When it comes to car repairs or upgrades, knowing the exact part number is crucial. Imagine ordering a new component, waiting for its arrival, only to find out it’s the wrong fit for your vehicle. This not only wastes time but also money. Finding the correct car part number ensures compatibility, saves you from unnecessary hassles, and helps you get your car back in top shape efficiently. Whether you’re dealing with routine maintenance or a more complex repair, understanding how to locate this number is a valuable skill for any car owner.
Why Finding the Right Part Number Matters?
Identifying the correct part number for your car is more than just a matter of convenience; it’s about ensuring accuracy and compatibility. Using the wrong part can lead to a host of problems, from poor performance and potential damage to safety hazards. Here’s why getting it right is so important:
- Guaranteed Fit: The part number acts as a unique identifier, ensuring that the component you purchase is specifically designed for your car’s make, model, and year. This precision fit is critical for proper function and safety.
- Avoid Compatibility Issues: Cars are complex machines with numerous variations even within the same model line. A seemingly similar part from a different year or trim level might not be compatible, leading to installation difficulties or functional failures.
- Save Time and Money: Ordering the wrong part leads to delays, return hassles, and potentially additional shipping costs. By finding the right part number upfront, you streamline the repair process and avoid these unnecessary expenses.
- Access the Right Information: Part numbers often unlock access to detailed information about the component, such as specifications, diagrams, and installation guides, which can be invaluable for DIY repairs or when communicating with mechanics.
- Maintain Vehicle Value: Using correct, high-quality parts, especially Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts, helps maintain your vehicle’s performance, reliability, and ultimately, its resale value.
Understanding OEM, Genuine, and Aftermarket Parts
Before diving into how to find a part number, it’s helpful to understand the different categories of car parts available:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Parts: These parts are made by the same manufacturers who supplied components for your car when it was originally built. OEM parts are produced to the exact specifications and standards of the original car manufacturer. They guarantee quality and fit, often coming with a warranty. While sometimes branded with the car manufacturer’s logo, they can also be sold without it if produced by an approved external company.
-
Genuine Parts: Genuine parts are essentially OEM parts but always branded with the car manufacturer’s logo. These are the exact same parts that were used when your car rolled off the assembly line. They are typically sold through car dealerships and are guaranteed to be of the highest quality and fit.
-
Aftermarket Parts: These parts are manufactured by third-party companies, not directly affiliated with the original car manufacturer. Aftermarket parts can vary significantly in quality and price. Some aftermarket parts are designed to be direct replacements and can offer good value, while others may be of lower quality. However, the aftermarket also offers performance upgrades and specialized components not available as OEM.
Knowing these distinctions can influence your choice once you find your part number, especially when balancing cost and quality.
Methods to Find Your Car Part Number
Locating the part number can sometimes feel like a treasure hunt, but there are several reliable methods to uncover this crucial piece of information.
Method 1: Check the Part Itself
The most direct method is to examine the car part you need to replace. Most car components, especially OEM parts, will have the part number directly printed or engraved on them.
- Locate the Part: First, safely access and locate the car part in question. This might require opening the hood, accessing the undercarriage, or removing interior panels depending on the part.
- Examine for Markings: Carefully inspect the part’s surface. Look for any stickers, labels, or engravings. Often, the part number will be accompanied by a quality control sticker or plate.
- Identify Alphanumeric Codes: OEM part numbers are typically alphanumeric codes, meaning they contain both letters and numbers. They may also include dashes or hyphens. Be patient and look closely; the number might be small or subtly placed.
- Clean if Necessary: If the part is dirty or greasy, gently clean the area where you suspect the number might be located to improve visibility.
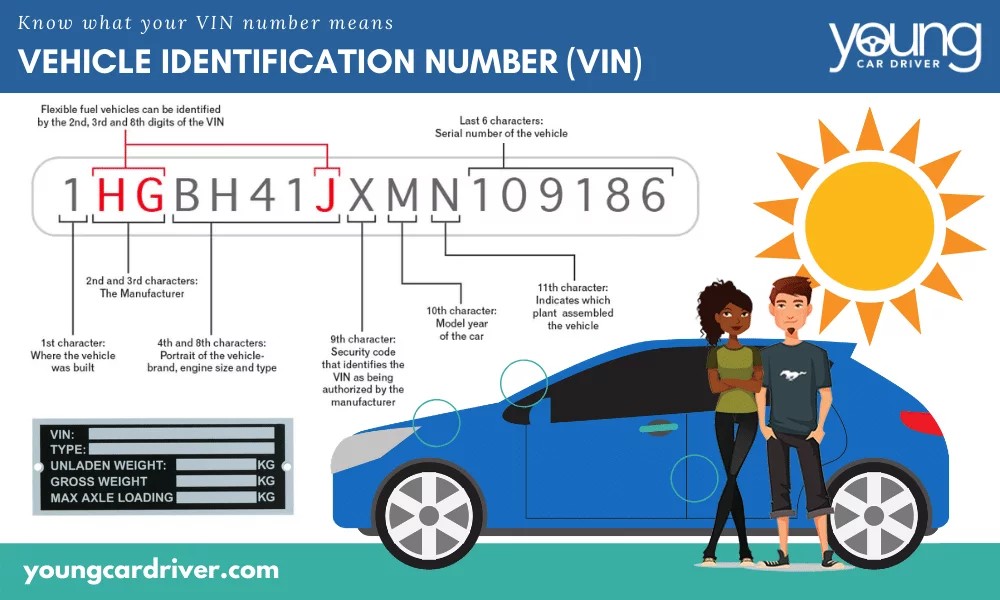
Note: While the image above is used in the original article and is related to VIN, for the purpose of illustrating “markings on a part”, imagine a similar close-up image showing a part with an OEM number.
Method 2: Contact the Original Manufacturer or Dealership
If the part number on the component is illegible due to damage or wear, or if you don’t have the old part to examine, contacting the car manufacturer or a dealership is a reliable alternative.
- Gather Vehicle Information: Before contacting them, collect essential information about your car. This includes:
- VIN (Vehicle Identification Number): This unique 17-digit code is crucial for accurate part identification. (More on VIN in Method 3).
- Make, Model, and Year of your car: This basic information helps narrow down the search.
- Specific Part Needed: Be as specific as possible about the part you are looking for (e.g., “front left brake caliper,” “windshield wiper motor”).
- Contact a Local Dealership or Manufacturer’s Customer Service: You can find contact information for your car’s manufacturer online or through your owner’s manual. Dealerships are also excellent resources.
- Provide Vehicle and Part Information: Explain that you need to find the OEM part number for a specific component and provide them with the vehicle details and part description you gathered.
- Request the Part Number: The dealership or manufacturer’s representative should be able to use your VIN and part description to locate the correct OEM part number for your vehicle.
Method 3: Utilize Your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number)
Your VIN is like your car’s unique fingerprint. This 17-digit alphanumeric code contains a wealth of information about your vehicle, including its manufacturing details and specific options. It’s an invaluable tool for finding compatible parts.
-
Locate Your VIN: The VIN is typically found in several locations:
- Dashboard: Look at the bottom corner of your windshield on the driver’s side. The VIN is usually visible from outside the car.
- Driver’s Side Doorjamb: Open the driver’s side door and check the doorjamb area. There’s often a sticker containing the VIN.
- Vehicle Registration and Insurance Documents: Your VIN is printed on your car’s registration documents and insurance cards.
- Owner’s Manual: The VIN might also be listed in your car’s owner’s manual.
-
Use Online VIN Decoders or Parts Websites: Many online resources can use your VIN to identify parts compatible with your car.
- OEM Parts Websites: Websites of dealerships or OEM parts suppliers often have VIN lookup tools. Enter your VIN, and you can browse parts specifically for your vehicle.
- Aftermarket Parts Websites: Reputable aftermarket parts websites also use VIN lookup to ensure compatibility, although focus on OEM part searches for part numbers initially.
- VIN Decoder Websites: General VIN decoder websites can provide detailed information about your car’s specifications, which can be helpful when searching for parts.
-
Consult with Parts Dealers: When contacting auto parts stores, either online or local, provide your VIN. Parts professionals can use the VIN to accurately identify the correct part numbers for your car, ensuring you get the right component.
Decoding OEM Part Numbers: A Non-Standard System
It’s important to note that there isn’t a universal, standardized format for OEM part numbers across all car manufacturers. Each manufacturer has its own system, which can seem confusing at first glance.
- Varied Formats: OEM part numbers can be entirely numeric, alphanumeric, or combinations with dashes and other characters.
- Manufacturer-Specific Logic: The structure and logic behind these numbers are usually specific to each car manufacturer. They might encode information about the part type, manufacturing location, or even specific vehicle models.
- Examples of Different Formats:
- Volvo: Often uses straightforward numeric part numbers (e.g., 30640811).
- Mazda: Employs alphanumeric codes with dashes, sometimes divided into multiple sections (e.g., KD33-43-55 YD).
Due to this lack of uniformity, it’s less about “decoding” the number yourself and more about accurately finding and using the complete part number in your searches or when communicating with parts suppliers. Online OEM parts catalogs and dealership systems are designed to understand these varied formats.
OEM vs. Aftermarket: Making the Right Choice After Finding Your Part Number
Once you’ve successfully found the OEM part number, you have a crucial piece of information. Now you need to decide whether to go with an OEM or aftermarket part. Both have their advantages and disadvantages:
-
OEM Parts – Pros:
- Guaranteed Fit and Quality: Designed to original specifications, ensuring perfect fit and reliability.
- Warranty Coverage: Often covered by the car’s warranty, providing peace of mind.
- Maintain Vehicle Value: Helps preserve your car’s original quality and resale value.
-
OEM Parts – Cons:
- Higher Cost: Typically more expensive than aftermarket alternatives.
-
Aftermarket Parts – Pros:
- Lower Price: Generally more affordable, offering potential cost savings.
- Wider Availability: Easily accessible from various retailers and online sources.
- Performance Upgrades: Some aftermarket parts offer enhanced performance or features compared to OEM.
-
Aftermarket Parts – Cons:
- Variable Quality: Quality can vary significantly between brands; research is crucial.
- Potential Fit Issues: While many are designed to fit, perfect fit isn’t always guaranteed.
- Warranty Concerns: Using aftermarket parts might sometimes affect your car’s warranty (check your warranty terms).
Making an Informed Decision:
Consider these factors when deciding between OEM and aftermarket parts:
- Type of Part: For critical components like brakes or engine parts, OEM might be preferable for guaranteed quality and safety. For less critical parts, high-quality aftermarket options can be suitable.
- Budget: Aftermarket parts can offer significant savings, but balance cost with quality and reliability.
- Vehicle Age and Value: For older vehicles, aftermarket parts can be a cost-effective solution. For newer cars or those you plan to resell, OEM parts might be a better investment.
- Warranty: Consider the warranty implications, especially for newer vehicles.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Car Repairs with Part Number Knowledge
Finding the correct part number for your car component is a fundamental step in ensuring successful repairs and maintenance. By using the methods outlined – checking the part itself, contacting manufacturers, and leveraging your VIN – you can confidently identify the precise part you need. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions when purchasing replacement parts, whether you choose OEM for guaranteed quality or explore reliable aftermarket options. Armed with the right part number, you can streamline your car repair journey, save time and money, and keep your vehicle running smoothly for years to come.