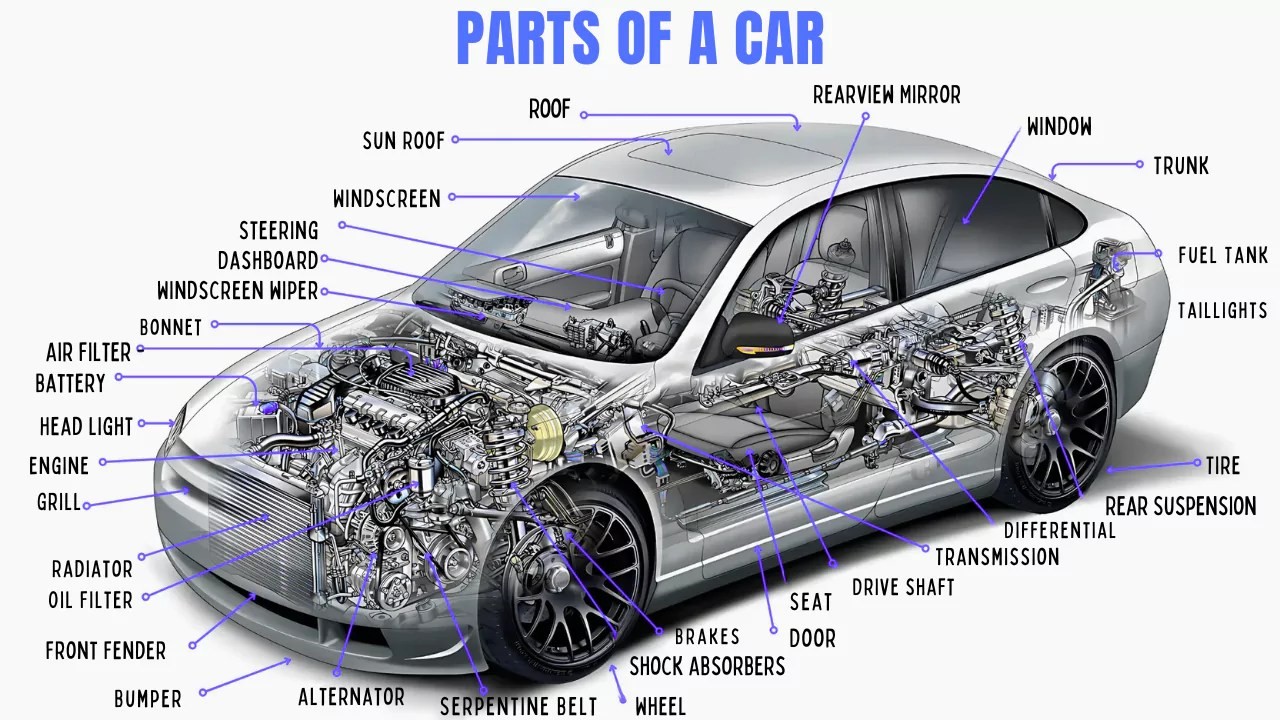
Your car is a complex machine, a symphony of interconnected parts working harmoniously to get you where you need to be. Understanding the names and functions of these car parts isn’t just for mechanics; it empowers you as a car owner. Whether you’re troubleshooting a minor issue, communicating with a technician, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge, knowing your car parts is a valuable asset.
This comprehensive guide will provide you with a detailed Car Parts Name List, exploring both the essential components and the supporting systems that make up your vehicle. From under the hood to the chassis, we’ll cover the names and functions of crucial car parts, helping you become a more informed and responsible car owner.
Essential Car Parts Name List:
Here’s a quick car parts name list to get you started, covering some of the most common and important components:
- Seat Belt
- Headlights
- Taillights
- Indicator Lights
- Windshield
- Windshield Wipers
- Proximity sensors
- Car Hood (Bonnet)
- Trunk (Boot)
- Wheel / Tire
- Fuel Pump
- Fuel Gauge
- Speedometer
- Temperature Gauge
- Odometer
- RPM Gauge (Tachometer)
- Cruise control
This is just a starting point. Let’s delve deeper into the major systems and explore a more extensive car parts name list.
Understanding Key Car Parts: A Detailed Breakdown
To truly understand your vehicle, it’s helpful to categorize car parts by their primary systems. This approach will give you a clearer picture of how everything works together.
1. Engine Components: The Heart of Your Car
The engine is arguably the most critical part of your car, converting fuel into the power that drives your wheels. Here are some key car parts names within the engine system:
#1. Engine
The engine itself is the core component. Most cars use internal combustion engines (ICE), which burn fuel (gasoline or diesel) to create mechanical energy. This energy is generated by igniting fuel and air within cylinders, driving pistons that turn the crankshaft. Engine size is often described by the number of cylinders (e.g., V6, V8) and their total volume (displacement). Electric vehicles (EVs) don’t have engines; they use motors that convert electrical energy into motion.
#2. Transmission
The transmission is crucial for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. It allows the engine to operate efficiently at different speeds. Automatic transmissions shift gears automatically, while manual transmissions require the driver to use a clutch and gearshift. The transmission adjusts the gear ratio between the engine and wheels as the car speeds up or slows down.
#3. Battery
The battery provides the initial electrical power to start the engine and powers electrical components like lights and accessories. It’s part of the starting system, which also includes the ignition switch and starter. Battery specifications like Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Reserve Capacity are important considerations when choosing a replacement.
#4. Alternator
The alternator recharges the battery while the engine is running and provides power to the car’s electrical systems. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy using a serpentine belt. A failing alternator can lead to symptoms like dimming headlights or difficulty starting the car.
#5. Radiator
The radiator is a key component of the cooling system, preventing the engine from overheating. It dissipates heat from the engine coolant as it circulates through the system. The cooling system also includes hoses, a fan, and a thermostat to regulate engine temperature.
#6. Serpentine Belt
The serpentine belt (or multi-rib belt) is a long, winding belt that drives multiple engine accessories, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. It’s a critical component for ensuring these systems function properly.
#7. Cooling System
The cooling system is responsible for maintaining the engine at an optimal operating temperature. It includes the radiator, coolant, hoses, fan, thermostat, and water pump. This system prevents overheating and ensures efficient engine performance.
#8. Lubrication System
The lubrication system delivers oil to the engine’s moving parts to reduce friction and wear. An oil pump circulates oil throughout the engine, lubricating components like pistons, crankshaft bearings, and camshafts.
#9. Ignition System
The ignition system is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in gasoline engines. Key components include the ignition coil, spark plugs, and spark plug wires (though newer cars often use coil-on-plug systems without wires).
#10. Timing Belt
The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring the engine valves open and close at the correct times. This precise timing is crucial for engine operation and preventing damage.
#45. Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is responsible for transferring fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. In modern cars, it’s typically an electric pump located inside the fuel tank, ensuring consistent fuel delivery and pressure.
#46. Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge on your dashboard displays the engine coolant temperature, alerting you to potential overheating issues.
#48. Rev Counter (Tachometer)
The rev counter or tachometer shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM), indicating how fast the engine crankshaft is rotating.
#33. Air Filter
The air filter cleans the air entering the engine, removing dirt and debris that could cause damage. A clean air filter is essential for efficient combustion and engine performance.
#9. Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is part of the exhaust system and reduces harmful emissions. It converts pollutants like hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances.
#10. Muffler
The muffler reduces engine noise, making your car quieter. It uses a series of chambers and tubes to cancel out sound waves.
#30. O2 Sensor
The O2 sensor (oxygen sensor) measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. This data is used by the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion and reduced emissions.
#31. Resonator
The resonator, often used in conjunction with the muffler, further refines exhaust sounds, targeting specific frequencies to eliminate droning noises and create a more pleasant exhaust note.
#47. Car Trip Meter (Odometer)
The car trip meter, or odometer, measures the distance traveled by the vehicle. Modern cars often have both a trip odometer (resettable for tracking individual journeys) and a main odometer (recording total mileage).
#44. Fuel Gauge
The fuel gauge indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the tank, helping you avoid running out of gas.
#45. Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine.
#49. License Plate / Bumper Stickers
While not technically engine parts, license plates are legally required for vehicle identification, and bumper stickers are a common form of car accessory.
#50. Accessories
Car accessories encompass a wide range of features that enhance comfort, safety, and convenience, including headlights, taillights, windshield wipers, and in-car entertainment systems.
2. Drivetrain Components: Transferring Power to the Wheels
The drivetrain system takes the power generated by the engine and delivers it to the wheels, making the car move. Here are essential car parts names in the drivetrain:
#18. Powertrain
The powertrain encompasses all the components that generate power and transmit it to the wheels. This includes the engine, transmission, driveshaft, axles, and differential.
#6. Front Axle & #11. Rear Axle
Axles are rods or shafts that rotate the wheels and support the vehicle’s weight. Front axles are located at the front, while rear axles are at the back. They can be “live” (rotating with the wheels) or “dead” (supporting weight but not rotating).
#20. Propeller Shaft (Driveshaft)
The propeller shaft or driveshaft transmits rotational power from the transmission to the rear axle in rear-wheel-drive vehicles.
#21. Differential
The differential allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds, which is necessary when turning corners. It distributes power while accommodating this difference in wheel speed.
#22. Gear Shift
The gear shift (or gear selector) allows the driver to select different gears in manual and automatic transmissions, controlling the vehicle’s speed and power. In manual cars, it’s often called a “stick shift”.
#19. Clutch
The clutch is found in manual transmission vehicles. It disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing the driver to change gears smoothly.
3. Chassis and Suspension Components: Ride and Handling
The chassis and suspension systems are crucial for a comfortable and safe ride, absorbing road shocks and maintaining stability. Here are key car parts names in this category:
#7. Front Steering and Suspension & #12. Rear Suspension
The suspension system is a network of components that cushions the car from bumps and keeps the tires in contact with the road. It includes springs, shock absorbers, and linkages. Front suspension and rear suspension work together to provide a balanced ride.
#8. Brakes
Brakes are essential for stopping the vehicle. They use friction to convert kinetic energy into heat, slowing the car down. Common types are disc brakes and drum brakes.
#13. Steering System
The steering system allows the driver to control the direction of the vehicle. It typically uses a steering wheel, steering column, and steering gear (like rack-and-pinion or recirculating ball systems).
#24. Suspension System
The suspension system as a whole is responsible for ride comfort and handling. It includes springs, shocks, and anti-sway bars.
#25. Shock Absorber
Shock absorbers (or dampers) control the movement of the suspension springs, preventing excessive bouncing and maintaining tire contact with the road.
4. Body and Exterior Components: Protection and Visibility
These car parts names refer to the visible and protective parts of your vehicle:
#1. Seat Belt
Seat belts are crucial safety devices that restrain occupants during a crash, preventing ejection and minimizing injuries.
#36. Headlights
Headlights illuminate the road ahead for safe driving at night or in low visibility conditions.
#37. Tail Lights
Tail lights make your vehicle visible from behind, especially at night, and indicate braking and turning.
#38. Windshield / Windscreen
The windshield (or windscreen) is the front window, providing visibility and protecting occupants from wind, debris, and weather.
#39. Windshield Wipers
Windshield wipers clear rain, snow, and debris from the windshield to maintain visibility.
#40. Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors assist with parking and can detect nearby objects, enhancing safety and convenience.
#41. Car Hood (Bonnet)
The car hood (or bonnet) covers the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance and repairs.
#42. Trunk (Boot)
The trunk (or boot) is the main storage compartment in the rear of most cars.
#28. Wheel / Tire
Wheels are the metal structures that tires are mounted on. Tires are the rubber coverings that provide traction and cushioning.
#29. Exhaust System
The exhaust system removes combustion gases from the engine, routing them away from the vehicle. It includes components like the catalytic converter, muffler, resonator, and tailpipe.
#43. Speedometer
The speedometer displays the vehicle’s current speed.
#32. Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The electronic control unit (ECU) is a computer that controls various electronic systems in the car, from engine management to airbags.
#34. Airbags
Airbags are inflatable safety cushions that deploy in a collision to protect occupants from impact.
#35. Seat Belt
Seat belts are essential safety devices that restrain occupants during a crash.
#37. TailLights
Tail lights are red lights at the rear of the vehicle, making it visible to drivers behind.
#38. Windshield/Windscreen
The windshield is the front window of the car, providing visibility and protection.
#39. Windshield Wipers
Windshield wipers clear the windshield of rain, snow, and debris to ensure clear vision.
#40. Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are used in parking assist systems and security systems to detect nearby objects or intrusions.
#41. Car Hood
The car hood covers the engine compartment and provides access for maintenance.
#42. Trunk
The trunk is the main storage compartment of the car, usually located at the rear.
#43. Speedometer
The speedometer displays the car’s speed.
#44. Fuel gauge
The fuel gauge shows the amount of fuel left in the tank.
#45. Fuel Pump
The fuel pump delivers fuel from the tank to the engine.
#46. Temperature gauge
The temperature gauge indicates the engine coolant temperature, helping to prevent overheating.
#47. Car trip meter
The car trip meter measures the distance traveled, often used for tracking mileage between fill-ups or trips.
#48. Rev counter
The rev counter (tachometer) shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM).
#49. License Plate/Bumper Stickers
License plates are for vehicle identification, and bumper stickers are decorative or expressive additions.
#50. Accessories
Accessories cover a wide range of optional or add-on features for comfort, convenience, and personalization.
#26. Fuel Tank
The fuel tank stores the car’s fuel supply. It’s designed for safety and durability.
#27. Tailpipe
The tailpipe is the end of the exhaust system, where exhaust gases are expelled from the vehicle.
Car Parts Video
[Include a relevant YouTube video here about car parts if available – search for “car parts explained” or “basic car parts”]
FAQs about Car Parts Names
### What is the most basic part of a car?
While all car parts are important for the vehicle to function as a whole, the most fundamental components are often considered to be the engine, transmission, chassis (frame), and wheels. These are the core elements required for basic mobility.
### What is the main part of a car?
Many would argue that the engine is the main part of a car, as it’s the source of power. Without an engine (or motor in an EV), the car cannot move. However, a car is a system, and the “main” part depends on your perspective. The chassis is essential for structure, the transmission for power delivery, and so on.
### What are the two main parts of a car?
Breaking it down very broadly, you could say the two main parts are the chassis/frame which provides the structural base, and the body which includes all the external panels and interior. Alternatively, from a functional standpoint, the powertrain (engine and transmission) and the chassis/suspension could be considered the two main functional categories.
### How many car parts are in a car?
The number of parts in a car is surprisingly high. Estimates range around 30,000 components, from tiny fasteners to large assemblies like the engine and transmission. This number can vary depending on the complexity of the vehicle model.
### Related Post
[Link to a relevant internal article on your website, for example, “Basic Car Maintenance Tips for Beginners”]
Understanding this car parts name list and the function of each component is a great step towards becoming a more knowledgeable car owner. Continue exploring and learning about your vehicle to ensure its longevity and your safety on the road.