Just as the exterior of a car speaks to its style and aerodynamics, the interior is where comfort, functionality, and technology converge for the driver and passengers. After exploring the exterior parts of a car in our previous article, we now turn our attention inwards. In this guide, we’ll delve into the essential interior parts of a car, highlighting their names, functions, and significance for a superior driving experience.
Understanding the interior components of your vehicle is more than just automotive knowledge; it’s about informed decision-making. Whether you’re considering buying a new car, upgrading specific elements, or simply want to be more familiar with your current vehicle, this knowledge is invaluable. From enhancing safety features to personalizing comfort, the interior parts play a crucial role in your daily drives.
Many car owners look to personalize and upgrade their car interiors. Popular upgrades range from custom LED lighting and durable seat covers to advanced gauges and infotainment systems. These modifications not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve the overall driving experience. Let’s explore the names and functions of these crucial interior elements.
Essential Interior Car Parts: Names and Functions
Here’s a comprehensive list of the primary interior parts you’ll find within a car:
- Steering Wheel and Horn
- Ignition System
- Pedals (Accelerator, Brake, Clutch)
- Gear Shifter/Selector
- Dashboard and Instrument Cluster
- Hazard Lights/Emergency Flashers
- Seat Belts
- Airbags
- Rearview Mirrors (Interior and Exterior)
- Parking Brake/Emergency Brake
- Turn Signal Lever/Indicator Stalk
- Center Console
- Glove Compartment/Glove Box
- Power Window and Door Lock Controls
- Interior Door Handles
- Audio System/Car Speakers
- Central Control Screen/Infotainment System
- Sun Visors
- Car Seats
- Floor Mats
- Roof and Headliner
Interior Car Parts Diagram
To visualize these components, refer to the Interior Parts Of A Car Diagram below for a clear understanding of their placement within the vehicle.
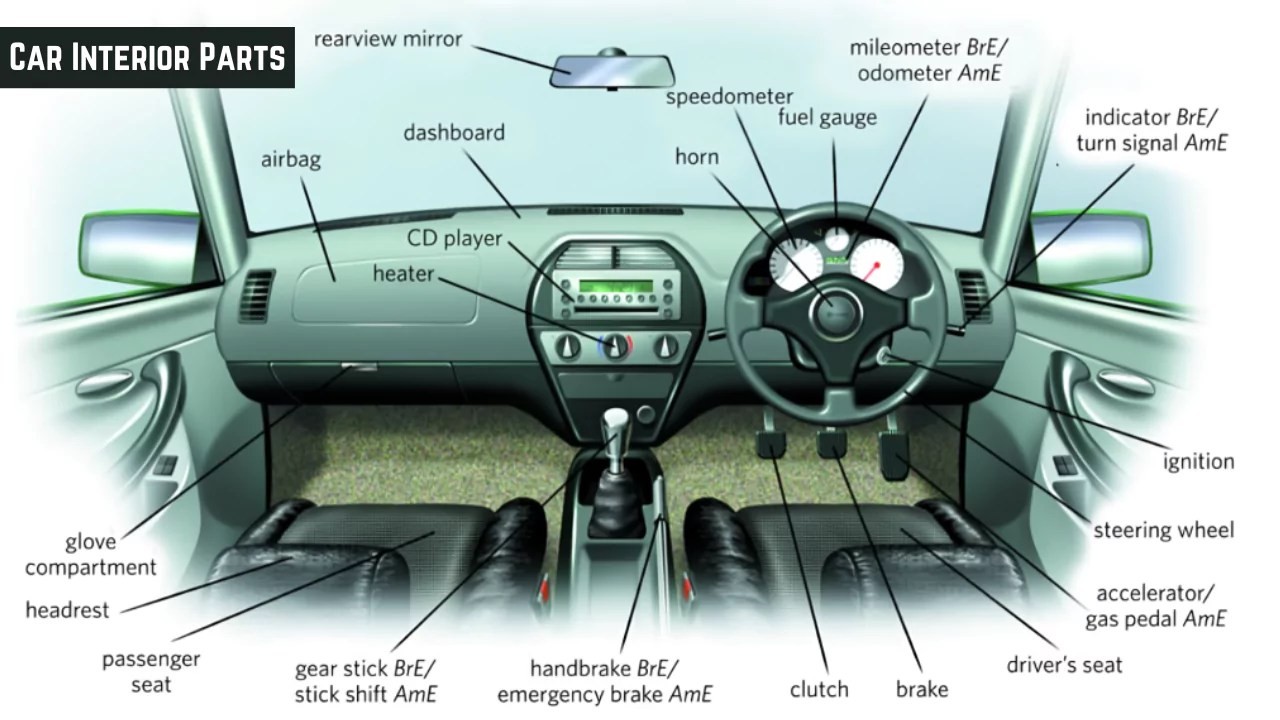 Diagram illustrating interior car parts names
Diagram illustrating interior car parts names
Detailed Look at Car Interior Parts
Let’s explore each of these interior car parts in detail:
#1. Steering Wheel and Car Horn
The steering wheel is arguably the most fundamental control in a vehicle. It translates the driver’s rotational input into directional changes via the car’s front wheels. This system involves a complex interplay of joints and hydraulic lines, ensuring precise handling and maneuverability.
Modern steering wheels have evolved beyond basic steering control. Many now integrate features like cruise control, audio system management, and even heating elements for added comfort in colder climates. Custom steering wheel covers are a popular aftermarket upgrade, offering enhanced aesthetics and a more comfortable grip through various materials like leather and unique designs.
The car horn, a critical safety component, is typically activated by pressing the center of the steering wheel. It serves as an audible warning signal to alert other road users of your presence or potential hazards, playing a vital role in preventing accidents.
#2. Ignition System
The ignition system is the gateway to starting your car. Usually located on the steering column or dashboard, it’s where you insert your key or press a start button to bring the engine to life.
Turning the ignition key or pressing the start button activates the ignition switch, which in turn provides power to the entire ignition system and subsequently, the engine. This initial electrical surge is essential to initiate the combustion process and get your vehicle moving.
#3. Pedals: Accelerator, Brake, and Clutch
Looking down at the driver’s footwell, you’ll typically find two or three pedals. In automatic vehicles, the pedal on the right is the accelerator (gas pedal), controlling the fuel supply to the engine and thus, the car’s speed. The larger pedal to its left is the brake pedal, used to decelerate and bring the vehicle to a complete stop.
Manual transmission cars include a third pedal on the far left – the clutch pedal. The clutch is essential for manual gear shifting, allowing the driver to disengage the engine from the transmission to change gears smoothly. In manual cars, the pedal arrangement is typically clutch (left), brake (middle), and accelerator (right).
#4. Gear Shifter/Gear Selector
The gear shifter (in manual transmissions) or gear selector (in automatic transmissions) is located between the driver and front passenger seats. In manual cars, the gear shifter is a lever used to manually change gears, featuring a knob indicating the shift pattern.
In automatic transmission vehicles, the gear selector, often referred to as the “PRNDL” (Park, Reverse, Neutral, Drive, Low), allows the driver to choose driving modes without manual gear changes.
Operating a manual transmission gear shifter requires coordination with the clutch pedal. Pressing the clutch disengages the engine, allowing the driver to move the shifter to the desired gear. This action involves synchronizers and sleeves within the transmission to smoothly engage the selected gear for varied driving conditions and speeds.
#5. Dashboard and Instrument Cluster
The dashboard is a crucial interior component located at the front of the car. It serves as a central panel housing essential gauges and indicator lights, and acts as a separation between the front of the vehicle and the cabin.
Dashboard designs vary significantly across car models, reflecting different brands and feature sets. A typical dashboard incorporates several key instruments:
- Fuel Gauge: Displays the amount of fuel remaining in the tank, enabling drivers to monitor fuel levels and plan refueling stops.
- Speedometer: Indicates the vehicle’s current speed, crucial for maintaining safe and legal driving speeds. It can be analog (pointer-based) or digital.
- Tachometer: Shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM), vital for ensuring the engine operates within safe limits and for gear shifting in manual transmission vehicles.
- Temperature Gauge: Displays the engine’s operating temperature, warning against overheating which could signal engine problems or low coolant levels.
Furthermore, the dashboard houses numerous warning lights and indicator lights to alert drivers to potential issues or system malfunctions within the vehicle.
#6. Hazard Lights/Emergency Flashers
Emergency flashers, also known as hazard lights, are activated by a dedicated button on the dashboard, often marked with a red triangle.
When engaged, hazard lights cause all four turn signal lights to flash simultaneously. This serves as a universal warning signal to other drivers, indicating an emergency, vehicle breakdown, or that the car is parked in a potentially hazardous location.
#7. Seat Belts
Seat belts are paramount safety devices designed to significantly reduce the risk of fatalities and injuries in car accidents, provided they are used correctly.
Proper seat belt usage is crucial because unbelted occupants are far more likely to be ejected from the vehicle during a crash, leading to severe injuries or death. Even if not ejected, unrestrained individuals become projectiles within the car, endangering themselves and other occupants.
#8. Airbags
Airbags are inflatable safety cushions strategically placed within the vehicle’s interior to protect occupants during collisions. They deploy rapidly to prevent occupants from hitting hard interior surfaces or external objects.
In a crash, sensors detect the impact severity and, if deemed significant, trigger inflators to fill the airbags with gas in milliseconds.
Airbags typically require no maintenance unless deployed. Deployed airbags must be replaced by qualified technicians using original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts to guarantee proper functionality and avoid counterfeit replacements, which could malfunction or cause further harm during deployment.
#9. Rearview Mirrors: Interior and Exterior
Rearview mirrors are adjustable reflective surfaces designed to provide the driver with visibility of the road, traffic, and objects behind the vehicle.
Regulations, such as those in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, mandate that passenger cars must have an interior rearview mirror, a driver-side exterior mirror, and a passenger-side exterior mirror.
The interior rearview mirror is usually mounted centrally on the dashboard or windshield. It’s a unit magnification mirror, presenting a true-size reflection of objects behind the car. Exterior mirrors, on the other hand, are often convex to provide a wider field of view.
#10. Parking Brake/Emergency Brake
The parking brake, also known as the emergency brake, is an independent braking system separate from the primary hydraulic brakes used for regular stopping. This redundancy ensures a backup braking system in case of primary brake failure.
While primary brakes are designed for slowing and stopping the vehicle during normal driving, the parking brake is primarily intended to hold the vehicle stationary when parked.
However, in an emergency situation where the primary brakes fail, the parking brake can be used to gradually slow down and stop the car. It’s recommended to engage the parking brake every time you park, regardless of the terrain or vehicle type.
#11. Turn Signal Lever/Indicator Stalk
The turn signal lever, or indicator stalk, is typically located on the steering column. It’s used to activate the turn signals (indicators), essential for communicating intended direction changes to other road users.
Operating the signal lever activates the corresponding front and rear turn signal lights, ensuring safe lane changes and turns by clearly indicating the driver’s intentions.
#12. Center Console
The center console is the storage and control hub located between the driver and front passenger seats. It’s a feature common in modern cars, positioned behind the gear shifter/selector. Center consoles are not feasible in vehicles with front bench seats.
The center console area often encompasses the part of a car’s floorplan above the transmission tunnel. Modern center consoles can incorporate a variety of features, including storage compartments, cupholders, power outlets, audio controls, climate control interfaces, and infotainment screens.
#13. Glove Compartment/Glove Box
The glove compartment, or glove box, is a storage compartment embedded within the dashboard, typically on the passenger side above the footwell.
Despite its name, the glove compartment is used for general storage of items like owner’s manuals, insurance documents, maps, flashlights, and other small essentials.
#14. Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Power windows and door locks are electrically operated systems. Power window controls, usually buttons or switches, allow for raising and lowering vehicle windows without manual cranks. Power door lock controls enable the driver or front passenger to simultaneously lock or unlock all vehicle doors with a single button or switch.
#15. Interior Door Handles
Interior door handles are located inside the car doors and are used to disengage the door latch mechanism, allowing occupants to open the door from the inside. Modern interior door handles are often made of plastic.
The internal mechanisms connecting both interior and exterior door handles are situated within the door structure, behind the door panel.
#16. Audio System/Car Speakers
A car audio system comprises all components related to sound reproduction within the vehicle. This includes speakers, amplifiers, and source units (like head units or receivers). The car audio system is essential for in-car entertainment, providing music and other audio playback.
#17. Central Control Screen/Infotainment System
The central control screen, also known as the infotainment system or multimedia display, is a prominent feature in modern car interiors. It serves as a centralized interface for various vehicle functions and information.
Infotainment systems integrate “information” and “entertainment,” offering a blend of services from digital radio and navigation to smartphone integration and vehicle settings. These systems act as in-built car computers, often featuring touchscreen displays, button panels, and voice command capabilities.
#18. Sun Visors
Sun visors are located above the windshield on the interior roof of the car. They are hinged flaps designed to be adjusted downwards to block glare from sunlight, improving visibility for the driver and front passenger.
#19. Car Seats
Car seats are designed for support, comfort, and safety. They typically consist of a robust frame made of metal or high-strength materials and padding for cushioning and shock absorption.
Many car seats offer adjustable features like seat height, backrest angle, and lumbar support, allowing occupants to customize their seating position for optimal comfort.
Regular car seat maintenance includes vacuuming to remove dirt and dust, and applying leather or fabric conditioners to maintain material quality and prevent wear. Seat covers are a popular accessory to protect seats, enhance comfort, and simplify cleaning and maintenance.
#20. Floor Mats
Floor mats are essential for maintaining the cleanliness and protecting the car’s interior flooring. They trap dirt, mud, and spills, and can be easily removed for cleaning.
Some floor mats utilize fixation points to keep them securely in place. In some vehicles, like commercial and off-road vehicles, permanently fitted rubber carpets may negate the need for removable floor mats.
#21. Roof and Headliner
The car roof and headliner assembly is an integral part of the vehicle’s interior, providing structural integrity, insulation, and aesthetic appeal.
The roof provides structural rigidity, contributing to vehicle body strength and occupant protection, especially in rollover accidents. It also provides weather protection, keeping the cabin dry and comfortable.
The headliner, the interior fabric layer beneath the roof, offers sound absorption and thermal insulation, helping to regulate cabin temperature and reduce noise levels, thus enhancing overall comfort and ride quality.
FAQs about Car Interior Parts
What are the interior parts of a car called?
The main interior parts of a car include: Steering Wheel and Horn, Ignition, Pedals, Gear Shifter, Dashboard, Emergency Flashers, Seat Belts, and Airbags, among others detailed in this guide and shown in the interior parts of a car diagram.
What is an interior panel in a car?
Interior car panels are more than just decorative coverings inside the doors. They serve functional roles such as protecting the window mechanism when lowered and concealing electrical wiring and motors for windows and door locks.
What is the top inside of a car called?
The top inside of a car is called the headliner. It’s a fabric material that covers the vehicle’s ceiling. Beyond aesthetics, the headliner provides thermal and acoustic insulation and hides wiring and hardware for various vehicle components.
What is a dashboard in a car?
A dashboard in a car is the front-facing interior component that houses instrument panels, indicator lights, and controls. It serves as the primary interface for the driver, providing essential information and vehicle controls.
What is the interior of a car made of?
Modern car interiors utilize a range of materials, with polymers being prominent. These include lightweight seats, instrument panels, durable upholstery, sound-dampening fabrics, headliners, dashboards, and door panels.
What are the different types of car interiors?
Car interiors vary in material types, primarily:
- Nylon Upholstery: A common and durable fabric choice.
- Polyester Upholstery: Another popular fabric option.
- Vinyl Upholstery: A non-fabric, durable, and easy-to-clean option.
- Leather Upholstery: Considered a premium interior material, offering luxury and durability.
This detailed guide, enhanced with an “interior parts of a car diagram”, provides a comprehensive understanding of the essential components within your vehicle, improving your car knowledge and driving experience.
