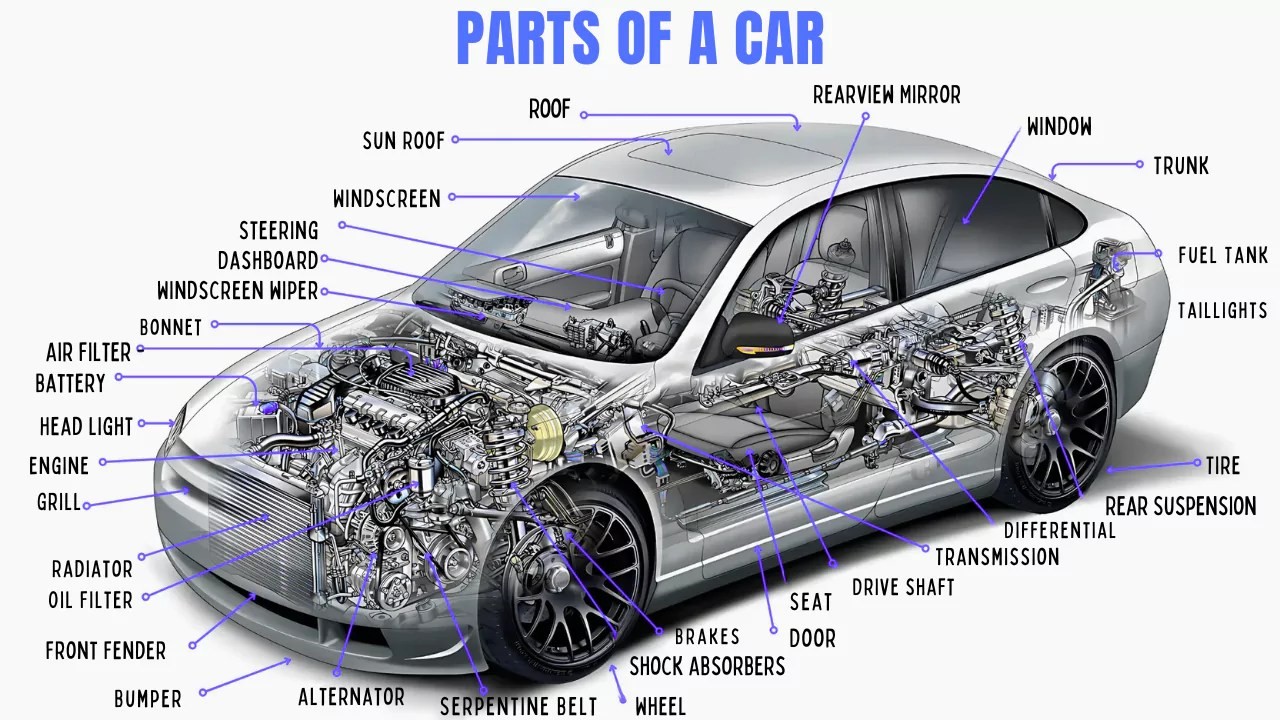
Understanding the various parts of your car is essential for any vehicle owner. Every component, from the smallest bolt to the largest engine part, plays a crucial role in keeping your vehicle running smoothly and safely. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or a new driver, familiarizing yourself with car parts and their names can empower you to communicate effectively with mechanics, troubleshoot minor issues, and make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of car parts, complete with images and names to help you learn the basics of automotive anatomy.
Car Parts Images and Names
Below is a list of common car parts, accompanied by names and visual aids to help you identify them. Understanding these components is the first step towards becoming a more informed car owner.
List of Car Parts Names:
- Seat Belt
- Headlights
- Taillights
- Indicator Lights
- Windshield
- Windshield Wipers
- Proximity sensors
- Car Hood
- Trunk
- Wheel/Tire
- Fuel Pump
- Fuel Gauge
- Speedometer
- Temperature Gauge
- Odometer
- RPM Gauge
- Cruise control
Understanding the Major Systems of Your Car
While the list above provides a good starting point, let’s delve deeper into the major systems that make your car function. Knowing how these systems work and the key car parts within them will provide a more comprehensive understanding of your vehicle.
1. Engine System
The engine is the heart of your car, responsible for converting fuel into the power needed for motion. Most cars utilize internal combustion engines (ICE), which burn fuel to drive pistons and turn the crankshaft, ultimately powering the wheels.
- Engine (Motor): The core component that generates power. Electric vehicles use motors instead of engines, converting electrical energy into motion.
- Cylinders: Chambers within the engine where fuel combustion occurs. Engines are often classified by the number and arrangement of cylinders (e.g., V8, inline-4).
- Pistons: Moving parts within cylinders that are driven by combustion, transferring energy to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: A rotating shaft that converts the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion, which is then transmitted to the wheels.
Car Engine Parts Diagram with Labels
2. Transmission System
The transmission plays a vital role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels. It manages the gear ratio, allowing the engine to operate efficiently at different speeds.
- Transmission: The system that manages power transfer from the engine to the wheels, adjusting gear ratios for varying speeds and driving conditions.
- Automatic Transmission: Shifts gears automatically based on speed and engine load, requiring no driver input for gear changes.
- Manual Transmission: Requires the driver to manually shift gears using a clutch pedal and gear stick.
- Gears: Different gear ratios allow the engine to operate efficiently at low and high speeds. Lower gears provide more torque for acceleration, while higher gears are for fuel-efficient cruising.
Car Transmission System Diagram with Parts
3. Electrical System
The electrical system powers all of your car’s electronic components, starting with the battery.
- Battery: Provides the initial electrical energy to start the engine and power electrical accessories when the engine is off.
- Alternator: Generates electricity while the engine is running, recharging the battery and powering electrical systems.
- Starter: An electric motor that cranks the engine to initiate combustion and start the car.
- Ignition Switch: Activates the starting system when you turn the key or press the start button.
- Fuses and Relays: Protect electrical circuits from overloads and control the flow of electricity to various components.
Car Battery and Electrical Components Diagram
4. Cooling System
The cooling system is crucial for regulating engine temperature and preventing overheating.
- Radiator: Dissipates heat from the engine coolant, keeping the engine at an optimal operating temperature.
- Coolant (Antifreeze): A liquid mixture that circulates through the engine, absorbing heat and transferring it to the radiator.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine and cooling system.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant temperature, ensuring the engine warms up quickly and stays within the optimal temperature range.
- Hoses: Carry coolant between the engine, radiator, and other cooling system components.
- Cooling Fan: Draws air through the radiator to enhance cooling, especially when the car is stationary or moving slowly.
Diagram of Car Engine Cooling System Parts
5. Braking System
The braking system is essential for safety, allowing you to slow down or stop your vehicle effectively.
- Brakes (Disc and Drum): Friction devices that slow or stop the wheels when the brake pedal is applied. Disc brakes are more common on front wheels and offer better stopping power, while drum brakes are often used on rear wheels.
- Brake Pads and Shoes: Friction materials that press against the rotors (disc brakes) or drums (drum brakes) to create friction and slow the wheels.
- Brake Rotors (Discs): Metal discs that rotate with the wheels and are clamped by brake pads to slow the vehicle.
- Brake Drums: Cylindrical drums that rotate with the wheels and are pressed upon by brake shoes to slow the vehicle.
- Brake Calipers: Hydraulic clamps that hold brake pads and press them against the rotors in disc brake systems.
- Brake Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders that push brake shoes against the drums in drum brake systems.
- Brake Lines: Pipes that carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brakes at each wheel.
- Master Cylinder: The main control for the hydraulic brake system, converting pedal pressure into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Pedal: The foot pedal that the driver presses to activate the braking system.
Car Braking System Diagram with Component Names
6. Suspension and Steering System
The suspension and steering systems work together to provide a comfortable ride and allow you to control the vehicle’s direction.
- Suspension System: Absorbs shocks from road irregularities, providing a smoother ride and maintaining tire contact with the road.
- Springs: Support the vehicle’s weight and absorb vertical shocks.
- Shock Absorbers (Dampers): Control spring oscillations, preventing excessive bouncing and ensuring a stable ride.
- Control Arms: Connect the wheels to the vehicle’s frame and allow for suspension movement.
- Struts: Combine the functions of springs and shock absorbers into a single unit, commonly used in front suspensions.
- Sway Bar (Anti-roll Bar): Reduces body roll during cornering, improving stability.
- Steering System: Allows the driver to control the direction of the vehicle.
- Steering Wheel: The primary control for steering the vehicle.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear.
- Steering Gearbox (Rack and Pinion or Recirculating Ball): Reduces steering effort and translates steering wheel rotation into wheel movement.
- Tie Rods: Connect the steering gearbox to the steering knuckles, transmitting steering forces to the wheels.
- Power Steering Pump and Fluid: Provides hydraulic assistance to reduce steering effort, making it easier to turn the steering wheel.
Diagram of Car Steering and Suspension System Parts
7. Exhaust System
The exhaust system removes combustion gases from the engine and reduces harmful emissions and noise.
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful pollutants in exhaust gases, converting them into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: Reduces engine noise, making the vehicle quieter.
- Resonator: Further reduces noise and tunes the exhaust note.
- Tailpipe: The final section of the exhaust system, discharging exhaust gases into the atmosphere.
- O2 Sensor (Oxygen Sensor): Monitors the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, helping the engine control unit (ECU) optimize the air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion and reduced emissions.
Car Exhaust System Diagram with Parts Labeled
8. Fuel System
The fuel system stores and delivers fuel to the engine for combustion.
- Fuel Tank: Stores the car’s fuel supply.
- Fuel Pump: Pumps fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes contaminants from the fuel, protecting the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Pipes that carry fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Injectors (or Carburetor in older cars): Spray fuel into the engine’s cylinders for combustion.
- Fuel Gauge: Indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the tank.
Diagram of Car Fuel System Components
9. Safety System
Safety systems are designed to protect occupants in the event of a collision.
- Airbags: Inflatable cushions that deploy in a crash to protect occupants from impacts.
- Seat Belts: Restraints that hold occupants securely in their seats during a collision, preventing ejection and reducing injury.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during hard braking, maintaining steering control.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): Helps maintain vehicle stability by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Prevents wheel spin during acceleration, improving traction.
- Proximity Sensors: Warn the driver of nearby objects, aiding in parking and maneuvering.
Car Safety System Diagram with Names
10. Body and Exterior Parts
Body and exterior parts provide the car’s shape, protect internal components, and contribute to aerodynamics and aesthetics.
- Car Hood (Bonnet): Hinged cover over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance.
- Trunk (Boot): Storage compartment, typically at the rear of the vehicle.
- Doors: Provide access to the vehicle’s interior.
- Fenders (Wings): Body panels that surround the wheels, protecting the car from road debris.
- Bumpers: Front and rear protective structures designed to absorb impact in low-speed collisions.
- Windshield (Windscreen): Front window, providing visibility and protection from the elements.
- Windshield Wipers: Clean the windshield, ensuring clear visibility in rain and snow.
- Headlights: Illuminate the road ahead for nighttime driving.
- Taillights: Indicate the vehicle’s presence to drivers behind, especially at night and during braking.
- Indicator Lights (Turn Signals): Signal intended turns or lane changes.
- Wheels and Tires: Allow the vehicle to roll and provide traction with the road surface.
- License Plate: Identification plate for the vehicle.
Diagram of Car Body Parts with Names
11. Interior Parts and Controls
Interior parts and controls provide comfort, convenience, and driver interface.
- Steering Wheel: Controls the direction of the vehicle.
- Dashboard: The panel in front of the driver, containing instruments and controls.
- Speedometer: Indicates the vehicle’s speed.
- Tachometer (RPM Gauge): Indicates the engine’s revolutions per minute.
- Fuel Gauge: Indicates the fuel level.
- Temperature Gauge: Indicates the engine coolant temperature.
- Odometer: Records the total distance traveled by the vehicle.
- Trip Meter: Records the distance traveled on a particular trip, often resettable.
- Gear Shift: Selects gears in manual and automatic transmissions.
- Pedals (Accelerator, Brake, Clutch): Control vehicle speed and braking (and clutch in manual transmissions).
- Seats: Provide seating for occupants.
- Seat Belts: Safety restraints for occupants.
- Air Vents: Distribute heating and air conditioning.
- Radio/Infotainment System: Provides entertainment and vehicle information.
- Climate Controls (Heating and Air Conditioning): Regulate cabin temperature.
- Windows and Window Controls: Provide visibility and ventilation.
- Mirrors (Rearview and Side Mirrors): Provide visibility to the rear and sides of the vehicle.
Car Interior Parts Diagram with Labels
Conclusion
Understanding the names and functions of car parts is more than just automotive trivia; it’s a practical skill for every car owner. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you’ll be better equipped to understand vehicle maintenance, communicate with mechanics, and ensure your car remains in top condition. This visual guide with Car Parts Images And Names is a starting point for your automotive knowledge journey, empowering you to be a more informed and responsible car owner.
FAQs
What are the most basic parts of a car?
The most basic car parts include the engine, transmission, battery, brakes, wheels, and chassis (frame). These are the fundamental components required for a vehicle to function.
What are the essential parts for a car to run?
For a car to run, the essential parts are the engine (to provide power), the fuel system (to supply fuel), the electrical system (to start and power components), the cooling system (to prevent overheating), the transmission (to transfer power to wheels), and the wheels and tires (for movement).
How many main parts does a car have?
While the exact number is debatable depending on how you categorize parts, a car can be broadly divided into several main systems: engine, transmission, electrical, cooling, braking, suspension, steering, exhaust, fuel, safety, body, and interior. Within these systems, there are numerous individual parts, estimated to be around 30,000 in total, including even the smallest components.
Where can I find more car parts images and names?
Beyond this guide, you can find more detailed car parts images and names in your car’s owner’s manual, online automotive parts catalogs, repair manuals, and websites dedicated to automotive information and repair, like carparteu.com.