Just like the cockpit of an airplane, the dashboard of your car is packed with essential instruments and controls. Understanding the Names Of Car Dashboard Parts and their functions is crucial for every driver. It empowers you to monitor your vehicle’s health, operate it safely, and respond effectively to different driving situations.
This guide will illuminate the world of your car’s dashboard, clearly labeling each component and explaining its role. Whether you’re a new driver or a seasoned автомобилист, knowing your dashboard inside and out enhances your driving experience and safety.
Essential Car Dashboard Parts: An Overview
The dashboard, also known as the instrument panel, is the control center of your car’s interior, situated directly in front of the driver. It’s more than just a pretty facade; it’s where vital information about your vehicle is displayed and many critical controls are located. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas and parts you’ll find:
- Steering Column Area: This area, directly behind the steering wheel, houses controls for driving and signaling.
- Instrument Cluster: Located directly behind the steering wheel, this is your primary information display.
- Center Stack: The central vertical section of the dashboard, often containing infotainment and climate controls.
- Glove Compartment Area: The passenger side area, often including storage and sometimes part of the airbag system.
Let’s dive deeper into the specific names of car dashboard parts you’ll encounter in each of these zones.
Instrument Cluster: Gauges and Warning Lights
The instrument cluster is arguably the most important part of your dashboard, providing real-time feedback on your car’s performance and condition. Here are the key gauges and indicators you’ll find:
1. Speedometer
The speedometer is perhaps the most frequently checked gauge. It displays your vehicle’s current speed, usually in both miles per hour (mph) and kilometers per hour (km/h). Keeping an eye on your speedometer is essential for adhering to speed limits and driving safely.
2. Tachometer (RPM Gauge)
The tachometer, often abbreviated as RPM (Revolutions Per Minute), measures your engine’s speed. It indicates how many times the engine’s crankshaft is rotating per minute. While less critical for everyday driving than the speedometer, the tachometer is useful for understanding engine performance and is particularly important in manual transmission vehicles for optimal gear shifting. Keeping the RPM in the optimal range improves fuel efficiency and engine longevity.
3. Fuel Gauge
The fuel gauge displays the amount of fuel remaining in your car’s tank. It’s crucial for avoiding running out of gas. Fuel gauges typically range from “F” (Full) to “E” or “0” (Empty). Modern cars often include a low fuel warning light that illuminates when the fuel level is getting low, prompting you to refuel soon.
4. Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge indicates the engine coolant temperature. It’s vital to monitor this gauge to prevent engine overheating. A normal operating temperature is usually in the middle range. If the gauge rises into the red zone, it signals overheating, which can cause serious engine damage. Pull over safely and allow the engine to cool down if this occurs.
5. Warning Lights and Indicator Lights
Dashboard warning lights and indicator lights are symbols or text displays that alert you to various vehicle conditions. They can be broadly categorized as:
- Warning Lights (often red or amber): These signal potential problems that require attention. Examples include:
- Check Engine Light: Indicates a problem with the engine or emissions system.
- Oil Pressure Light: Signals low engine oil pressure, which can cause severe engine damage.
- Battery Light: Indicates a problem with the charging system.
- Brake Warning Light: Can indicate the parking brake is engaged, low brake fluid, or a problem with the braking system.
- Airbag Warning Light: Signals a malfunction in the airbag system.
- Temperature Warning Light: Indicates engine overheating (often in addition to the temperature gauge).
- ABS Warning Light: Indicates a problem with the Anti-lock Braking System.
- Indicator Lights (often green or blue): These indicate that a system is active or functioning. Examples include:
- Turn Signal Indicators: Flash when you activate the turn signals.
- Headlight Indicators: Indicate when headlights are on (low beam or high beam).
- Cruise Control Indicator: Lights up when cruise control is engaged.
- Fog Light Indicators: Show when fog lights are activated.
It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the meaning of each warning light in your car’s owner’s manual. Ignoring warning lights can lead to more significant and costly repairs.
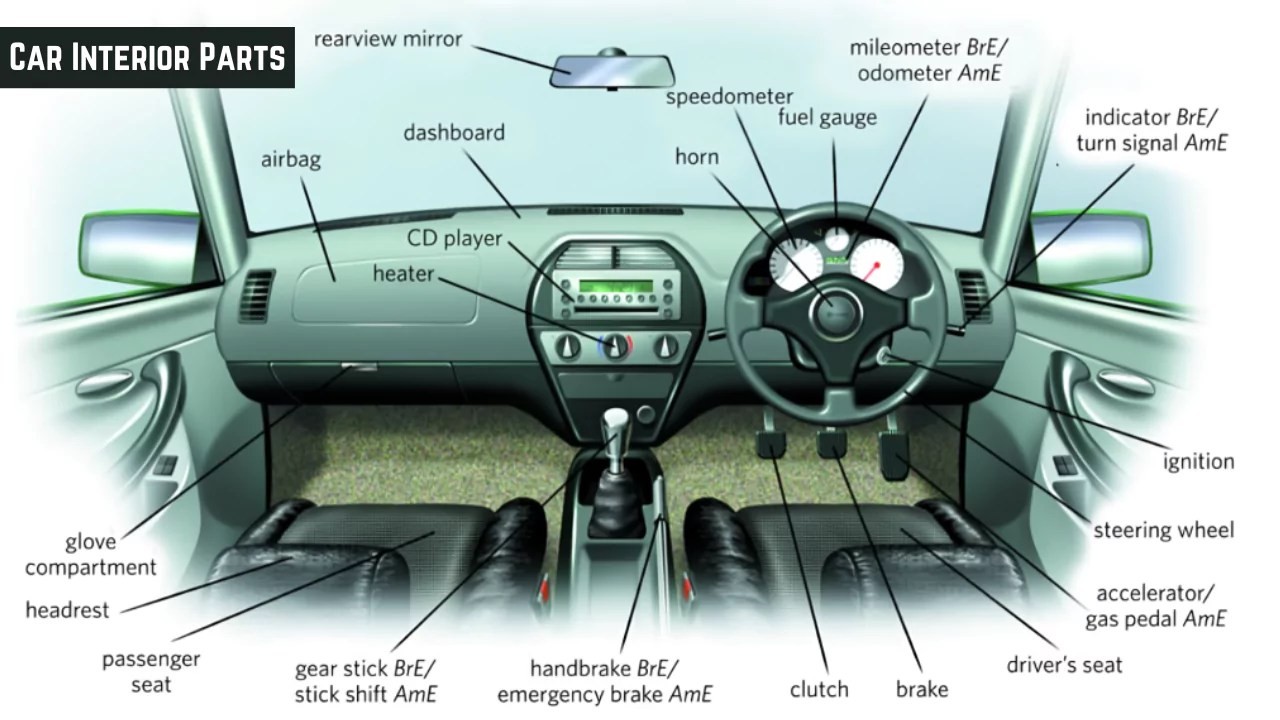 interior car parts names with diagram
interior car parts names with diagram
Steering Column Controls: Driving and Signaling
The area around the steering column is home to several crucial controls that directly affect driving and signaling:
6. Steering Wheel and Car Horn
The steering wheel is the primary control for steering the vehicle, allowing you to direct the car’s movement. Modern steering wheels often integrate additional controls for convenience and safety:
- Horn: Located in the center of the steering wheel, the horn is used to alert other drivers and pedestrians.
- Cruise Control Buttons: Allow you to set and maintain a constant speed.
- Audio Controls: Control the car’s audio system volume, track selection, and source.
- Bluetooth/Phone Controls: Enable hands-free phone calls and voice commands.
7. Ignition Switch
The ignition switch is where you insert your car key or press a start/stop button to start and stop the engine. It’s typically located on the steering column or sometimes on the dashboard itself in newer push-button start systems.
8. Car Signal Lever (Turn Signal Stalk)
The car signal lever, also known as the turn signal stalk or indicator stalk, is usually located on the left side of the steering column. Moving this lever up or down activates the turn signals (indicators) to signal your intention to turn right or left. Often, pushing the lever in or out will activate high beams or flash-to-pass function.
9. Windshield Wiper Controls
Typically found on a stalk on the right side of the steering column, the windshield wiper controls allow you to activate and adjust the speed of the windshield wipers to clear rain, snow, or debris from the windshield. Often integrated are controls for windshield washer fluid.
Center Stack: Infotainment and Comfort
The center stack is the central vertical section of the dashboard, often housing controls for entertainment, climate, and vehicle settings:
10. Car Central Control Screen (Infotainment System)
The car central control screen, or infotainment system, is a display screen in the center of the dashboard. It integrates various functions, including:
- Audio System: Controls for radio, media playback, and sometimes streaming services.
- Navigation System: Provides GPS navigation and directions.
- Climate Control: Displays and controls for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC).
- Vehicle Settings: Access to customize various vehicle functions and settings.
- Backup Camera Display: Shows the view from the rearview camera when reversing.
- Smartphone Integration: Apple CarPlay and Android Auto for seamless smartphone connectivity.
11. Audio System Controls
Even in cars with central control screens, there are often physical buttons or knobs for basic audio functions like volume control and tuning, located on the center stack.
12. Climate Control Controls
Climate control knobs or buttons allow you to adjust the temperature, fan speed, and airflow direction for the car’s heating and air conditioning system.
13. Emergency Flashers Button
The emergency flashers button, usually marked with a red triangle, activates all four turn signals simultaneously. Use hazard lights to warn other drivers of emergencies or when your vehicle is stopped in a potentially hazardous location.
Other Dashboard and Interior Parts
Beyond the main dashboard areas, there are other important interior parts to be aware of:
14. Pedals
Located on the floor in the driver’s footwell, the pedals control acceleration and braking:
- Accelerator Pedal (Gas Pedal): The rightmost pedal, used to increase engine speed and accelerate the vehicle.
- Brake Pedal: Located to the left of the accelerator pedal, used to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Clutch Pedal (Manual Transmissions Only): The leftmost pedal in manual transmission vehicles, used to disengage the engine from the transmission for gear shifting.
15. Gear Shifter
The gear shifter, located on the center console or steering column, allows you to select different gears for driving (Park, Reverse, Neutral, Drive, etc. in automatics; and numbered gears in manuals).
16. Center Console
The center console is the area between the driver and passenger seats, often housing the gear shifter, cupholders, storage compartments, and sometimes controls for features like parking brake or drive modes.
17. Glove Compartment
The glove compartment, or glove box, is a storage compartment built into the passenger side dashboard, used for storing vehicle documents, maps, and other small items.
18. Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Located on the door panels or center console, these controls operate the power windows and door locks.
19. Interior Door Handle
The interior door handle is used to open the car doors from the inside.
20. Car Seats and Seat Belts
Car seats provide seating for occupants and, along with seat belts, are critical safety features. Seat belts restrain occupants in the event of a crash, significantly reducing the risk of injury.
21. Airbags
Airbags are inflatable safety cushions that deploy in a collision to protect occupants from impact. Dashboard airbags are located within the dashboard structure and deploy in frontal collisions.
22. Rearview Mirrors
Rearview mirrors (interior and side mirrors) provide visibility to the rear and sides of the vehicle, essential for safe driving and maneuvering.
23. Emergency Brake (Parking Brake)
The emergency brake, or parking brake, is used to mechanically hold the vehicle stationary when parked. It can also be used as a backup braking system in emergencies.
24. Sun Visors
Sun visors, located above the windshield, can be flipped down to block sunlight and reduce glare.
25. Floor Mats
Floor mats protect the car’s floor carpeting and make cleaning easier.
26. Roof and Headliner
The roof provides structural integrity and protection, while the headliner is the interior fabric covering of the roof, providing insulation and sound dampening.
Conclusion
Understanding the names of car dashboard parts and all interior components is more than just automotive trivia – it’s a key aspect of responsible and informed driving. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you’ll be better equipped to understand your car’s signals, operate it effectively, and ensure a safer and more enjoyable driving experience. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific details about your car’s dashboard and interior features.