Disclaimer: I am not an expert or a professional, just an enthusiast who successfully followed these steps. This guide is for informational purposes only, and you proceed at your own risk. I am not responsible for any damage, malfunction, or unforeseen consequences that may arise from following these instructions, including but not limited to equipment failure, ECU damage, or any other issues. By attempting this DIY project, you acknowledge and accept full responsibility for any outcomes.
Tools You’ll Need:
- Wire strippers/cutters
- Needle-nose pliers
- Molex crimping tool (optional, but recommended for professional crimping)
- Soldering iron (recommended for a more secure connection, but optional)
Parts List:
- 4-Pin Connector (Link to Part; Pin/Wire Size = 22-16AWG; Insulation/Seal Size = 1.3-1.7mm)
- OBD-II Cable (Link to Part)
Note: If you have spare wires available, you can purchase just the female OBD-II connector and use your own wires to connect the OBD-II and 4-pin connectors. Ensure your wire size is compatible with the 4-pin connector specifications.
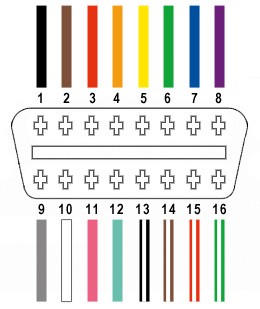
From the 16 wires in the OBD-II connector (referred to as OBD2C), we will only be using four essential wires:
- Pin 4 (Chassis Ground; Orange wire on OBD2C)
- Pin 6 (CAN [J-2234] High; Green wire on OBD2C)
- Pin 14 (CAN [J-2234] Low; Brown wire with white stripe on OBD2C)
- Pin 16 (Battery Power; Green wire with white stripe on OBD2C)
Step 1: Preparing the OBD-II Cable Wires
Based on recommendations for minimizing interference, it’s advisable to twist pairs of wires. To prepare the OBD2C, carefully remove the outer sheath and shielding from the cable. Isolate the four wires we’ll be using from the rest. Secure the remaining 12 wires by zip-tying them together to keep them out of the working area.
Step 2: Preparing Wires for the 4-Pin Connector
The wires in the OBD2C are 26AWG, which is slightly smaller than the 22AWG size intended for the 4-pin connector (referred to as 4PC) pins. To compensate for this difference and ensure a secure connection, we need to thicken the wire ends. The OBD2C wires come pre-stripped with about 1/8″ of exposed wire. Strip an additional 1/4″ of insulation to have about 3/8″ of exposed wire. Fold the exposed wire over itself and twist it to effectively double its thickness, making it more suitable for the 4PC pins. Slide a rubber seal from the 4PC kit onto each of the four wires.
Step 3: Attaching Wires to 4-Pin Connector Pins
The pins for the 4PC have two sets of prongs. The front set is designed to crimp onto the exposed wire, and the rear set is for crimping onto the wire seal. Insert the exposed, thickened wire into the front part of the pin, ensuring it aligns with the front prongs. The image below highlights the size difference between the thin wire and the connector pin. Using needle-nose pliers can be helpful to hold the wire in place for the next step.
Step 4: Soldering the Wires to the Connector Pins (Recommended)
Soldering provides a robust and reliable connection, which is particularly beneficial given the small gauge of the OBD2C wires. While crimping is an option, soldering ensures better conductivity and mechanical strength, especially when working with thinner wires. If you are new to soldering, numerous online resources, such as this helpful YouTube video, offer valuable tips and techniques. Solder the wire to the pin connector, aiming for a solid joint.
Step 5: Crimping the Connector Pins (Alternative Method)
If you have a Molex crimping tool, use it to crimp the front prongs of the connector pin securely around the wire. If you don’t have this specialized tool, needle-nose pliers can be used as an alternative. Carefully and gradually fold one prong at a time over the wire using the pliers, working at an angle to ensure a tight crimp. This YouTube video on crimping techniques can be a helpful guide if you are unfamiliar with this process. For added security, you can further compress the crimped prongs with pliers, though this might be considered overkill.
Step 6: Crimping the Seal Prongs
Slide the rubber seal up the wire until it sits between the rear prongs of the connector pin. Use the same crimping technique as in the previous step to fold these prongs over the rubber seal. This secures the seal and provides strain relief for the wire.
Step 7: Wire Pairing and Twisting
It is recommended to twist specific wire pairs together to minimize electromagnetic interference and improve signal integrity, although the exact reason may not be definitively known. Pair and twist the wires as follows:
- Pin 4 (Orange) & Pin 16 (Green with white stripe)
- Pin 6 (Green) & Pin 14 (Brown with white stripe)
Step 8: Inserting Pins into the 4-Pin Connector Housing
Insert the completed pins into the 4PC housing in the correct orientation as shown below:
- Pin 14 (Brown w/white stripe) > Connector Slot A
- Pin 6 (Green) > Connector Slot B
- Pin 16 (Green w/white stripe) > Connector Slot C
- Pin 4 (Orange) > Connector Slot D
Push each pin into the rear of the connector housing until you hear a click, indicating it is locked securely in place. Using needle-nose pliers to gently pull the wire from the rear can help ensure the pin is fully seated and locked.
Congratulations! Your homemade OBD2 to USB cable is now complete.
This DIY OBD2 to USB cable has been successfully tested to diagnose and clear car error codes.
If any step is unclear or requires further explanation, please ask, and I will do my best to clarify or provide additional photos.