Understanding the intricate workings of your vehicle might seem daunting, but grasping the basics of Car Main Parts is incredibly beneficial for every car owner. This knowledge empowers you to be a more informed consumer, enabling effective communication with automotive technicians and facilitating better car maintenance. From the powerful engine to the responsive brakes, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring your vehicle operates smoothly and safely.
While becoming a master mechanic isn’t necessary, familiarizing yourself with the fundamental parts of a car can significantly aid in troubleshooting common issues and fostering responsible car ownership. This guide will walk you through the key components of your vehicle, explaining their functions and importance.
Let’s delve into the essential car main parts that keep you moving.
Exploring the Core Components of Your Car
To truly appreciate your vehicle’s capabilities, it’s essential to build a foundational understanding of its major components. Knowing the names of these car main parts and how they contribute to your car’s overall performance will be invaluable for years to come.
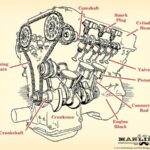
Engine: The Heart of Your Vehicle
The engine is undeniably the most critical component of any vehicle, acting as its powerhouse. Modern cars primarily utilize internal combustion engines, which generate power by combusting a mixture of air and fuel. This controlled explosion creates energy that drives the vehicle.
Increasingly, electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity, employing electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. Electric motors offer instant torque, resulting in quicker acceleration compared to traditional combustion engines. Regardless of whether your car is powered by gasoline or electricity, the engine (or motor) is indispensable for its operation.
Battery: Powering the Start and Electrical Systems
The car battery is essential for multiple functions, most notably providing the initial surge of electricity needed to start your engine. Beyond starting the car, the battery also supplies power to all of your vehicle’s electrical components when the engine is off. This includes your headlights, interior lights, radio, and security system.
Alt Text: Car battery with red and black terminals, providing power to vehicle electrical systems.
A failing battery can leave you stranded, requiring a jump-start. Be attentive to warning signs such as a clicking sound when you turn the ignition key, or dimming headlights, as these may indicate a weakening battery.
Alternator: Keeping the Battery Charged
The alternator is responsible for generating electricity while your car is running. It essentially acts as a miniature power station, converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This generated electricity serves two crucial purposes: it powers the car’s electrical systems while driving and simultaneously recharges the battery. By constantly replenishing the battery’s charge, the alternator ensures consistent power for all electrical functions throughout your journey.
Alt Text: Car alternator with pulley and electrical connections, charging the battery and powering electrical components.
Similar to battery issues, symptoms of a failing alternator include dimming headlights and difficulty starting the car. Ignoring alternator problems can lead to battery drain and potential breakdowns.
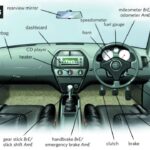
Brakes: Ensuring Safety and Control
Brakes are paramount for safety, responsible for slowing down and stopping your vehicle effectively. They also play a vital role in holding your car stationary when parked. Most vehicles are equipped with either disc brakes or drum brakes, or a combination of both.
Alt Text: Car disc brake system components including rotor, caliper, and brake pads, essential for vehicle stopping power.
Disc brake systems utilize calipers, rotors, and brake pads to create friction and slow the wheels. Drum brake systems employ brake drums and shoes for the same purpose. All brake components are subject to wear and tear over time. Any unusual noises or changes in brake pedal feel should be promptly investigated by a mechanic.
Radiator: Managing Engine Temperature
The engine generates a significant amount of heat during operation. The radiator is a key component of the engine cooling system, designed to dissipate this heat and maintain optimal engine temperature. It functions by cooling the engine coolant before it recirculates back through the engine to absorb more heat.
The radiator prevents engine overheating, which is crucial for maintaining engine efficiency, performance, and longevity. Regularly checking coolant levels is a simple yet effective way to ensure your radiator is functioning correctly.
Transmission: Transferring Power to the Wheels
The transmission, often referred to as the gearbox, is responsible for channeling the engine’s power to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. Without a transmission, the engine’s power would not be effectively transferred to propel the car.
Alt Text: Car automatic transmission, a complex system responsible for transferring engine power to the wheels.
Transmissions are available in two main types: manual and automatic. Manual transmissions require the driver to manually shift gears using a clutch and gear lever, while automatic transmissions shift gears automatically based on speed and engine load. Regular transmission fluid changes, as recommended by the manufacturer, are vital for maintaining transmission health and preventing premature wear.
Shock Absorbers: Ensuring a Smooth and Stable Ride
The suspension system, including shock absorbers, is designed to stabilize the vehicle and provide a comfortable ride. Shock absorbers are crucial components within the suspension system.
Alt Text: Car shock absorber, a suspension component that dampens vibrations and ensures tire contact with the road.
The primary function of shock absorbers is to maintain consistent tire contact with the road surface. This ensures optimal handling, braking performance, and a smoother ride, even on uneven roads. Worn shock absorbers can lead to vehicle vibrations, uneven tire wear, and reduced braking effectiveness.
Catalytic Converter: Reducing Harmful Emissions
As the engine operates, it produces exhaust fumes containing harmful gases and pollutants. The exhaust system, and specifically the catalytic converter, plays a critical role in reducing these emissions.
The catalytic converter transforms harmful compounds in the exhaust gases into less harmful gases before they are released into the atmosphere through the tailpipe. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can result in decreased engine performance and reduced fuel efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions About Car Components
How are car parts identified?
Car parts are identified through various methods to ensure accurate identification for cataloging and replacement purposes. Typically, each part is assigned a unique part number by the manufacturer. You’ll often find OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) labels or aftermarket labels. Modern car parts increasingly incorporate barcodes or QR codes for easier tracking and inventory management.
Approximately how many individual parts make up a car?
The number of parts in a car is substantial, ranging from approximately 30,000 to 40,000 individual components. The exact number varies depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and complexity, with more sophisticated vehicles generally containing a higher number of parts.
Expanding Your Automotive Knowledge
Gaining a solid understanding of car main parts is a significant step towards becoming a more informed and proactive car owner. Continued learning about your vehicle’s systems can further enhance your ability to maintain its performance and longevity. Stay tuned to carparteu.com for more in-depth articles and guides on automotive care and maintenance.