For anyone passionate about cars, understanding the different components and how they function is crucial. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or just starting to learn about automobiles, knowing the terminology and function of each part is essential for maintenance, repair, and overall car appreciation. Let’s delve into the world of car parts, with a special focus on a key component known as “Marcha Car Part.”
Join us as we explore the various categories of car parts, from the interior comforts to the powerful engine components under the hood.
Exploring Essential Car Part Categories
To effectively understand car parts, it’s helpful to categorize them based on their location and function within the vehicle. We can broadly classify them into interior parts, exterior parts, under-the-hood components, and instrument panel elements. Within these categories, we’ll highlight the significance of “marcha car part” and its role in vehicle operation.
Inside the Car: Interior Car Parts
The interior of a car is where the driver and passengers interact most directly with the vehicle. These parts are essential for control, comfort, and safety.
| English | Function |
|---|---|
| Accelerator | Controls the speed of the vehicle by regulating fuel intake. |
| Brake | Used to slow down or stop the vehicle through friction. |
| Clutch | Found in manual transmission vehicles, it disengages the engine from the transmission to allow gear changes. |
| Gears (Marcha Car Part) | “Marcha car part,” commonly referred to as gears or gearshift, is a fundamental part of the transmission system. Gears are crucial for managing the engine’s power and torque to drive the wheels effectively at different speeds and loads. The gearshift lever allows the driver to select different gear ratios. |
| Glove Compartment | A storage space located in the dashboard, often used for documents and small items. |
| Handbrake (Parking Brake) | A mechanical brake system used to keep the vehicle stationary when parked, especially on inclines. |
| Horn | A sound signaling device used to alert other drivers or pedestrians. |
| Mats (Floor Mats) | Protective coverings for the car’s floor, designed to trap dirt and moisture. |
| Rearview Mirror | Provides the driver with a view of the area behind the vehicle. |
| Seatbelt | A safety restraint system designed to secure occupants in their seats and minimize injury in case of a collision. |
| Seats | Provide seating for the driver and passengers, designed for comfort and support. |
| Steering Wheel | Used to control the direction of the vehicle by turning the front wheels. |
| Steering Power (Power Steering) | An assistance system that reduces the effort needed to turn the steering wheel, making maneuvering easier. |


Outside the Car: Exterior Car Parts
Exterior car parts define the vehicle’s aesthetics and contribute to safety and protection from the elements.
| English | Function |
|---|---|
| Bumper | Designed to absorb impact in low-speed collisions, protecting the car’s body. |
| Door Handles | Used to open and close the vehicle’s doors. |
| Doors | Provide access to the vehicle’s interior and contribute to structural integrity. |
| Front and Back Fenders | Body panels that surround the wheel wells, protecting the car from road debris and reducing spray. |
| Grill | Located at the front of the car, it allows airflow to the radiator and engine while often serving as a styling element. |
| Headlights | Provide illumination for driving in low-light conditions, increasing visibility for the driver and others. |
| Hood | A hinged cover over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance and repairs. |
| Hub Caps (Wheel Covers) | Decorative covers for the center of the wheels, improving appearance and sometimes aerodynamics. |
| Indicator Lights (Turn Signals) | Flashing lights that signal the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes. |
| License Plate (Number Plate) | A unique identification tag for the vehicle, required for legal operation. |
| Outside Mirrors (Side Mirrors) | Provide the driver with a view of the sides and rear of the vehicle, essential for safe lane changes and maneuvering. |
| Roof | The top panel of the vehicle, providing protection from weather and contributing to structural rigidity. |
| Sunroof (Moonroof) | An opening in the vehicle’s roof that allows light and fresh air to enter the cabin. |
| Tail Light | Red lights at the rear of the vehicle that indicate its presence and illuminate when braking. |
| Trunk (Boot) | A compartment at the rear of the vehicle designed for cargo storage. |
| Wheels | Circular components that allow the vehicle to move by rotating, typically fitted with tires for traction and cushioning. |
| Windows | Transparent panels in the vehicle’s body that allow visibility and light into the cabin. |
| Windshield (Windscreen) | The front window of the vehicle, providing a clear view of the road ahead and protection from wind and debris. |
| Windshield Wipers | Mechanical arms with rubber blades that clear rain, snow, and debris from the windshield to maintain visibility. |
Under the Hood: Engine and Mechanical Car Parts
These are the core mechanical components that make the car function. Understanding these “under the hood” parts is crucial for anyone interested in car mechanics and maintenance.
| English | Function |
|---|---|
| Air Filter | Cleans the air entering the engine, preventing dust and debris from causing damage. |
| Alternator | Generates electrical power to recharge the battery and run the car’s electrical systems while the engine is running. |
| Battery | Stores electrical energy to start the engine and power electrical components when the engine is off. |
| Belt (Serpentine Belt, Timing Belt) | Transfers power from the engine’s crankshaft to various components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The timing belt synchronizes crankshaft and camshaft rotation. |
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of engine valves, regulating the intake of air and fuel and the exhaust of gases. |
| Carburetor | In older vehicles, it mixes air and fuel to create a combustible mixture for the engine. Modern cars use fuel injection instead. |
| Catalytic Converter | Reduces harmful emissions from the exhaust gases by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. |
| Coil (Ignition Coil) | Increases the battery’s voltage to create a spark at the spark plugs, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders. |
| Combustion Chamber | The space within the engine cylinder where the air-fuel mixture is burned to produce power. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which is then transmitted to the wheels through the transmission system, including the “marcha car part” (gears). |
| Gas Pump (Fuel Pump) | Pumps fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. |
| Ignition | The system that initiates the combustion process in the engine cylinders, usually involving spark plugs. |
| Piston Rod (Connecting Rod, Biela) | Connects the pistons to the crankshaft, transmitting the force of combustion to rotate the crankshaft. |
| Pulley | A grooved wheel that guides and tensions belts, transmitting rotational motion between components. |
| Radiator | Cools the engine coolant, preventing the engine from overheating. |
| Escape Valve (Exhaust Valve) | Opens to allow exhaust gases to exit the combustion chamber after the combustion process. |
| Thermostat | Regulates the engine’s temperature by controlling the flow of coolant to the radiator. |
| Vacuum Diaphragm | Used in various engine systems to control airflow or fuel flow based on vacuum pressure. |
| Valve | A mechanical device that controls the flow of liquids or gases, used in the engine to regulate intake and exhaust, and in other systems. |
| Voltage | The electrical potential difference, crucial for the operation of the car’s electrical systems. |
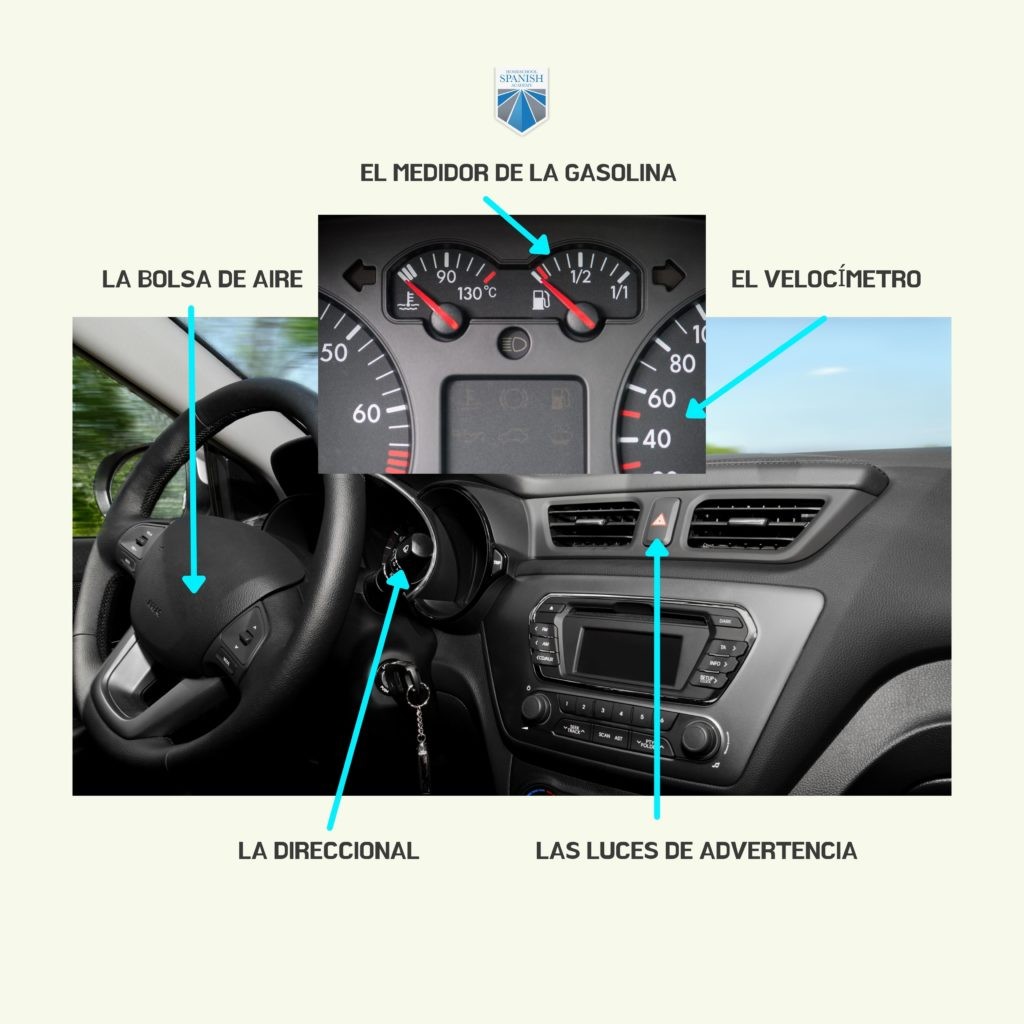
Instrument Panel Car Parts
The instrument panel, or dashboard, provides the driver with essential information about the vehicle’s operation.
| English | Function |
|---|---|
| Air Bag | A safety device that inflates rapidly in a collision to cushion occupants and reduce injury. |
| Gas Gauge (Fuel Gauge) | Indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the fuel tank. |
| Speedometer | Displays the vehicle’s current speed. |
| Turn Signal Indicator | Visual confirmation that the turn signals are activated, usually flashing lights on the dashboard. |
| Warning Lights | Illuminated symbols that alert the driver to potential problems or malfunctions in various vehicle systems. |
Understanding the “Marcha Car Part” in Detail
As highlighted earlier, “marcha car part” refers to the gears within a vehicle’s transmission system. The transmission is a critical component that manages the power generated by the engine and delivers it to the wheels. Gears are essential because they allow the engine to operate efficiently across a range of speeds and driving conditions.
Think of gears like levers: they change the relationship between engine speed and wheel speed.
- Lower Gears (e.g., first gear): Provide more torque (rotational force) at the wheels, necessary for starting from a standstill, climbing hills, or towing heavy loads. In lower gears, the engine rotates faster relative to the wheels.
- Higher Gears (e.g., fifth or sixth gear): Provide less torque but allow for more efficient cruising at higher speeds. In higher gears, the engine rotates slower relative to the wheels, saving fuel and reducing engine wear at highway speeds.
The gearshift lever, connected to the transmission, allows the driver to select the appropriate gear for the driving situation. In automatic transmissions, the gear selection is done automatically by the car’s computer based on speed, engine load, and other factors. However, the fundamental principle of “marcha car part” – using different gear ratios to optimize engine power and efficiency – remains the same.
Expanding Your Car Part Knowledge
Understanding car parts is an ongoing journey. By familiarizing yourself with these essential components and their functions, especially the crucial “marcha car part,” you’ll be better equipped to maintain your vehicle, communicate effectively with mechanics, and deepen your appreciation for automotive engineering. Whether you are troubleshooting a minor issue or simply want to expand your automotive vocabulary, a solid grasp of car part terminology is invaluable.