For owners of a classic 1989 Chevy 1500, understanding your vehicle’s diagnostic system is crucial for maintenance and repair. A common question that arises is whether this model year is equipped with OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II). The short answer is no, the 1989 Chevy 1500 does not have OBD2. Instead, it utilizes an earlier system known as OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics I).
To elaborate, OBD2 became mandatory in the United States for all cars and light trucks manufactured from 1996 onwards. Vehicles produced before this period, including your 1989 Chevy 1500, are equipped with OBD1 systems. OBD1 is less standardized and less comprehensive than OBD2, but it still provides valuable diagnostic information.
So, how can you diagnose issues with your 1989 Chevy 1500? While you won’t find the standardized OBD2 port, there are effective methods to access the diagnostic codes stored in your truck’s computer.
One popular method, especially favored by experienced mechanics, involves using a scan tool specifically designed for OBD1 systems. A well-regarded option for this vintage GM product is the Snap-On MT2500 scanner. These scanners, often available on platforms like eBay, can reliably retrieve trouble codes from your 1989 Chevy 1500. When seeking an MT2500, ensure it includes the GM1 ALDL adapter, along with Primary and Troubleshooter cartridges and the necessary cables compatible with your model year to ensure proper connectivity and functionality.
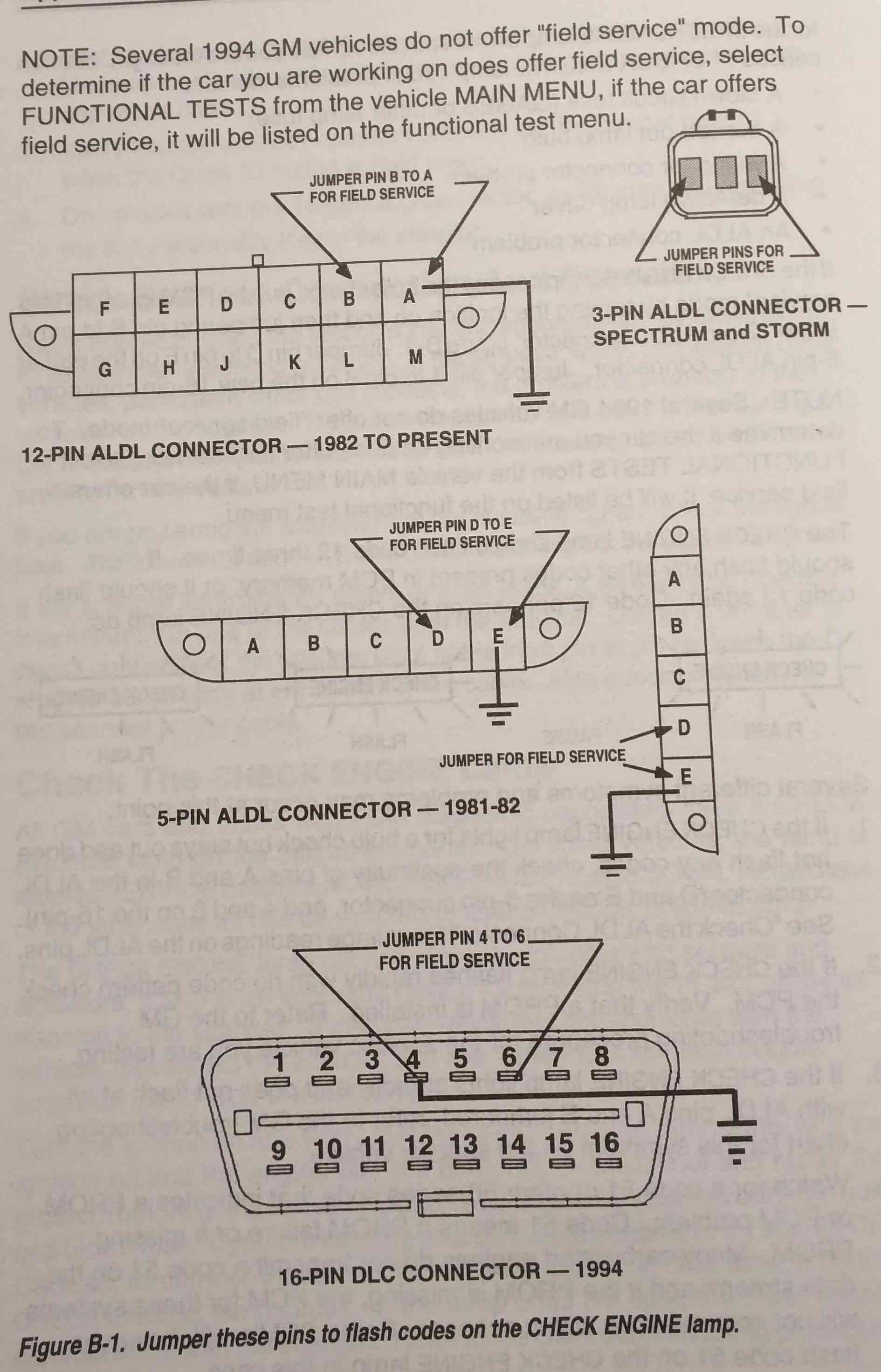 GM ALDL Connector Pins for Code Retrieval
GM ALDL Connector Pins for Code Retrieval
Alternatively, for a more basic approach without a dedicated scanner, you can use a paper clip or jumper wire to manually retrieve codes. This involves shorting specific pins on the Assembly Line Diagnostic Link (ALDL) connector, which is the diagnostic port for OBD1 systems. By shorting the correct pins with the ignition key in the “Key On, Engine Off” (KOEO) position, the check engine light will flash, indicating stored codes.
The codes are communicated through a series of flashes. Long flashes represent the first digit of a code, and short flashes indicate the second digit. For example, code 12, indicating no codes are stored or the system is in diagnostic mode, is represented by one long flash followed by two short flashes.
Here is a list of common OBD1 codes for your 1989 Chevy 1500 to help you understand the check engine light flashes:
- 12 – Diagnostic mode or no codes present
- 13 – O2 Sensor or Circuit
- 14 – Coolant Sensor or Circuit/ High Temp Indicated
- 15 – Coolant Sensor or Circuit/ Low Temp Indicated
- 16 – System Voltage Out of Range
- 19 – Crankshaft Position Sensor or Circuit
- 21 – Throttle Position Sensor or Circuit – Voltage High
- 22 – Throttle Position Sensor or Circuit – Voltage Low
- 23 – Mixture Control (M/C) Solenoid or Circuit (Carbureted Models) / Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) Sensor or Circuit (1990 and earlier models) / Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit (Fuel-Injected Models)
- 24 – Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) or Circuit
- 25 – Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) Sensor or Circuit – High Temperature Indicated (1990 and earlier models) / Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor or Circuit – High Temperature Indicated (1991 and later models)
- 26 – Quad Driver Module Circuit
- 27 – Quad Driver Module Circuit
- 28 – Quad Driver Module Circuit
- 29 – Quad Driver Module Circuit
- 31 – Park/Neutral Position (PNP) Switch Circuit
- 32 – Baro Sensor or Circuit (Carbureted Models) / EGR Circuit (Fuel-Injected Models)
- 33 – Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Signal Voltage High / Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor or Circuit – Excessive Airflow Indicated
- 34 – Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Signal Voltage Low / Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Signal – Low Airflow Indicated
- 35 – Idle Speed Control (ISC) Switch or Circuit (Shorted) (Carbureted Models) / Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve/ Circuit
- 38 – Brake Switch Circuit
- 39 – Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Circuit
- 41 – No Distributor Signals to ECM, or Faulty Ignition Module (Carbed Models) / Cylinders Select Error- MEM-CAL or ECM Problem (Fuel-Injected Models) / Cam Sensor Circuit (3.8 Engine)
- 42 – Bypass or Electronic Spark Timing (EST) Circuit
- 43 – Low Voltage at ECM Terminal L (Carbureted Models) / Knock Sensor Circuit
- 44 – Oxygen Sensor or Circuit – Lean Exhaust Detected
- 45 – Oxygen Sensor or Circuit – Rich Exhaust Detected
- 46 – Power Steering Pressure Switch Circuit
- 48 – Misfire Diagnosis
- 51 – PROM, MEM-CAL or ECM Problem
- 52 – CALPAK or ECM Problem
- 53 – EGR Fault (Carbureted Models Only) / System Over-Voltage (ECM over 17.7 Volts)
- 54 – Mixture Control (M/C) Solenoid or Circuit (Carbureted Models) / Fuel Pump Circuit (1986 and later models)
- 55 – Oxygen Sensor Circuit or ECM / Fuel Lean Monitor (2.2L Engine)
- 61 – Oxygen Sensor Signal Faulty (Possible Contaminated Sensor)
- 62 – Transaxle Gear Switch Signal Circuits
- 63 – Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Voltage High (Low Vacuum Detected)
- 64 – Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Voltage Low (High Vacuum Detected)
- 66 – Pressure Sensor or Circuit Air Conditioning
In conclusion, your 1989 Chevy 1500 is equipped with an OBD1 system, not OBD2. Understanding this difference and knowing how to retrieve diagnostic codes, either with a scanner or by manually reading flashes, is essential for maintaining your classic truck. While OBD1 is less advanced than OBD2, it still offers valuable insights into your vehicle’s health, allowing for effective troubleshooting and repairs.