectors, housings, and mounting brackets.
Professional replacement by a qualified mechanic ensures proper installation, alignment, and electrical connections. This minimizes the risk of errors, ensures optimal headlight performance, and avoids potential safety issues. For modern vehicles with complex lighting systems, professional installation is often recommended.
Choosing the Right Headlight Assembly: Compatibility and Options
Vehicle Compatibility and OE vs. Aftermarket Parts
When replacing a headlight assembly, ensuring vehicle compatibility is paramount. Always check your vehicle’s year, make, and model to confirm that the replacement assembly is designed to fit your specific vehicle. Consulting your owner’s manual or using online parts finders can help identify the correct headlight assembly for your car.
You’ll typically have a choice between OE (Original Equipment) parts and aftermarket parts. Both options have their pros and cons:
OE (Original Equipment) Parts:
- Quality: Manufactured to the vehicle manufacturer’s exact specifications, ensuring original equipment quality and performance.
- Fitment: Guaranteed perfect fitment as they are designed for your specific vehicle model.
- Warranty: Usually come with a warranty from the vehicle manufacturer.
- Price: Generally more expensive than aftermarket parts.
- Performance: Match the vehicle’s original performance standards.
- Brand Reputation: Backed by the vehicle manufacturer’s reputation.
Aftermarket Parts:
- Quality: Quality can vary widely among aftermarket manufacturers. Premium aftermarket brands can offer comparable or even improved quality to OE parts, while budget options may compromise on quality.
- Fitment: Fitment can vary; some aftermarket parts offer excellent fitment, while others may require adjustments.
- Warranty: Warranty terms vary depending on the aftermarket manufacturer.
- Price: Often more cost-effective than OE parts, offering a range of price points.
- Performance: Performance characteristics can differ; some aftermarket parts aim to match OE performance, while others may offer enhanced brightness, styling, or features.
- Brand Reputation: Aftermarket brands vary in reputation; research and choose reputable manufacturers.
Reputable Brands and Manufacturers
When choosing aftermarket car headlight parts, consider reputable brands known for quality and reliability. Some leading manufacturers in the aftermarket headlight industry include:
- Carlightvision: Specializes in premium aftermarket LED headlights, known for innovative designs and high performance.
- JC Whitney: A long-standing retailer offering a wide range of automotive parts and accessories, including headlight assemblies for various makes and models.
- Replacement: Focuses on providing cost-effective alternatives to OEM parts, offering affordable and reliable headlight assemblies.
- Anzo: Known for stylish and high-performance lighting solutions, including LED and projector headlights, often with distinctive designs.
- Crown Automotive: Specializes in durable headlight assemblies, particularly for Jeeps and off-road vehicles, designed to withstand rugged conditions.
Conclusion: Illuminating the Road Ahead Safely
Key Takeaways on Car Headlight Parts
Understanding car headlight parts is crucial for every car owner. From the bulbs that generate light to the lenses that focus it and the housings that protect it, each component plays a vital role in ensuring safe and effective nighttime driving. Replacing a damaged or outdated headlight assembly can significantly improve visibility and enhance your vehicle’s safety profile. While DIY replacement is possible for some, professional installation is often recommended, especially for modern, complex lighting systems.
Prioritizing Headlight Maintenance for Safety
Proper headlight maintenance is not just about aesthetics; it’s a fundamental aspect of vehicle safety. Headlights are precision-engineered systems, and understanding their structure and technology allows for informed maintenance and care. Regular inspections, bulb replacements when needed, and lens cleaning are essential steps to maintain optimal headlight performance. By ensuring your car headlight parts are in good working order, you are actively contributing to safer driving conditions for yourself and everyone on the road. Don’t underestimate the importance of these illuminating marvels – they are a critical line of defense on the road, ensuring you can navigate safely, no matter the driving conditions.