Have you ever wondered about the different parts that make up the exterior of your car? Just like the human body has different parts that work together, a car’s exterior is composed of various components, each with its own name and function. Understanding these parts is not only fascinating but also practical for car maintenance, repairs, and even just communicating with mechanics.
In this guide, we will explore the names of exterior car body parts, providing you with a clear diagram and detailed descriptions to enhance your automotive knowledge. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a student learning about automobiles, or simply a car owner wanting to be more informed, this article will break down the anatomy of your vehicle’s exterior.
Exploring the Main Exterior Car Body Parts
Here’s a list of the primary exterior components you’ll find on most cars:
- Body Shell
- Hood (or Bonnet)
- Front Bumper
- Rear Bumper
- Grille
- Headlights
- Fog Lights
- Indicator Lights (Turn Signals)
- Wiper Blades
- Radiator Grille
- Cowl Panel
- Quarter Panel
- Fender
- Fender Liners
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Mirrors (Side Mirrors)
- Doors
- Door Handles
- Window Glass
- Quarter Window
- Trunk (or Decklid)
- Mud Flaps
- Wheels
- Hubcaps
- Dashboard (While technically interior, it’s often discussed in body context)
- License Plate
- Taillights
Car Exterior Body Parts Diagram
To help visualize these parts, refer to the diagram below:
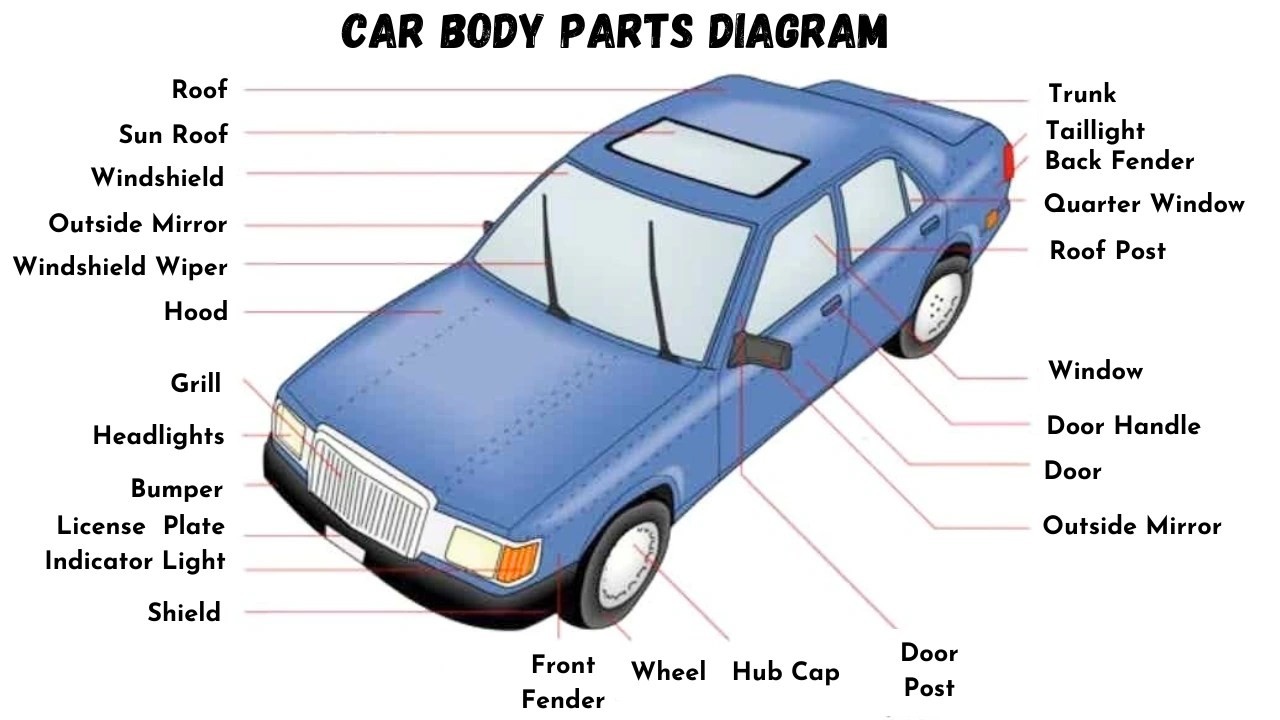 Car Body Parts Diagram
Car Body Parts Diagram
Alt text: Diagram illustrating the exterior car body parts names, including hood, bumper, headlights, grille, fender, doors, roof, trunk, taillights, wheels, and mirrors.
Detailed Look at Car Body Exterior Parts
Let’s delve deeper into each of these exterior car parts, understanding their function and importance:
#1. Body Shell
The body shell is the foundational structure of the car’s exterior. It’s essentially the main frame or skeleton upon which all other body panels and components are attached. Think of it as the underlying structure that gives the car its shape. The body shell excludes detachable parts like doors, hoods, and exterior trim. It’s crucial for the car’s structural integrity and safety.
#2. Hood / Bonnet
The hood, also known as the bonnet in some regions, is the hinged cover at the front of the car that protects the engine compartment. It provides a barrier against the elements, shielding the engine and related components from rain, snow, and debris. The hood also allows easy access to the engine for maintenance and repairs. Typically made of steel or aluminum, aftermarket hoods can also be found in materials like carbon fiber for weight reduction and styling.
#3. Front Bumper
The front bumper is a safety component designed to absorb impact in low-speed collisions, protecting the car’s body and occupants. It extends across the front of the vehicle and often wraps around the corners, partially covering the wheel arches. Bumpers are usually constructed from energy-absorbing materials like plastic or reinforced polymers, and may include internal supports for added protection.
#4. Rear Bumper
Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper provides protection to the rear of the vehicle. It helps to minimize damage in rear-end collisions and often houses the taillights and sometimes parking sensors. Rear bumpers are also designed to protect exhaust components and the trunk area.
#5. Grille
Located at the front of the car, between the headlights, the grille is primarily an aesthetic and functional component. Its main function is to allow airflow to the radiator and engine bay for cooling purposes. Grilles come in various designs and patterns, often unique to specific car brands and models. The design of the grille can significantly impact engine cooling efficiency and contribute to the car’s overall styling.
#6. Headlights
Headlights are essential for safe driving in low-light conditions or at night. They illuminate the road ahead, ensuring visibility for the driver and making the vehicle visible to other road users. Modern headlights can use halogen, LED, or xenon technology, offering different levels of brightness and efficiency.
#7. Fog Lights
Fog lights are designed to improve visibility in adverse weather conditions like fog, heavy rain, or snow. They are typically mounted lower than headlights and produce a wide, low beam to illuminate the road surface and reduce glare reflecting back at the driver in foggy conditions.
#8. Indicator Lights / Turn Signals
Indicator lights, also known as turn signals or blinkers, are crucial for communicating your intended direction to other drivers. Located at the front and rear of the car, these flashing lights signal left or right turns, lane changes, or hazards. They are vital for road safety and preventing accidents.
#9. Roof
The roof is the top panel of the car, providing structural integrity and protection from the elements for the occupants. Roofs can be made of steel, aluminum, or even glass (for panoramic roofs). The design and shape of the roof contribute to the car’s aerodynamics and overall appearance.
#10. Sunroof
A sunroof is an optional opening in the car’s roof that allows light and fresh air into the cabin. Sunroofs can be manually operated or power-operated and come in various types, including pop-up, sliding, and panoramic versions. They enhance the driving experience by providing a more open and airy feel.
#11. Doors
Doors provide access to the car’s interior for passengers and the driver. They are hinged panels that swing open and are equipped with latches and locks for security. Car doors are designed for safety, incorporating side impact beams and robust construction. They also house windows, door handles, and interior trim.
#12. Windows
Car windows are transparent panels made of glass that allow visibility and light into the cabin while protecting occupants from the elements and wind noise. The main windows include the windshield (front), side windows, and rear window. Side windows are often rollable for ventilation.
#13. Mirrors (Side Mirrors)
Side mirrors, also known as door mirrors, are essential for driver visibility to the sides and rear of the vehicle. They help drivers monitor traffic conditions and perform maneuvers safely, such as lane changes and parking. Modern side mirrors often include features like electric adjustment, heating, and integrated turn signals.
#14. Quarter Panel
The quarter panel is a body panel located between the rear door and the trunk, extending around the wheel well. It’s a significant structural panel and often incorporates styling lines of the car’s design. Damage to the quarter panel can be more complex to repair due to its structural nature.
#15. Fender
Fenders are the body panels that surround the wheel wells. Their primary function is to protect the car and other road users from debris, water, and stones thrown up by the tires. Fenders also contribute to the car’s styling and aerodynamic efficiency. Fender liners, usually made of plastic, are often fitted inside the fenders for additional protection.
#16. Trunk / Decklid
The trunk, also known as the decklid or boot in some regions, is the hinged cover that provides access to the car’s storage compartment at the rear. It’s designed to be secure and weatherproof, protecting luggage and cargo. Trunks can vary in size and configuration depending on the vehicle type.
#17. Taillights
Taillights are located at the rear of the car and serve multiple safety functions. They include brake lights (illuminated when braking), taillights (for visibility at night), and often integrated turn signals and reverse lights. Taillights are crucial for indicating the car’s presence, braking, and intended movements to following vehicles.
#18. Mud Flaps / Splash Guards
Mud flaps, also called splash guards or mudguards, are fitted behind the wheels, especially the rear wheels. They help to minimize the spray of water, mud, and road debris kicked up by the tires, protecting the car’s undercarriage and other vehicles behind from stone chips and dirt.
#19. Wheels
Wheels are fundamental components that allow the car to move. They are typically made of steel or aluminum alloy and are fitted with tires. The design and size of wheels can significantly affect the car’s handling, ride comfort, and aesthetics.
#20. Hubcaps / Wheel Covers
Hubcaps or wheel covers are decorative discs that cover the center portion of the wheel. They are primarily for aesthetic purposes, enhancing the appearance of the wheels and concealing less attractive steel wheels. They can be made of plastic or metal and come in various designs.
#21. Wiper Blades
Wiper blades are essential for maintaining clear visibility through the windshield in rain, snow, or when the windshield is dirty. They are made of rubber and are attached to wiper arms that sweep across the windshield, removing water and debris.
#22. License Plate
The license plate, or number plate, is a mandatory identification tag attached to the front and rear of the vehicle. It displays the car’s unique registration number, which is used for vehicle identification and legal purposes.
#23. Cowl Panel
The cowl panel is the area at the base of the windshield, often housing the windshield wipers and vents for the car’s ventilation system. It bridges the gap between the hood and the windshield and can also contain the car’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
#24. Door Handles
Door handles are the mechanisms used to open and close the car doors. They can be exterior handles for outside access and interior handles for opening the door from inside. Door handle designs vary widely, from traditional levers to more modern flush or hidden designs.
#25. Fender Liners / Wheel Well Liners
Fender liners, also known as wheel well liners, are protective inner panels fitted inside the fenders. They are typically made of plastic and provide an additional barrier against water, salt, and debris, preventing corrosion and damage to the fender and surrounding areas.
Conclusion
Understanding the names and functions of exterior car body parts is beneficial for any car owner. It empowers you to better understand your vehicle, communicate effectively with mechanics, and appreciate the engineering and design that goes into making a car. By familiarizing yourself with these components using this guide and diagram, you’re taking a step towards becoming a more informed and engaged car enthusiast or owner.
