Just like the exterior of your vehicle makes the first impression, the interior of car parts is where you, the driver and passengers, spend all your time. Understanding the names and functions of these interior car parts names is not only fascinating for car enthusiasts but also incredibly practical. Whether you’re planning an upgrade, diagnosing a problem, or simply want to be more informed about your vehicle, knowing your way around the cabin is key.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of interior car parts names. We will explore each component in detail, explaining its role and how it contributes to your driving experience. From the essential controls to comfort and safety features, get ready to become an expert on your car’s inner workings. Understanding these interior car parts names empowers you to make informed decisions about maintenance, customization, and even your next car purchase.
Essential Interior Car Parts: Names and Functions
Here’s a breakdown of the key interior car parts names you’ll find in most vehicles:
- Steering Wheel and Horn
- Ignition System
- Pedals (Accelerator, Brake, Clutch)
- Gear Shifter/Selector
- Dashboard
- Hazard Lights Button
- Seat Belts
- Airbags
- Rearview Mirrors (Interior)
- Parking Brake
- Turn Signal Lever
- Center Console
- Glove Compartment
- Power Window and Door Lock Controls
- Interior Door Handles
- Audio System
- Central Control Screen (Infotainment)
- Sun Visors
- Car Seats
- Floor Mats
- Roof and Headliner
Let’s explore each of these interior car parts names in detail:
#1. Steering Wheel and Car Horn: Command and Control
The steering wheel is arguably the most fundamental control inside your car. Its primary function is to control the direction of the vehicle by translating the driver’s input into the movement of the front wheels. This is achieved through a complex steering system, which may include mechanical linkages, hydraulic assistance (power steering), or even electric power steering (EPS) in modern vehicles.
Beyond direction, modern steering wheels often integrate a host of secondary controls. You might find buttons for:
- Cruise control: Maintaining a set speed.
- Audio system controls: Adjusting volume, changing tracks, or muting audio.
- Bluetooth connectivity: Answering phone calls or activating voice commands.
- Paddle shifters: In some automatic vehicles, allowing manual gear changes.
- Heated steering wheel: For added comfort in cold climates.
The car horn, a crucial safety feature, is typically activated by pressing the center of the steering wheel. It serves as an audible warning signal to alert other road users of your presence or potential hazards.
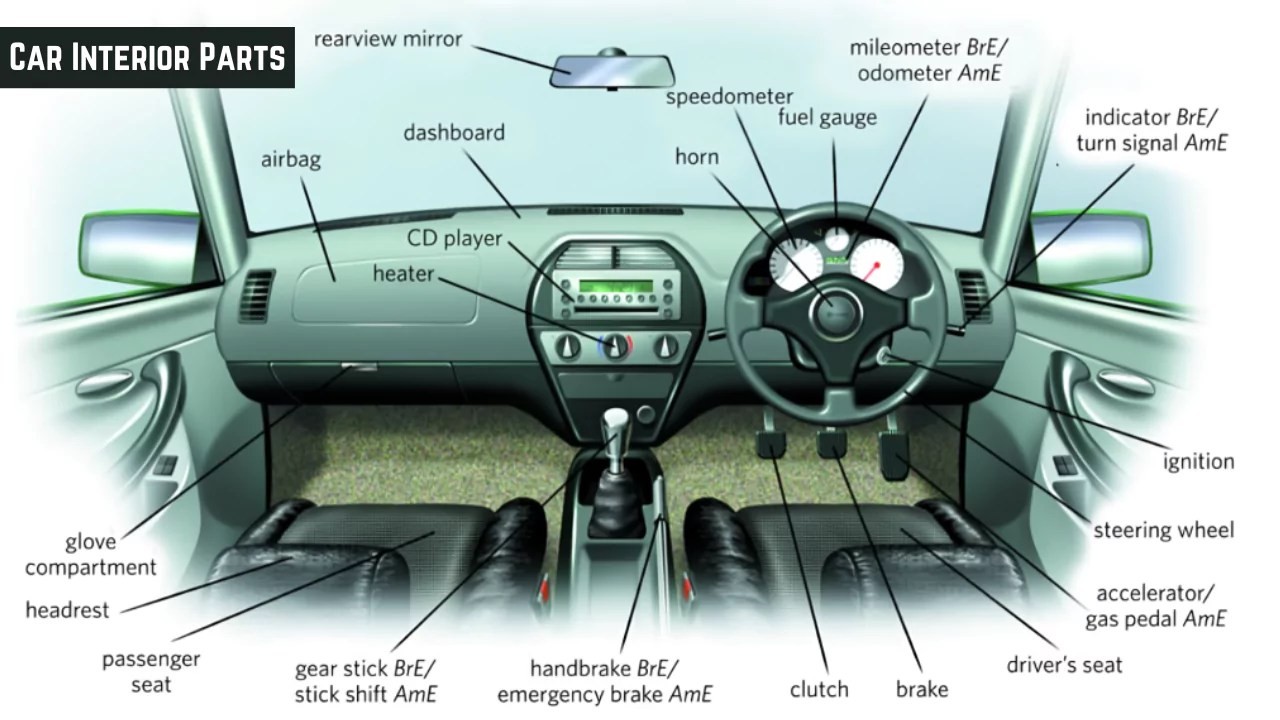 interior car parts names with diagram
interior car parts names with diagram
#2. Ignition System: Starting Your Engine
The ignition system is where your journey begins. This is the mechanism that initiates the engine’s operation. Traditionally, this was a physical ignition switch where you insert and turn your car key. Modern vehicles are increasingly using keyless ignition systems, often referred to as “push-button start”.
In both types, the ignition system activates the necessary electrical circuits to:
- Engage the starter motor, which cranks the engine.
- Supply power to the spark plugs (in gasoline engines) or glow plugs (in diesel engines) for combustion.
- Activate the fuel delivery system.
- Power up the vehicle’s electrical systems.
#3. Pedals: Acceleration, Braking, and Clutch Control
Located in the driver’s footwell, the pedals are your primary controls for speed and stopping. In most cars, you’ll find two or three pedals:
- Accelerator pedal (Gas pedal): Usually the rightmost pedal, it controls the amount of fuel delivered to the engine, thereby regulating the vehicle’s speed. Pressing down increases speed, releasing it decreases speed.
- Brake pedal: Typically located to the left of the accelerator, the brake pedal activates the braking system to slow down or stop the vehicle. Modern cars use hydraulic brake systems for efficient and powerful stopping force.
- Clutch pedal (Manual transmissions only): Found to the left of the brake pedal in vehicles with manual transmissions. The clutch pedal disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing the driver to change gears using the gear shifter. Automatic cars do not have a clutch pedal.
#4. Gear Shifter/Selector: Managing Gear Ratios
The gear shifter (manual transmissions) or gear selector (automatic transmissions) allows the driver to choose the appropriate gear for driving conditions.
- Manual Gear Shifter: A lever located between the front seats, used in conjunction with the clutch pedal to manually select gears. The shift pattern is usually indicated on the shift knob.
- Automatic Gear Selector: Also typically located between the front seats or sometimes on the steering column, it allows the driver to select driving modes like “Park” (P), “Reverse” (R), “Neutral” (N), and “Drive” (D), and sometimes manual shift modes (“M” or numbered gears). The gear selector manages gear changes automatically based on speed and engine load.
#5. Dashboard: The Information Hub
The dashboard is the panel located directly in front of the driver, housing critical information and controls. It’s the central information hub of your car, displaying vital data about the vehicle’s operation. Key components of the dashboard include:
- Instrument Cluster: This is the main display area, usually containing:
- Speedometer: Indicates the vehicle’s current speed.
- Tachometer: Shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM), crucial for gear shifting in manual cars and monitoring engine health.
- Fuel Gauge: Displays the amount of fuel remaining in the tank.
- Temperature Gauge: Indicates the engine coolant temperature, warning of potential overheating.
- Warning Lights and Indicator Lights: A system of illuminated symbols that alert the driver to various vehicle conditions, from low fuel and oil pressure to engine problems and engaged safety systems like ABS or traction control.
- Center Stack: The central portion of the dashboard, often housing:
- Infotainment System Screen: For navigation, audio, vehicle settings, and more.
- Climate Controls: Knobs or buttons to adjust heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC).
- Air Vents: Direct airflow from the HVAC system.
#6. Hazard Lights Button: Signaling Emergencies
The hazard lights button (emergency flashers) is typically a red, triangular button located on the dashboard, often prominently placed for easy access. When activated, it causes all four turn signal lights to flash simultaneously, warning other drivers of a hazard, breakdown, or emergency situation. It’s essential to use hazard lights when your vehicle is stopped in a potentially dangerous location or when you need to alert others to a problem.
#7. Seat Belts: Primary Safety Restraint
Seat belts are fundamental safety devices designed to restrain occupants in the event of a collision, significantly reducing the risk of serious injury or ejection from the vehicle. They work by:
- Securing the occupant against forward movement during sudden stops or impacts.
- Distributing crash forces across stronger parts of the body, like the chest and pelvis.
- Preventing occupants from colliding with the vehicle’s interior or other passengers.
It is crucial to wear seat belts correctly on every journey, for both the driver and all passengers, regardless of seating position or trip length.
#8. Airbags: Supplemental Restraint System
Airbags are supplemental restraint systems (SRS) that work in conjunction with seat belts to provide additional protection in collisions. Sensors detect sudden deceleration indicative of a crash, triggering the rapid inflation of airbags. These inflatable cushions:
- Provide a cushioning barrier between occupants and hard interior surfaces like the steering wheel, dashboard, and windshield.
- Help to prevent head and chest injuries in frontal and side impacts.
- Work most effectively when used in combination with seat belts.
Airbags are designed for single-use deployment and must be replaced by qualified technicians after activation.
#9. Rearview Mirrors: Seeing What’s Behind
Rearview mirrors are essential for driver awareness, providing visibility of the road and traffic behind the vehicle. Vehicles are typically equipped with:
- Interior Rearview Mirror: Mounted centrally at the top of the windshield, offering a direct view to the rear. Many modern interior rearview mirrors are auto-dimming to reduce glare from headlights at night.
- Exterior Side Mirrors (Driver and Passenger Side): Located on the doors, providing wider views of the sides and rear of the vehicle, crucial for lane changes and maneuvering. These can be manually or electrically adjustable and may include features like heating (for defrosting) and blind-spot monitoring indicators.
#10. Parking Brake: Securing Your Parked Car
The parking brake (emergency brake) is a secondary braking system designed to hold the vehicle stationary when parked, especially on inclines. It operates independently of the primary hydraulic brake system. Parking brakes can be:
- Hand-lever operated: A lever typically located in the center console.
- Foot-pedal operated: A pedal located to the left of the brake pedal.
- Electronically operated: Activated by a button or switch, often engaging automatically when the vehicle is put into “Park.”
It’s recommended to engage the parking brake every time you park, regardless of the terrain. In emergencies where the primary brakes fail, the parking brake can be used cautiously to help slow down and stop the vehicle.
#11. Turn Signal Lever: Indicating Directional Changes
The turn signal lever (indicator stalk) is usually located on the left side of the steering column. Moving it up or down activates the turn signals (indicator lights) on the corresponding side of the vehicle (right or left). These lights are crucial for communicating your intention to turn or change lanes to other road users, promoting safe and predictable driving. Many modern cars also feature a “lane change assist” function where a gentle push of the lever will trigger a few flashes of the turn signal for lane changes.
#12. Center Console: Storage and Controls in Reach
The center console is the area between the front seats, often extending from the dashboard to the rear of the front seating area. It serves as a central hub for storage, controls, and features, and typically includes:
- Storage Compartment: A covered bin for storing personal items.
- Cupholders: Recesses designed to hold drinks securely.
- Gear Selector/Shifter Location: In many vehicles.
- Parking Brake Lever/Switch Location: In some vehicles.
- Auxiliary Power Outlets (12V, USB): For charging devices.
- Infotainment System Controls: Sometimes integrated into the console.
- Armrest: For driver and passenger comfort.
#13. Glove Compartment: Convenient Storage
The glove compartment (glove box) is a small, enclosed storage compartment typically located in the dashboard on the passenger side. It’s designed for storing vehicle documents, like the owner’s manual and insurance paperwork, as well as other small personal items.
#14. Power Window and Door Lock Controls: Electronic Convenience
Power window controls and power door lock controls allow for convenient operation of the vehicle’s windows and door locks at the touch of a button. These controls are usually located on the door panels, within easy reach of the occupants. The driver’s side often has master controls for all windows and door locks, while passenger doors may have individual controls for their respective windows.
#15. Interior Door Handles: Opening from the Inside
Interior door handles are used to open the car doors from the inside. They disengage the door latch mechanism, allowing the door to be pushed open. Modern interior door handles are designed for ease of use and safety, often incorporating child safety locks to prevent rear doors from being opened from the inside.
#16. Audio System: Entertainment on the Go
The audio system (car stereo, sound system) provides entertainment and information through audio playback. Components typically include:
- Head Unit: The central control unit, often integrated with the infotainment system screen, providing source selection (radio, CD, Bluetooth, USB), volume control, and sometimes navigation and other features.
- Speakers: Located throughout the cabin to reproduce sound. The number and quality of speakers vary greatly depending on the vehicle and audio system.
- Amplifier (Optional): Used in higher-end systems to boost audio signal power for louder and clearer sound.
#17. Central Control Screen (Infotainment): Integrated Vehicle Interface
The central control screen (infotainment system, multimedia display) is a prominent feature in modern car interiors, acting as a central interface for various vehicle functions. It integrates:
- Navigation: GPS-based directions.
- Audio Entertainment: Radio, streaming services, smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto).
- Climate Control Interface: Digital controls for HVAC.
- Vehicle Settings: Customization of vehicle features and driver profiles.
- Backup Camera Display: Video feed from the rear of the vehicle when reversing.
- Connectivity Features: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi hotspot.
Infotainment systems are increasingly sophisticated, offering touchscreen interfaces, voice control, and integration with smartphone apps and services.
#18. Sun Visors: Blocking Glare
Sun visors are hinged flaps located above the windshield, on the interior roof lining. They can be flipped down to block glare from the sun, improving driver visibility and comfort. Some sun visors also include vanity mirrors and lights.
#19. Car Seats: Comfort and Support
Car seats provide comfortable and supportive seating for the driver and passengers. They are designed with:
- Frames: Providing structural support, typically made of metal.
- Padding: Cushioning for comfort, often made of foam and fabric or leather upholstery.
- Adjustability: Many seats offer adjustments for seat position (forward/backward), seat height, seatback angle, and lumbar support to personalize comfort.
- Headrests: Providing whiplash protection.
Seat covers are a popular accessory to protect seats from wear and tear, spills, and sun damage, and to enhance interior aesthetics.
#20. Floor Mats: Protecting the Floor
Floor mats are removable coverings placed on the vehicle’s floor to protect the carpet from dirt, mud, water, and wear. They are typically made of rubber, carpet, or all-weather materials and are designed to be easily removed for cleaning. Floor mats help maintain the cleanliness and resale value of the vehicle’s interior.
#21. Roof and Headliner: Cabin Enclosure and Insulation
The roof provides structural integrity to the vehicle and protection from the elements. The headliner is the fabric or material covering the interior of the roof. Together, they contribute to:
- Structural Support: The roof provides rigidity and rollover protection.
- Weather Protection: Shielding the cabin from rain, snow, and sun.
- Insulation: The headliner and roof structure provide thermal and acoustic insulation, reducing heat transfer and noise levels inside the cabin.
- Interior Aesthetics: The headliner contributes to the overall look and feel of the car’s interior.
FAQs about Interior Car Parts Names
What are common interior car parts names?
The most common interior car parts names include: steering wheel, dashboard, seats, pedals, gear shifter, and door handles. This guide has covered many more!
What is the panel inside the car door called?
The panel on the inside of the car door is called the door panel or interior door trim. It covers the door structure and houses controls like power window switches and door lock buttons.
What is the ceiling inside a car called?
The ceiling inside a car is called the headliner. It provides insulation, sound absorption, and a finished look to the vehicle’s interior roof.
What is the dashboard for in a car?
The dashboard is the central information and control panel in a car. It houses the instrument cluster (speedometer, tachometer, etc.), warning lights, infotainment system, and climate controls.
What materials are used for car interiors?
Modern car interiors use a variety of materials, including:
- Plastics and Polymers: For dashboards, door panels, trim, and some structural components – lightweight and durable.
- Fabrics (Nylon, Polyester): For seat upholstery and headliners – cost-effective and versatile.
- Vinyl: For seat upholstery and trim – durable and water-resistant.
- Leather: For premium seat upholstery and trim – luxurious and durable.
- Metal and Aluminum: For structural components, trim accents, and some control surfaces.
- Wood Trim: For decorative accents in luxury vehicles.
Understanding the Interior Of Car Parts Names is more than just automotive trivia; it’s about gaining a deeper connection with your vehicle and becoming a more informed driver and car owner. This knowledge empowers you to communicate effectively with mechanics, make smart upgrade choices, and appreciate the engineering and design that goes into your daily drive.