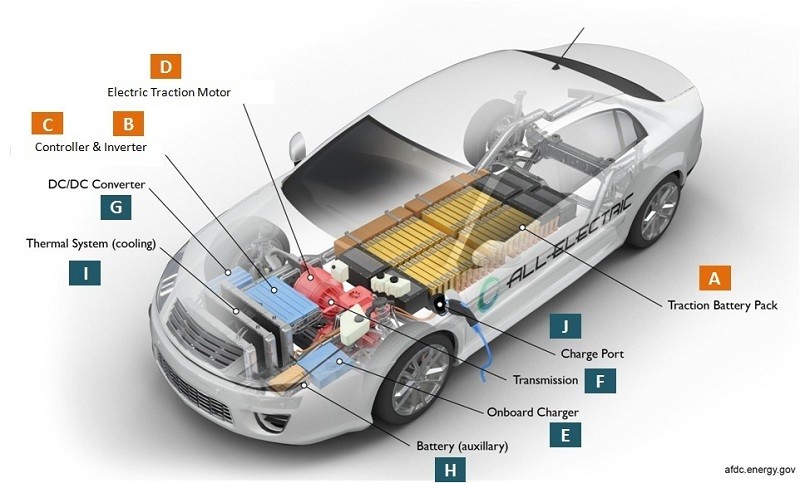
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, and understanding their components is becoming increasingly important. Just like traditional gasoline cars, EVs rely on a system of parts working together, but the components are fundamentally different. This article delves into the key Ev Car Parts and their functions, providing a comprehensive overview for anyone interested in electric vehicle technology.
Understanding How Electric Cars Operate
Before diving into specific ev car parts, it’s crucial to understand the basic operating principle of a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), the most common type of EV. When you press the accelerator pedal in an EV:
- Controller [C]: Acts as the brain, regulating the flow of electrical energy from the high-voltage battery [A] and inverter [B].
- Inverter [B]: Based on the controller’s signals, the inverter delivers a precise amount of electrical energy to the motor, dictated by the accelerator pedal input.
- Electric Motor [D]: This crucial ev car part converts electrical energy into mechanical energy in the form of rotational motion.
- Transmission: The motor’s rotation is transferred to the wheels via the transmission, propelling the vehicle forward.
Image alt text: A detailed diagram illustrating the main electric vehicle components, labeled A through J, showcasing their interconnectedness and roles within an EV system. This visual representation is useful for understanding good quality electric car components and their placement in an electric vehicle.
Key Electric Vehicle Components
Electric cars utilize a unique set of components compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. Here are the fundamental ev car parts found in most electric vehicles:
1. Traction Battery Pack [A]: The EV Energy Reservoir
The traction battery pack is arguably the most vital ev car part. It serves as the energy storage system for the electric vehicle, holding direct current (DC) electricity. Upon receiving a signal from the controller, the battery pack discharges DC energy to the inverter, which then powers the electric motor.
These battery packs are composed of numerous rechargeable battery cells, typically lithium-ion due to their high energy density and longevity. For a deeper understanding of these critical ev car parts, explore resources detailing “Electric Car Batteries and Their Characteristics.”
2. Power Inverter [B]: Converting Power for the EV Motor
Image alt text: A close-up view of an electric car power inverter, a key component for converting DC battery power to AC for the motor. This image highlights the inverter as a vital ev car part for efficient energy management in electric vehicles.
The power inverter is another essential ev car part. Its primary function is to convert the DC electricity stored in the battery pack into alternating current (AC) electricity. Electric motors in EVs typically operate on AC power. Furthermore, inverters in many EVs are bi-directional. This allows them to convert AC current generated during regenerative braking back into DC current, which is then used to recharge the traction battery, enhancing energy efficiency.
3. Controller [C]: Managing EV Power Flow
The controller acts as the central management system for electrical energy within the EV. This ev car part regulates the electrical power flowing from both the battery pack and the inverter to the electric motor. It receives input from the accelerator pedal, interpreting the driver’s desired speed and power.
Based on the pedal input, the controller adjusts the frequency or voltage supplied to the motor, thereby controlling the motor’s speed and torque output. The controller is fundamental to how an electric car operates, precisely managing the power delivery to the motor.
4. Electric Traction Motor [D]: The EV Propulsion Force
Image alt text: A detailed image of an electric traction motor, a crucial ev car part responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion for vehicle propulsion. This motor is a key element in the efficiency and performance of electric vehicles.
The electric traction motor is the driving force of an EV. This ev car part receives electrical power from the controller and converts it into mechanical energy, causing the motor to rotate. This rotation is then transmitted to the wheels, propelling the vehicle. While some hybrid EVs utilize generator-motors for both propulsion and regeneration, Battery Electric Vehicles rely solely on electric traction motors for movement. Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are commonly used in EVs due to their efficiency and reliability.
Additional Electric Car Components
Beyond the core components, several other ev car parts contribute to the overall functionality and convenience of electric vehicles:
-
Charger [E]: This ev car part facilitates battery charging. Chargers convert AC electricity from external sources (like the power grid or solar panels) into DC electricity suitable for storing in the battery pack. EVs can have:
- On-board chargers: Integrated within the vehicle.
- Off-board chargers: External charging stations.
-
Transmission [F]: Similar to traditional cars, the transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric motor to the wheels, enabling vehicle movement. However, EVs often utilize simpler single-speed transmissions due to the motor’s torque characteristics.
-
DC/DC Converter [G]: This ev car part steps down the high-voltage DC power from the traction battery to a lower voltage DC power. This lower voltage is essential for powering vehicle accessories like lights, infotainment systems, and recharging the auxiliary battery.
-
Auxiliary Battery [H]: A low-voltage battery (typically 12V) powers the car’s accessories. This battery is kept charged by the DC/DC converter and is separate from the main traction battery.
-
Thermal System – Cooling [I]: Maintaining optimal operating temperatures is crucial for ev car parts, especially the battery, motor, and power electronics. The thermal management system regulates the temperature of these components, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient operation and longevity.
-
Charge Port [J]: The charge port is the interface for connecting the vehicle to an external power source for charging the traction battery pack. It allows for both AC and DC charging, depending on the charging infrastructure and vehicle capabilities.
For a deeper dive into ev car parts and their functionalities, consider exploring training programs offered by organizations like Omazaki Group. Their training resources, available on the Omazaki Training page, provide comprehensive insights into electric vehicles and their support systems.