Have you ever glanced at your vehicle and wondered about the names of its various components? Just like the human body, a car is composed of numerous parts working in harmony. Understanding these “body parts” of your car is not only fascinating but also practical for maintenance, repair, and general car knowledge.
This guide, brought to you by carparteu.com’s auto repair experts, will take you on a detailed journey through the essential components of a car’s body. We’ll explore each part, learn its name, and understand its critical function. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or just starting to learn, this comprehensive overview will enhance your automotive vocabulary and understanding.
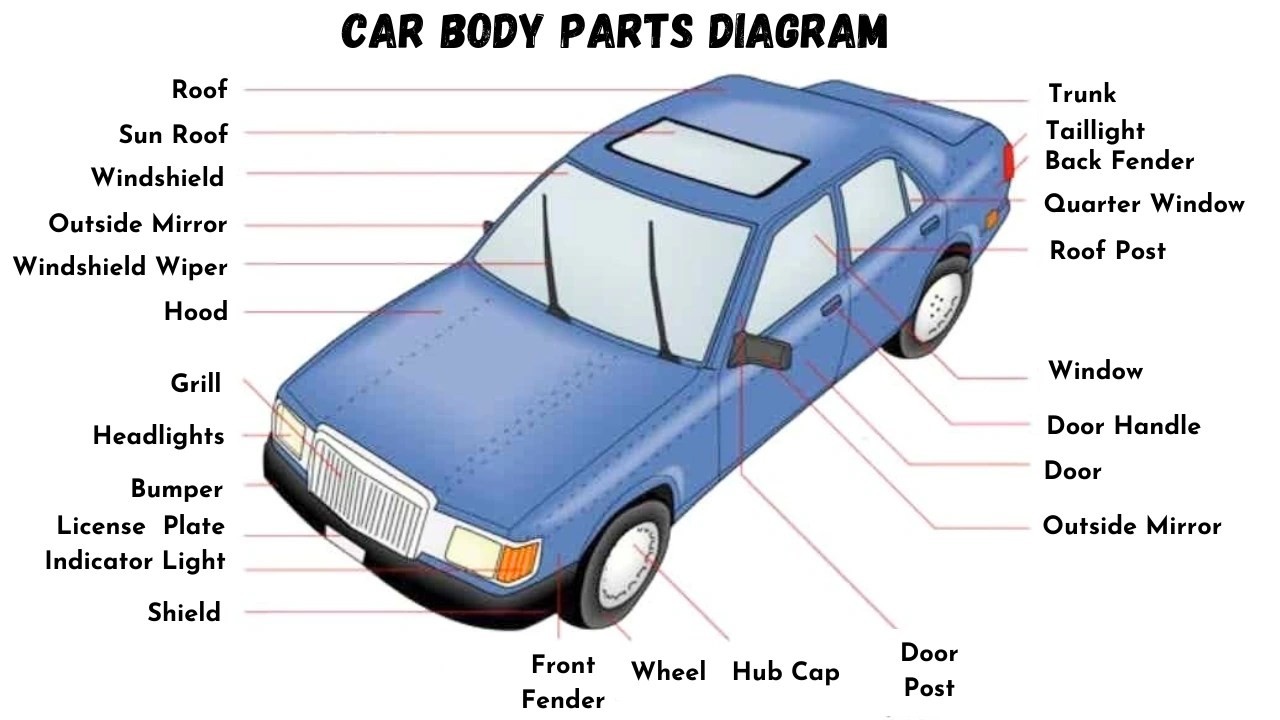
Essential Car Body Parts: Names and Functions
Here’s an extensive list of the primary car body parts, each playing a vital role in the vehicle’s structure, safety, and aesthetics:
- Body Shell
- Hood or Bonnet
- Front Bumper
- Rear Bumper
- Bumper Grille
- Crash Guard or Bullbar
- Headlight
- Fog Lamp
- Indicator Lights
- Wiper Blade
- Radiator
- Radiator Supports
- Cowl Panel
- Quarter Panel
- Fender
- Fender Liners
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Mirrors
- Doors
- Door Handle
- Window Glass
- Quarter Window
- Trunk or Decklid
- Mud Flaps
- Wheels
- Hubcap
- Dashboard
- Number Plate
- Taillights
Exploring the Parts of a Car Body in Detail
Let’s delve deeper into each of these car body parts, understanding their purpose and design:
#1. Body Shell
The body shell is the foundational structure of the car. It’s the main frame onto which all other components are attached, including the engine, chassis, and interior. Think of it as the skeleton of the car, providing overall shape and structural integrity. It excludes detachable parts like doors and external trims.
 Car Body Shell
Car Body Shell
#2. Hood/Bonnet
Located at the front, the hood, also known as the bonnet, is a hinged cover protecting the engine compartment. It shields the engine and related components from weather elements and road debris. Crucially, it provides easy and safe access to the engine bay for maintenance and repairs. Hoods are typically made of steel or aluminum, with aftermarket options in materials like carbon fiber for performance vehicles.
#3. Front Bumper
The front bumper is a safety component designed to absorb impact during low-speed collisions. Positioned at the frontmost part of the car, it protects the body and internal components from damage in minor accidents. Modern front bumpers often integrate with vehicle styling and may house sensors for parking assistance or adaptive cruise control.
#4. Rear Bumper
Similar in function to the front bumper, the rear bumper safeguards the rear of the vehicle. It protects the trunk, exhaust system, and taillights from damage in rear-end collisions. Like front bumpers, rear bumpers are designed for impact absorption and increasingly incorporate design elements and sensor housings.
#5. Bonnet Grille
The grille is a distinctive part of the car’s front end, typically situated between the headlights. Often featuring a mesh design, the grille’s primary function is to allow airflow to the engine radiator for cooling. Grille designs vary significantly between car manufacturers and models, becoming a key styling element of vehicle brands. Beyond cooling, grilles contribute to the car’s aerodynamic profile.
#6. Bullbars or Crash Guards
Bull bars, or crash guards, are robust metal bars fitted to the front (and sometimes rear) of a vehicle. They are designed to provide enhanced protection to the vehicle’s body in collisions, particularly in off-road or rural driving conditions where animal strikes are possible. However, their use is sometimes debated due to pedestrian safety concerns in urban environments.
#7. Headlight
Headlights are essential for safe driving at night and in low-visibility conditions. Mounted at the front of the vehicle, they illuminate the road ahead, ensuring the driver’s vision and making the vehicle visible to other road users. Modern headlights come in various technologies, including halogen, LED, and laser, each offering different levels of brightness, efficiency, and beam patterns.
#8. Fog Lamp
Fog lamps are specialized lights designed to improve visibility in foggy conditions, heavy rain, or dust storms. Positioned lower than headlights, fog lamps aim to project a wide, flat beam of light that cuts through the fog, illuminating the road surface and reducing glare back to the driver.
#9. Signal Lights (Indicator Lights)
Signal lights, also known as indicator lights or turn signals, are crucial for communicating a vehicle’s intended direction to other drivers and pedestrians. Located at the front and rear corners of the car, these blinking lights signal left or right turns, lane changes, or hazards. Emergency lights, activated by hazard light switch, blink all signal lights simultaneously to indicate vehicle breakdown or emergency situation.
#10. Roof and Pillars
The roof forms the upper enclosure of the car, protecting occupants from the elements – sun, rain, snow, and debris. Car roofs are designed for structural strength and may incorporate features like sunroofs or roof racks. Pillars are the vertical supports that connect the roof to the car’s body. They are critical for structural integrity, especially in rollover accidents. Pillars are typically designated by letters (A, B, C, and sometimes D), starting from the front of the car.
#11. Doors and Windows
Doors provide access to the car’s interior for passengers and the driver. They are designed for security, safety, and weather sealing. Car doors incorporate various components like door locks, handles, window mechanisms, and side impact beams for safety. Windows, made of glass, provide visibility and can often be lowered or raised for ventilation. The windshield, a specialized front window, is crucial for forward visibility and structural integrity.
#12. Rear Panels
Rear panels encompass the structural sections at the back of the car. This area includes the rear fenders, taillight housings, and often integrates with the bumper and trunk opening. The rear panel design contributes to the car’s overall styling and aerodynamic efficiency.
#13. Front Panels
Front panels are the body sections at the front of the car, typically surrounding the engine compartment and headlights. They include fenders, the upper grille surround, and contribute to the mounting of the hood and bumper. Front panel design significantly impacts the car’s frontal appearance and aerodynamics.
#14. Steering Wheel and Car Wheels
While the steering wheel is an interior component, it is intrinsically linked to the car’s body in terms of control and function. The steering system, including the steering wheel and column, allows the driver to control the direction of the front wheels. Car wheels, attached to the axles, are essential for movement. They are body parts in the sense they are external and fundamental to the vehicle’s operation.
#15. Front and Rear View Mirrors and Windows
Mirrors, both interior rearview and exterior side mirrors, are vital for driver awareness of the surroundings. They enhance safety by providing visibility to the rear and sides of the vehicle, minimizing blind spots. Windows, as discussed earlier, provide essential visibility and protection.
#16. Bearings (Wheel Bearings)
Wheel bearings are critical components that enable the wheels to rotate smoothly and freely. They are located within the wheel hub assembly, connecting the wheel to the axle. Faulty wheel bearings can cause noise, vibration, and compromise wheel stability.
#17. Body Kits
Body kits are sets of aftermarket components designed to modify a car’s exterior appearance. They typically include front and rear bumper extensions, side skirts, spoilers, and sometimes hood scoops or fender flares. Body kits are primarily for aesthetic enhancement and can dramatically alter a vehicle’s style.
#18. Body Trim
Body trim refers to decorative elements added to the interior and exterior of a car to enhance its visual appeal. Trim can include chrome strips, moldings, badges, and accents around windows, grilles, and lights. Trim parts contribute to the vehicle’s overall finish and can denote different trim levels or model variants.
#19. Bumper Guards
Bumper guards are protective accessories designed to prevent scratches and minor damage to car bumpers, particularly in parking situations or light impacts. They are typically made of rubber or plastic and attach to the bumper surface, providing an extra layer of protection.
#20. Cabin Parts (Interior Body Parts)
While the focus is on exterior body parts, it’s worth noting that “cabin parts” refers to the interior components of the car’s body. This includes the dashboard, door panels, seats, headliner, and trim inside the passenger compartment.
#21. Cables (Wiring Harness)
Cables, specifically the wiring harness, are the electrical “nervous system” of the car. While not strictly exterior body parts, they run throughout the body shell, connecting all electrical components, from lights and sensors to the engine control unit and infotainment system.
#22. Coolant Bottle (Coolant Reservoir)
The coolant reservoir, or coolant bottle, is a plastic container in the engine compartment that holds extra coolant for the engine’s cooling system. It accommodates the expansion and contraction of coolant as the engine heats up and cools down, ensuring the system remains properly filled.
#23. Dashboard (Instrument Panel)
The dashboard, or instrument panel, is located inside the car, directly in front of the driver. It houses essential instruments and controls, including the speedometer, tachometer, fuel gauge, warning lights, and often the infotainment system. While interior, the dashboard is a major body component within the cabin.
#24. Fenders (Wings)
Fenders, also known as wings (especially in British English), are the body panels that frame the wheel arches. Their primary function is to prevent road spray, mud, and stones from being thrown up by the tires, protecting the car body and other vehicles. Fenders also contribute to the car’s styling and aerodynamics.
#25. License Plate and Brackets
The license plate, or number plate, is a legally required metal or plastic plate displaying the vehicle’s registration number. It is attached to the front and rear of the car using brackets. The license plate allows for vehicle identification and is a mandatory body component.
#26. Mud Flaps (Splash Guards)
Mud flaps, or splash guards, are flexible panels mounted behind the wheels, especially the rear wheels. They provide additional protection against mud, water, and road debris being thrown up by the tires, further protecting the undercarriage and following vehicles.
#27. Quarter Panels (Rear Wings)
Quarter panels, or rear wings (British English), are body panels located between the rear door and the trunk, wrapping around the rear wheel well. They form a significant part of the car’s side profile and contribute to structural rigidity and styling.
#28. Sunroof
A sunroof is a movable panel in the car’s roof that can be opened to allow light and fresh air into the cabin. Sunroofs can be manually operated or power-operated and come in various sizes and designs, enhancing the driving experience.
#29. Wheel Rim
The wheel rim is the outer edge of the wheel onto which the tire is mounted. It provides the structural support for the tire and is a crucial part of the wheel assembly. Rim design also plays a significant role in the vehicle’s aesthetics.
#30. Windshield Washer Motor (Pump)
The windshield washer motor, or pump, is a small electric motor that pumps windshield washer fluid from the reservoir to the windshield. It is a vital part of the windshield wiper system, ensuring clear visibility in inclement weather.
#31. Wiper (Wiper Blades and Arms)
Wipers are essential safety devices for clearing rain, snow, and debris from the windshield, ensuring clear driver vision. The system includes wiper arms that move the wiper blades across the windshield. Wiper blades are the rubber components that make direct contact with the glass to remove water and dirt.
FAQs About Car Body Parts
What are common body parts names on a car?
Common car body parts include the hood, bumper, fenders, doors, roof, trunk, and wheels. These are the most visible and frequently discussed exterior components.
What are the main panels on a car called?
The main body panels include the hood, roof, doors, fenders (front wings), and quarter panels (rear wings). These panels form the outer skin of the car and define its shape.
What is considered the core structure of a car?
The chassis is the core structural element of a car, providing the frame and supporting the body and all other components. The body shell is built upon the chassis.
How can I accurately identify a specific car part?
The most reliable way to identify a car part is using the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). The VIN is unique to your car and allows parts suppliers to identify the exact correct parts for your make and model. Part codes, if visible on the part itself, can also be helpful.
What is the British term for the front body of a car covering the engine?
In British English, the front part of a car covering the engine is called the bonnet. In American English, it is referred to as the hood.
Understanding the names and functions of car body parts empowers you as a car owner and enthusiast. Whether you’re discussing repairs with a mechanic, considering modifications, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge, this guide provides a solid foundation in automotive anatomy. Stay tuned to carparteu.com for more expert insights into the world of cars!