After exploring the exterior parts of a car in our previous article, it’s time to delve inside and understand the intricate world of car interior parts. This guide will take you through the names, functions, and significance of each component within your vehicle’s cabin, complete with a helpful Car Interior Parts Diagram.
Understanding your car’s interior is more than just knowing where everything is. It’s about appreciating the engineering and design that contribute to a comfortable, safe, and enjoyable driving experience. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a new driver, or simply curious, this comprehensive overview will enhance your knowledge of automotive interiors. From the essential controls to the comfort and safety features, we’ll cover everything you need to know.
Many of these interior parts can be customized and upgraded to personalize your vehicle. Consider enhancing your interior with custom LED light options to set the mood, adding durable seat covers for protection and style, installing modern gauges for improved vehicle feedback, or incorporating gadgets to make every drive more pleasurable. Let’s explore the fascinating components that make up your car’s interior.
Essential Car Interior Parts Names
Below is a list of the primary interior parts you’ll find in most cars. We’ll delve into each of these in detail, explaining their function and importance.
- Steering Wheel and Horn
- Ignition System
- Pedals (Accelerator, Brake, Clutch)
- Gear Shifter/Selector
- Dashboard
- Hazard Lights Button
- Seat Belts
- Airbags
- Rearview Mirrors (Interior)
- Parking Brake (Emergency Brake)
- Turn Signal Lever
- Center Console
- Glove Compartment
- Power Window and Door Lock Controls
- Interior Door Handles
- Audio System
- Central Control Screen (Infotainment System)
- Sun Visors
- Car Seats
- Floor Mats
- Roof and Headliner
Visualizing the Interior: Car Interior Parts Diagram
To help you visualize the location of these parts, refer to the car interior parts diagram below. This diagram provides a clear visual representation of where each component is situated within the vehicle’s cabin.
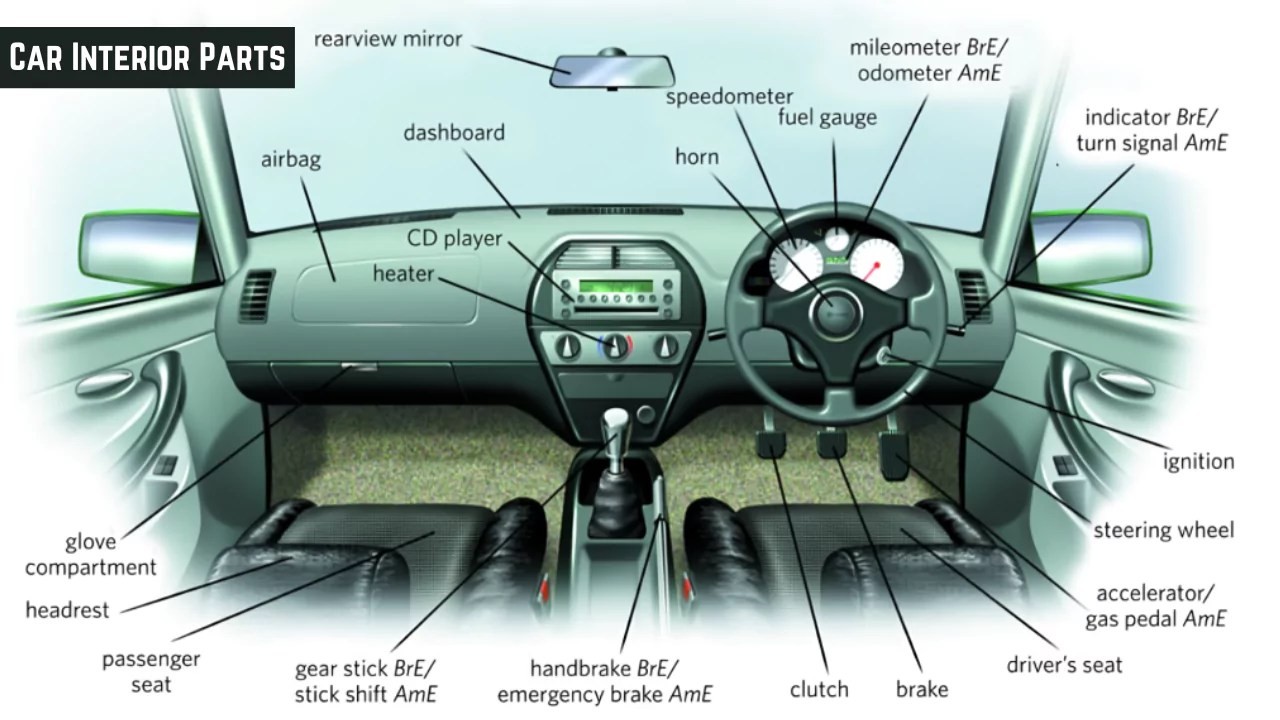 Car interior parts names with diagram
Car interior parts names with diagram
Detailed Exploration of Car Interior Parts
Let’s now take a closer look at each of these car interior components, understanding their individual roles and how they contribute to the overall driving experience.
#1. Steering Wheel and Car Horn
The steering wheel is arguably the most fundamental control within the car’s interior. It’s the primary interface for controlling the vehicle’s direction, translating the driver’s rotational inputs into the swiveling motion of the front wheels. This intricate system involves a series of joints and hydraulic lines, ensuring precise and responsive steering.
Modern steering wheels have evolved beyond basic directional control. Many now integrate accessory functions like cruise control for maintaining speed, audio system controls for entertainment management, and even heating elements for added comfort in cold climates.
Customizing your steering wheel with a new cover is a popular car interior modification. These covers not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve the tactile feel of the wheel, offering increased comfort and grip. Options range from stylish patterns to luxurious leather, providing a wide variety to match personal preferences.
The car horn, typically integrated into the steering wheel, is a critical safety feature. It allows the driver to audibly signal their presence to other road users, warn of potential hazards, or communicate intentions in various driving situations. A simple press of the horn button can significantly improve road safety.
#2. Ignition System
The ignition system is the gateway to starting your car’s engine. Located typically on the steering column or dashboard, it’s where you insert your key or press a start button to bring the vehicle to life.
When you turn the ignition key or press the start button, the ignition switch is activated. This action initiates the flow of electrical power to the engine’s starting system and other essential vehicle functions. The ignition system is the crucial first step in getting your car moving.
#3. Pedals: Accelerator, Brake, and Clutch
Positioned at the driver’s footwell, the pedals are essential for controlling the car’s speed and stopping power. The accelerator pedal, usually the rightmost pedal, controls the amount of fuel delivered to the engine, directly influencing the vehicle’s speed. Pressing down on this pedal increases engine power and speed.
The brake pedal, generally larger and located to the left or center-left of the accelerator, is responsible for slowing down and stopping the vehicle. Applying pressure to the brake pedal activates the braking system, reducing the car’s speed and bringing it to a halt when necessary.
In vehicles with a manual gearbox, a third pedal, the clutch pedal, is present. This pedal, located furthest to the left, is used to disengage the engine from the transmission during gear changes. Automatic cars do not have a clutch pedal, simplifying the driving process.
For manual transmission vehicles, the pedal arrangement from left to right is typically clutch, brake, and accelerator. Mastering the coordination of these pedals is fundamental to driving a manual car smoothly.
#4. Gear Shifter/Selector
The gear shifter, or gear selector in automatic vehicles, is located between the driver and front passenger seats. In manual transmission cars, it’s a stick used to manually change gears. It features a shift knob indicating the gear pattern.
For cars with automatic transmission, it’s termed the gear selector. Often referred to as the “PRNDL” (for Park, Reverse, Neutral, Drive, Low), regardless of the specific markings, this selector allows the driver to choose the driving mode.
Manual transmission gear shifting requires the driver to use the clutch pedal. Depressing the clutch pedal disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing for gear changes. Moving the gear shifter engages different gears within the transmission, altering the vehicle’s speed and power output. This process involves synchronizers and sleeves to ensure smooth gear transitions.
#5. Dashboard: The Command Center
The dashboard is a prominent feature of the car interior, situated at the front of the cabin. It serves as the central hub for displaying crucial vehicle information and separates the front of the car from the driver and passengers.
Dashboard designs vary significantly across car models, reflecting different brands and feature levels. More advanced dashboards often incorporate sophisticated technology and higher-quality materials. The dashboard typically houses several key instrument panels:
- Fuel Gauge: Indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the tank, allowing drivers to monitor fuel levels and plan refueling stops.
- Speedometer: Displays the vehicle’s current speed, usually via an analog needle or digital display, helping drivers maintain safe and legal speeds.
- Tachometer: Shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM), crucial for ensuring the engine operates within its optimal range and assisting gear changes in manual vehicles.
- Temperature Gauge: Monitors the engine’s operating temperature, warning of potential overheating that could indicate engine problems or coolant issues.
In addition to these gauges, the dashboard is also home to various warning lights and indicator lights. These lights illuminate to alert the driver to potential malfunctions or system issues, ensuring timely attention to vehicle maintenance.
#6. Hazard Lights Button (Emergency Flashers)
Emergency flashers, or hazard lights, are activated by pressing a dedicated button, usually marked with a red triangle.
These lights serve as a warning signal to other drivers, indicating an emergency situation or that the vehicle is stopped in a potentially hazardous location, such as on the side of the road.
When activated, the hazard lights cause all four turn signal lights to flash simultaneously, maximizing visibility and alerting surrounding traffic.
#7. Seat Belts: A Primary Safety Feature
Seat belts are critical safety devices designed to significantly reduce the risk of death and serious injury in vehicle accidents. Their effectiveness depends on proper usage.
Unbelted occupants are far more likely to be ejected from a vehicle during a crash, increasing the risk of severe injuries or fatalities. Ejection can lead to impacts with the road surface or being trapped under the vehicle.
Even if ejection doesn’t occur, unrestrained occupants become a danger to themselves and others inside the car during a collision. In a crash, loose objects, including people, become projectiles. Unrestrained passengers can cause serious harm to other occupants in the vehicle.
#8. Airbags: Supplemental Restraint System
Airbags are inflatable cushions designed to deploy rapidly in a collision, protecting vehicle occupants from impacting the interior of the vehicle or external objects.
Upon detecting a collision, sensors measure the impact severity. If the impact exceeds a certain threshold, the sensors trigger inflators to rapidly fill the airbags with gas. This deployment occurs within milliseconds, providing crucial cushioning during a crash.
Airbags generally require no maintenance unless they are deployed. After deployment, they must be replaced by a qualified repair shop using Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts. This ensures the replacement airbag meets safety standards and is not a counterfeit. Counterfeit airbags pose a significant risk, potentially failing to deploy correctly or even deploying with dangerous metal fragments.
#9. Rearview Mirrors: Enhancing Visibility
Rearview mirrors are adjustable reflective devices designed to provide the driver with a view of the road, vehicles, and other objects behind the car, minimizing blind spots and enhancing safety.
Regulations in many countries mandate specific rearview mirror configurations for passenger cars. Typically, this includes an interior rearview mirror and exterior rearview mirrors on both the driver and passenger sides.
The interior rearview mirror is mounted centrally, often on the dashboard or windshield. It’s designed as a unit magnification mirror, meaning it’s a flat mirror that reflects objects at their actual size and distance. This provides a realistic perspective of what’s behind the vehicle.
#10. Parking Brake (Emergency Brake)
The parking brake, also known as the emergency brake, is a secondary braking system that operates independently from the primary hydraulic brakes used for regular stopping. This redundancy is intentional, providing a backup braking system in case of primary brake failure.
While primary brakes are designed for slowing and stopping the car during normal driving, the parking brake is primarily intended to hold the vehicle stationary when parked.
However, in the event of primary brake failure, the parking brake can be used to slow down and stop the car in an emergency situation.
It’s recommended to engage the parking brake every time you park, regardless of the terrain, vehicle type (automatic or manual), or weather conditions. In an emergency braking situation, gradually applying the parking brake can help bring the vehicle to a stop.
#11. Turn Signal Lever: Indicating Direction
The turn signal lever, or indicator stalk, is located on the steering column and is used to activate the turn signals. These signals are essential for communicating intended direction changes to other road users.
Operating the signal lever activates the appropriate turn signal lights (left or right), clearly indicating the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes. This communication is crucial for safe navigation and preventing accidents.
#12. Center Console: Storage and Control Hub
The center console is the storage and control area located between the driver and front passenger seats. It’s a common feature in modern cars, positioned behind the gear shifter. Vehicles with bench seats in the front typically do not have a center console.
The center console area often corresponds to the part of the car’s floorplan where the transmission tunnel runs. However, the term can also refer to the central portion of the dashboard.
Center consoles can incorporate a variety of features, including storage compartments, cupholders, power outlets (like cigarette lighters or auxiliary power points), audio controls, climate control systems, and infotainment display screens. They serve as a central hub for convenience and control within the cabin.
#13. Glove Compartment: Convenient Storage
The glove compartment, also known as the glove box, is an enclosed storage space typically located within the dashboard on the passenger side, above the footwell.
Despite its name, it’s used for general storage rather than just gloves. Common items stored in the glove compartment include owner’s manuals, vehicle registration and insurance documents, maps, flashlights, napkins, and tire pressure gauges. It provides a convenient and accessible storage space for essential car-related items.
#14. Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Power windows and door locks provide electrically operated controls for raising and lowering windows and locking/unlocking doors. Instead of manual cranks, power windows use buttons or switches for operation.
Power door locks allow the driver or front passenger to simultaneously lock or unlock all vehicle doors with the press of a button or switch. These features enhance convenience and security, particularly in modern vehicles.
#15. Interior Door Handles: Opening the Door from Inside
The interior door handle is used to disengage the door latch mechanism from inside the vehicle, allowing the door to be opened. Most modern interior door handles are constructed from plastic.
The linkage connecting both the interior and exterior door handles to the door latch is located inside the door panel, beneath the trim.
#16. Audio System: Entertainment on the Go
A car audio system encompasses all the components related to sound within the vehicle, including speakers, amplifiers, and source units (like head units or receivers). The primary function of a car audio system is to play music and other audio content, enhancing the driving experience with entertainment.
#17. Central Control Screen (Infotainment System)
The car central control screen, also known as the infotainment system or multimedia display, is a prominent feature in contemporary vehicles. It serves as a central interface for various vehicle functions and information.
“Infotainment” is a combination of “information” and “entertainment.” Thus, a car infotainment system delivers a mix of information and entertainment services.
These systems are essentially in-built car computers, integrating a wide range of functions, from digital radio and navigation to smartphone integration and vehicle settings. Infotainment systems can include features like touchscreens, button panels, voice command interfaces, and more, offering a comprehensive control and information hub for the vehicle.
#18. Sun Visors: Blocking Glare
Sun visors are located on the interior roof, just above the windshield. They are hinged flaps that can be adjusted to block sunlight and reduce glare, improving visibility for both the driver and passengers, especially during sunrise or sunset.
#19. Car Seats: Comfort and Support
Car seats are designed for both support and comfort. They are typically constructed with a robust frame, often made of metal or high-strength materials, and padded for cushioning and shock absorption.
Many car seats feature adjustable components, including seat height, backrest angle, and lumbar support. These adjustments allow occupants to personalize their seating position for optimal comfort during driving.
For seat maintenance, regular vacuuming is recommended to remove dirt and dust. Leather or fabric conditioners can be applied to maintain the seat material’s softness and prevent cracking or fading.
Car seat covers are a popular accessory for ease of maintenance and seat protection. They are easy to install and remove, and materials like leatherette are easier to clean and maintain than original upholstery.
#20. Floor Mats: Protecting the Interior Floor
Floor mats are essential for maintaining the cleanliness and protecting the interior flooring of a car. They act as a barrier against dirt, spills, and wear and tear.
Most floor mats are designed to be easily removable for cleaning. Some feature fixation points to secure them in place. In vehicles with fitted rubber flooring, such as commercial vehicles or off-road vehicles, floor mats are often considered less necessary.
#21. Roof and Headliner: Structure, Insulation, and Aesthetics
Automotive roofs and headliners are integral to the vehicle interior, providing structural support, insulation, and aesthetic enhancement.
The car roof provides structural rigidity to the vehicle body, contributing to occupant protection in rollovers and collisions. It also withstands weather elements, keeping the interior dry and comfortable.
The headliner, the interior roof lining, provides sound absorption and thermal insulation. It helps regulate cabin temperature by reducing heat transfer from the roof and creating a more comfortable environment. Together, the roof and headliner create a functional, comfortable, and visually appealing cabin space.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the interior parts of a car called?
The main interior parts of a car include: Steering Wheel and Horn, Ignition, Pedals, Gear Shifter, Dashboard, Hazard Lights, Seat Belts, and Airbags. This guide provides a comprehensive list and explanation of these and other key interior components.
What is an interior panel in a car?
Interior car panels are more than just decorative coverings for the inside of doors and other cabin areas. They serve important functions such as protecting the window mechanism when lowered and concealing electrical wiring and motors for windows and door locks, contributing to both aesthetics and functionality.
What is the top inside of a car called?
The top inside of a car is called the headliner. It’s a material that covers the vehicle’s ceiling, providing insulation against heat and noise. It also conceals wiring and hardware for various components like lights, antennas, and other accessories, contributing to a clean and finished interior appearance.
What is a dashboard in a car?
The dashboard is located at the front of the car’s interior. It houses indicator panels for various vehicle systems and acts as a partition between the front of the car and the driver and passengers. It’s the central information and control interface for the driver.
What is the interior of a car made of?
Modern car interiors utilize a variety of materials, with polymers being increasingly common. These materials include lightweight seats, instrument panels, durable upholstery, sound control fabrics, headliners, dashboards, and door panels. Polymers offer a balance of durability, weight reduction, and design flexibility.
What are the different types of car interiors?
Car interiors can be categorized by upholstery material, including:
- Nylon Upholstery: A common and durable fabric choice.
- Polyester Upholstery: Another popular fabric option, often chosen for its stain resistance.
- Vinyl Upholstery: A non-fabric option, durable and easy to clean, often found in base models.
- Leather Upholstery: Considered a premium option, offering luxury, durability, and a distinctive feel.
Understanding the car interior parts diagram and the function of each component enhances your appreciation for automotive design and engineering. This knowledge can be valuable for car maintenance, upgrades, and making informed decisions when choosing a vehicle.
