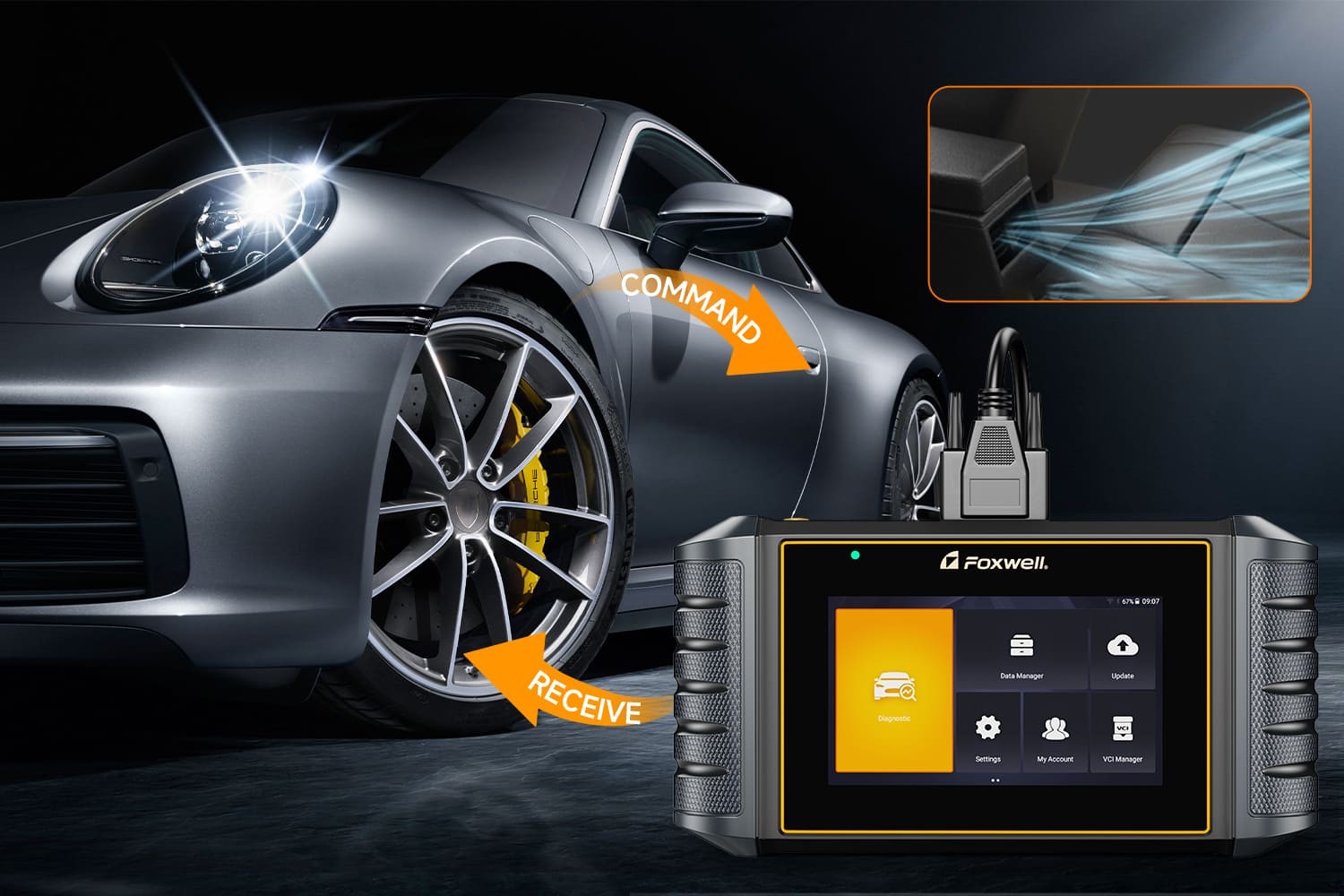
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port, typically found under your car’s dashboard, is commonly known as the gateway for automotive diagnostics. Mechanics use it to plug in scanners, read error codes, and assess vehicle health. However, the question arises: can this port be utilized for more than just diagnostics? Specifically, could it be used to perform actions like Obd2 Door Unlock or even engine starting? Let’s investigate the capabilities and limitations of the OBD2 port in relation to vehicle security.
Understanding the OBD2 Port’s Functionality
Since the mid-1990s, the OBD2 port has become a standard feature in virtually every car, acting as an interface to the vehicle’s computer systems. Its primary purpose is to facilitate vehicle diagnostics. This crucial port allows mechanics and car owners to connect diagnostic tools to read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes are invaluable for identifying issues when the check engine light illuminates, providing insights into potential malfunctions within the vehicle’s various systems. Beyond error codes, the OBD2 port also enables the monitoring of real-time data from various sensors throughout the car. This includes parameters like engine temperature, vehicle speed, and sensor readings, which are essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and diagnosing potential problems before they escalate.
OBD2 and Car Door Unlocking: Separating Fact from Fiction
The OBD2 port’s connection to your car’s central computer system raises the question of whether it could be manipulated for tasks beyond diagnostics, such as obd2 door unlock. While technically the OBD2 port is connected to systems that control door locks, directly using it for unlocking is not a straightforward process and is generally not possible in modern vehicles. The idea of sending commands via the OBD2 port to trigger door unlocking is often speculated, but it overlooks the sophisticated security measures implemented by car manufacturers. The OBD2 protocol itself is primarily designed for diagnostic communication, not for sending direct “pop” signals to actuate door locks.
Car manufacturers are acutely aware of potential security vulnerabilities and have implemented robust safeguards to prevent unauthorized access through the OBD2 port. A significant hurdle is the variation in security protocols across different manufacturers. What might theoretically work on an older vehicle or a specific make is unlikely to be effective on a different brand. Modern vehicles employ encrypted communication channels between the OBD2 port and the car’s internal systems. This encryption makes it significantly challenging for external devices to inject unauthorized commands via the OBD2 port to perform actions like obd2 door unlock.
Furthermore, authentication protocols are in place to ensure that only authorized devices can communicate with and control vehicle systems. These measures are designed to prevent unauthorized individuals from simply plugging into the OBD2 port and gaining control, enhancing vehicle security and protecting against unauthorized access and actions like obd2 door unlock.
OBD2 and Engine Ignition: Why It’s Not a Simple Start
Similarly to door unlocking, the possibility of using the OBD2 port to start a car engine is often discussed. The Engine Control Unit (ECU), the central computer managing engine operations, is indeed accessible through the OBD2 port. In theory, communication with the ECU via OBD2 could potentially allow for engine control, including starting. However, initiating engine start through the OBD2 port is far more complex than it appears and is highly unlikely in practice for security reasons.
Modern vehicles incorporate sophisticated immobilizer systems and rely on encrypted signals transmitted from the key fob to authorize engine start. Without the correct encrypted signal from a recognized key fob, the vehicle’s immobilizer will prevent the engine from starting, regardless of any commands sent through the OBD2 port. This security layer adds significant protection against unauthorized engine start, even if someone were to gain physical access to the OBD2 port.
Car manufacturers continuously update their security protocols to stay ahead of potential threats and hacking attempts. These evolving protocols are designed to ensure that only authorized methods, such as the car’s key fob, can initiate engine start, effectively preventing unauthorized engine ignition via the OBD2 port.
Security Implications and Responsible Scanner Use
While directly using the OBD2 port for actions like obd2 door unlock or engine start is highly improbable in modern, secure vehicles, it’s important to acknowledge that security vulnerabilities in car systems can exist and have been exploited in rare cases. Instances of car hacking, although uncommon, are a reminder of the need for robust automotive cybersecurity. These types of exploits typically require highly skilled individuals with in-depth knowledge of specific vehicle systems and are not easily executed.
The automotive industry is constantly working to enhance vehicle security and mitigate potential risks. Car manufacturers are collaborating with cybersecurity experts to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities. Regular updates to security protocols are implemented to counter emerging threats and ensure vehicles remain protected.
For car owners and professionals, utilizing OBD2 scanners for their intended purpose – vehicle diagnostics and maintenance – is crucial. Tools like the Foxwell NT809BT are invaluable for assessing vehicle health, reading and clearing DTCs, viewing live data, and performing system tests.
These scanners connect to the OBD2 port to provide detailed insights into various vehicle systems, including engine performance, transmission, ABS, and airbags, enabling proactive maintenance and issue identification. The wireless capabilities of advanced scanners further enhance convenience and efficiency in vehicle diagnostics, making maintenance tasks more streamlined.
Conclusion: OBD2 for Diagnostics, Not Door Unlocks
In conclusion, while the OBD2 port is a powerful interface to your vehicle’s systems, using it for actions like obd2 door unlock or engine start is not a practical reality in modern vehicles due to robust security measures. Car manufacturers invest heavily in encryption, authentication, and immobilizer technologies to protect against unauthorized access and control. The OBD2 port remains primarily a diagnostic tool, crucial for vehicle maintenance and health monitoring. It is not designed or intended to be a backdoor for bypassing vehicle security systems for actions like unlocking doors or starting engines.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of the OBD2 port in a vehicle?
The OBD2 port’s primary function is for vehicle diagnostics. It allows mechanics and car owners to connect diagnostic scanners to read trouble codes and monitor various systems for maintenance and repair purposes.
Are OBD2 ports vulnerable to hacking?
While theoretically possible, modern vehicles are equipped with security measures like encryption and authentication to protect the OBD2 port from unauthorized access and hacking attempts. Exploiting vulnerabilities is complex and not easily achieved.
Why are security updates important for modern car OBD2 systems?
Regular security updates are crucial for modern car OBD2 systems because car manufacturers continuously enhance security protocols to address new threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring vehicle safety and security against evolving hacking techniques.