Are you struggling to connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 system? Is your OBD2 interface not being recognized?
In this guide, we’ll explore the common reasons behind the “Easy Obd2 Interface Not Found” issue and provide practical troubleshooting steps to get you back on track. Understanding the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD2) protocol is crucial for modern vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. OBD2 allows you to access a wealth of data from your car, from engine performance to emissions, using a simple interface. However, sometimes this seemingly straightforward connection can fail, leaving you with a frustrating “interface not found” error.
This article will delve into the intricacies of OBD2, covering the OBD2 connector, communication protocols, and common pitfalls that lead to connection problems. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to diagnose and resolve these issues, ensuring you can effectively utilize your OBD2 interface.
You can also watch our OBD2 intro video or get the PDF for offline access.
Understanding OBD2 and Why Connection Matters
OBD2 is your car’s built-in diagnostic system, a standardized protocol mandated for most vehicles worldwide. It’s designed to monitor vehicle performance and emissions, reporting any issues through diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time data. The OBD2 system is accessed via a 16-pin OBD2 connector, typically located within easy reach inside your car’s cabin. Mechanics use OBD2 scanners to diagnose problems, and enthusiasts use interfaces to monitor performance and customize settings.
The “malfunction indicator light” (MIL), or check engine light, is often the first sign of an issue detected by the OBD2 system. When this light illuminates, it indicates that the car’s computer has stored a DTC. An OBD2 scanner, connected via an OBD2 interface, is the key to reading these codes and understanding the problem. However, if your OBD2 interface is not found, you lose this crucial diagnostic capability.
Caption: An OBD2 scanner diagnosing a car, highlighting the importance of a functional OBD2 interface for reading diagnostic information when the malfunction indicator light (MIL) is on.
Is Your Car OBD2 Compliant? Checking for Compatibility
Before troubleshooting an “easy OBD2 interface not found” error, it’s essential to confirm your vehicle is indeed OBD2 compliant. While most modern cars are, older models or vehicles from certain regions might not fully support the standard.
Generally, if your car was purchased new in the following regions and years, it’s likely OBD2 compliant:
- USA: Cars and light trucks from 1996 onwards, medium-duty vehicles from 2005, and heavy-duty vehicles from 2010.
- Europe: Gasoline cars from 2001, diesel cars (EOBD) from 2003.
However, the presence of a 16-pin OBD2 connector doesn’t guarantee OBD2 compliance. Some pre-OBD2 vehicles may have a similar connector for manufacturer-specific diagnostics. To be certain, check your vehicle’s owner’s manual for OBD2 compliance information or consult resources that list OBD2 compliant vehicles.
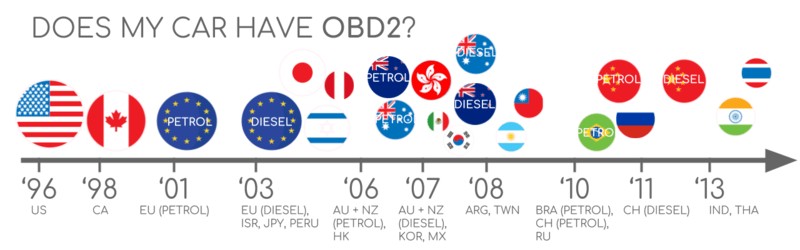
Caption: A chart showing OBD2 compliance timelines for different regions (EU, US, CAN) and vehicle types, helpful for verifying if your car should support OBD2.
Common Causes of “Easy OBD2 Interface Not Found” Errors
Encountering an “easy OBD2 interface not found” error can stem from various issues, ranging from simple connection problems to more complex protocol mismatches. Here are some of the most common reasons:
-
Loose or Incorrect Connection: The most basic issue is often overlooked. Ensure your OBD2 interface is firmly plugged into the OBD2 port in your vehicle. Sometimes, a slightly loose connection can prevent proper communication.
-
Faulty OBD2 Interface: The interface itself could be defective. Try using a different OBD2 interface or scanner to rule out a hardware problem with your device.
-
Software or Driver Issues: If you’re using an OBD2 interface with software on a laptop or phone, outdated or corrupted drivers or software can cause connection failures. Ensure you have the latest drivers and software versions installed.
-
Vehicle Ignition State: OBD2 communication typically requires the vehicle’s ignition to be in the “ON” position (but engine not necessarily running). Some interfaces might require the engine to be running. Check the interface’s instructions for the correct ignition state.
-
Protocol Mismatch: While OBD2 is a standard, there are different communication protocols within the standard (like CAN, KWP2000, etc.). A mismatch between the protocol your interface uses and the protocol your car supports will result in a connection error. Modern cars predominantly use CAN bus.
-
ECU Issues: In rare cases, the issue might lie with the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) or other control modules not responding properly to OBD2 requests. This could be due to ECU malfunction or software glitches.
-
Power Issues: The OBD2 port should provide power to the interface. A blown fuse or wiring problem affecting the OBD2 port’s power supply can prevent the interface from being detected.
-
Incompatible App or Software: Ensure the app or software you are using is compatible with your OBD2 interface and your vehicle’s make and model. Some apps may only support specific interfaces or vehicle types.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting for OBD2 Interface Not Found
When faced with the “easy OBD2 interface not found” message, follow these troubleshooting steps systematically:
1. Verify the Connection:
- Physically Inspect: Check that the OBD2 interface is securely plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port. Unplug and replug it firmly.
- Check for Damage: Examine the OBD2 connector and the vehicle’s port for any bent pins, debris, or damage.
2. Test with a Different Interface (If Possible):
- Borrow or Use a Spare: If you have access to another OBD2 scanner or interface, try using it with your vehicle. If the second interface connects successfully, the problem likely lies with your original interface.
3. Check Software and Drivers (for PC/Phone based Interfaces):
- Update Drivers: For PC-based interfaces, ensure you have the latest drivers installed from the manufacturer’s website.
- Update App/Software: If using a phone app or PC software, check for updates in the app store or software’s update settings.
- Restart Devices: Restart your phone, laptop, and even your car (turn ignition off and on again) to refresh connections.
4. Confirm Vehicle Ignition State:
- Follow Interface Instructions: Consult your OBD2 interface’s manual for the recommended ignition state. Try both “Ignition ON, Engine OFF” and “Ignition ON, Engine ON” positions.
5. Verify OBD2 Protocol and Compatibility:
- Check Interface Specs: Ensure your OBD2 interface supports the protocols used by your vehicle. Most modern interfaces support CAN bus, which is widely used.
- Vehicle Manual: Your car’s owner’s manual may specify the OBD2 protocols supported.
- Online Compatibility Checkers: Some OBD2 interface manufacturers offer online tools to check vehicle compatibility.
6. Check Vehicle Fuses:
- Locate Fuse Box: Consult your vehicle’s manual to find the location of the fuse box (usually under the dashboard or in the engine bay).
- Identify OBD2 Fuse: Look for the fuse related to the OBD2 port or auxiliary power outlets (they are often on the same circuit).
- Inspect and Replace: Check if the fuse is blown. If so, replace it with a fuse of the same rating.
7. Test OBD2 Port Power (Advanced):
- Multimeter: Use a multimeter to check if the OBD2 port is providing power on pin 16 (Battery Positive) and pin 4 or 5 (Ground). You should typically see around 12V. Note: This requires basic electrical knowledge and caution.
8. Try a Different App or Software:
- Compatibility Issues: If you suspect your app or software might be incompatible, try using a different OBD2 diagnostic app or software to see if the interface is recognized.
9. Consult a Mechanic (If Still Unresolved):
- Professional Diagnosis: If you’ve tried all the above steps and still face the “easy OBD2 interface not found” error, there might be a more complex issue with your vehicle’s ECU or wiring. Consult a qualified mechanic for professional diagnosis and repair.
Caption: OBD2 connector pinout diagram (Type A), useful for understanding pin functions and for advanced troubleshooting steps like checking power supply using a multimeter on pin 16 and ground pins.
Understanding OBD2 Standards and Protocols
To effectively troubleshoot OBD2 interface issues, a basic understanding of OBD2 standards and protocols is helpful. OBD2 communication is built upon lower-layer protocols, with CAN bus being the most prevalent in modern vehicles (ISO 15765-4 standard).
Key OBD2 Standards:
- SAE J1962 / ISO 15031-3: Specifies the 16-pin OBD2 connector.
- ISO 15765-4 (Diagnostics over CAN / DoCAN): Defines the use of CAN bus as the lower-layer protocol for OBD2, including bit-rates (250K or 500K), CAN IDs, and data frame structure.
- SAE J1979 / ISO 15031-5: Standardizes OBD2 diagnostic services (modes) and parameter IDs (PIDs).
- ISO 15765-2 (ISO-TP): Transport protocol used for OBD2 messages exceeding 8 bytes, enabling multi-frame communication for data like VIN or DTCs.
Common OBD2 Protocols (Lower-Layer):
- ISO 15765 (CAN bus): Dominant in modern vehicles (2008+ in the US).
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000): Used in some older vehicles, particularly in Asia.
- ISO 9141-2: Found in some European, Chrysler, and Asian cars (2000-2004).
- SAE J1850 (VPW & PWM): Used in older GM and Ford vehicles, respectively.
Caption: An OSI model representation of OBD2 over CAN bus, illustrating the layered communication architecture and the relevant ISO and SAE standards at each layer.
OBD2 and CAN Bus: The Foundation of Modern Diagnostics
Since 2008 in the US, CAN bus (ISO 15765-4) has been the mandatory lower-layer protocol for OBD2 in all cars. Understanding the relationship between OBD2 and CAN bus is key to grasping modern vehicle diagnostics.
Key aspects of OBD2 over CAN (ISO 15765-4):
- CAN Bit-rate: Standardized at 250K or 500K.
- CAN IDs: Can use 11-bit or 29-bit identifiers.
- Specific CAN IDs for OBD2: Functional addressing (0x7DF – 11-bit, 0x18DB33F1 – 29-bit) and physical addressing (0x7E0-0x7E7 – 11-bit).
- Data Frame Length: Diagnostic CAN frames are typically 8 bytes.
When troubleshooting “easy OBD2 interface not found,” especially with CAN-based interfaces, consider these CAN bus parameters. While most modern interfaces auto-detect the bit-rate, protocol mismatches can still occur.
Caption: A diagram illustrating the relationship between OBD2 and CAN bus, highlighting that OBD2 is a higher-layer protocol that often operates over a CAN bus physical layer in modern vehicles.
Practical Tips for Reliable OBD2 Connections
To minimize “easy OBD2 interface not found” errors and ensure reliable OBD2 connections, follow these best practices:
- Use Quality Interfaces: Invest in reputable OBD2 interfaces from known brands. Cheap, uncertified interfaces can be prone to connection issues and may not adhere to OBD2 standards properly.
- Check Compatibility Before Purchase: Before buying an OBD2 interface, verify its compatibility with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update the drivers and software associated with your OBD2 interface.
- Handle Connectors Carefully: Avoid forcing or yanking the OBD2 connector. Gentle handling prevents damage to pins and ensures a secure connection.
- Secure Connection: Make sure the interface is firmly seated in the OBD2 port until it clicks or feels securely in place.
- Correct Ignition State: Always follow the interface and software instructions regarding the vehicle’s ignition state during connection and data retrieval.
- Avoid Interference: Keep the OBD2 interface and cable away from sources of electromagnetic interference, if possible.
By understanding the common causes of “easy OBD2 interface not found” errors and following these troubleshooting steps and best practices, you can significantly improve your chances of establishing a reliable connection to your vehicle’s OBD2 system and unlock the valuable diagnostic and performance data it offers. If problems persist, remember to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic to diagnose potential vehicle-side issues.
Unlock Your Vehicle’s Data: Get Connected with OBD2
Don’t let “easy OBD2 interface not found” errors keep you from accessing your vehicle’s valuable data. By understanding the OBD2 system, common connection issues, and troubleshooting techniques, you can overcome these hurdles and leverage the power of OBD2 for diagnostics, performance monitoring, and more.
Need reliable OBD2 data logging solutions?
Explore our range of OBD2 data loggers and CAN bus tools to get connected and start analyzing your vehicle data today! Contact us for expert advice and support.
Recommended for you
OBD2 DATA LOGGER: EASILY LOG & CONVERT OBD2 DATA
CANEDGE2 – PRO CAN IoT LOGGER
[