Navigating the complexities of modern vehicle maintenance can be daunting, especially when the dreaded “Check Engine” light illuminates on your dashboard. This warning signal often accompanies an OBD2 error code, a message from your car’s onboard computer indicating a potential issue. Understanding these codes is crucial for every car owner to ensure vehicle longevity and optimal performance. This guide will delve into the world of OBD2 error codes, explaining what they are, how to interpret them, and what steps you can take to address them effectively.
Understanding OBD2 Codes: Your Car’s Diagnostic Language
On-board diagnostics (OBD-II) codes are essentially your vehicle’s way of communicating when something isn’t quite right. Think of them as digital alerts generated by your car’s computer system. This system monitors various components, from the engine and transmission to emission controls, constantly checking for irregularities.
When a problem is detected, the system generates a specific alphanumeric code. This code isn’t just random; it points towards the area of the malfunction, ranging from minor glitches to more serious mechanical concerns. The “Check Engine” light is the most common indicator that an OBD2 code has been triggered, signaling that a system within your vehicle’s engine or related systems is not performing as expected.
To access these codes, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. This tool connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner retrieves the stored error codes, providing you with a numerical trouble code. This code acts as a starting point, guiding you or a qualified mechanic to diagnose the root cause of the problem and decide on the necessary repairs or maintenance. Understanding OBD2 codes empowers you to take proactive steps in maintaining your vehicle’s health.
Exploring the Four Main Types of OBD2 Error Codes
When your OBD2 scanner displays a code, recognizing its category is the first step towards effective diagnosis. OBD2 codes are broadly classified into four main types, each relating to a different area of your vehicle:
Powertrain Codes: Engine and Transmission Issues
Powertrain codes, starting with the letter ‘P’, are the most common type of OBD2 error codes. They indicate problems within the powertrain system, which encompasses the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. These codes are critical as they relate to the core functions of your vehicle’s power and performance.
For instance, a common powertrain code is P0101, indicating a “Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem.” The MAF sensor is crucial for measuring the amount of air entering the engine, enabling the car’s computer to calculate the optimal fuel-air mixture. A malfunctioning MAF sensor, as indicated by code P0101, can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, poor engine performance, and even increased emissions. Addressing powertrain codes promptly is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s efficiency and preventing further engine damage.
Body Codes: Issues with Comfort and Safety Systems
Body codes, identified by the letter ‘B’, signal problems within the vehicle’s body systems. These systems include components related to comfort, convenience, and safety, such as lighting, airbags, power windows, and climate control. While not directly related to the engine’s mechanical operation, body codes can highlight important safety and functionality issues.
An example of a body code is B0020, which indicates a “Driver Side Frontal Stage 2 Deployment Control.” This code points to a potential malfunction in the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit. A problem in this system is a serious safety concern because it means the airbag may not deploy correctly in a collision, compromising driver safety. Body codes often relate to electrical or sensor issues within these comfort and safety systems.
Chassis Codes: Suspension, Steering, and Braking Concerns
Chassis codes, starting with the letter ‘C’, relate to issues within the vehicle’s chassis and its related systems. This category includes vital systems like suspension, steering, and brakes, all of which are crucial for vehicle handling, stability, and safety. Chassis codes can indicate problems that directly impact driving safety and control.
Consider the chassis code C1234, which signifies a “Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.” Wheel speed sensors are essential for various safety systems, including the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC). If a wheel speed sensor malfunctions, as indicated by code C1234, it can compromise braking effectiveness, stability control, and overall handling, especially in challenging driving conditions. Prompt attention to chassis codes is critical for ensuring safe vehicle operation.
Network Communication Codes: Problems in Vehicle Communication
Network communication codes, denoted by the letter ‘U’, indicate issues within the vehicle’s communication network. Modern vehicles are complex networks of modules and sensors that communicate with each other to ensure all systems work in harmony. ‘U’ codes signal disruptions in this communication, which can affect various vehicle functions.
A common network communication code is U0100, indicating “Lost Communication With ECM/PCM ‘A’.” The Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is the brain of the engine management system. A U0100 code suggests a loss of communication with this critical module, often due to electrical issues, wiring problems, or module malfunction. Symptoms can range from reduced engine power and poor fuel efficiency to, in severe cases, engine stalling. Addressing network communication codes requires careful diagnosis to pinpoint the communication breakdown and restore proper vehicle network function.
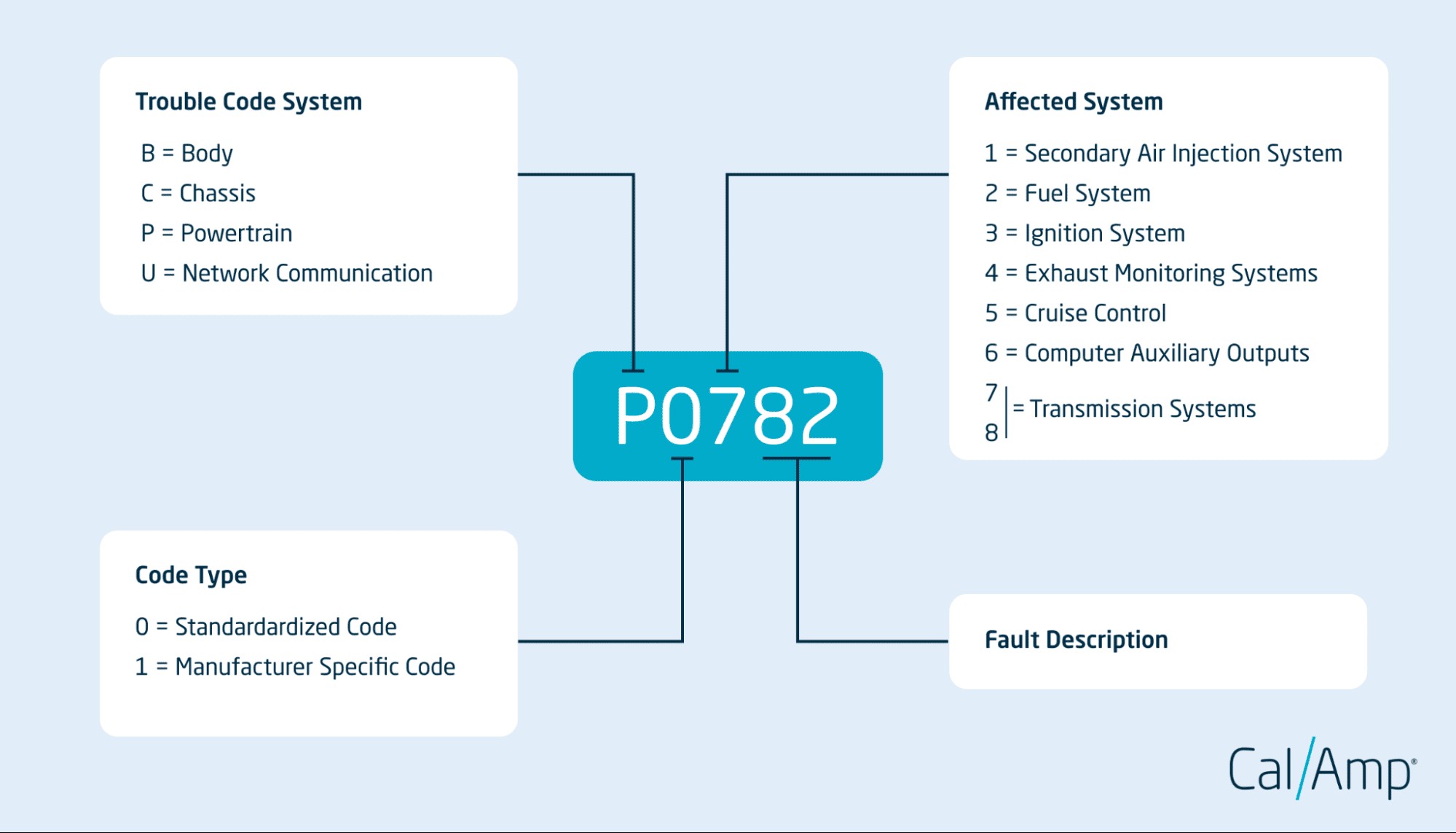 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Understanding OBD2 code structure, including trouble code system, code type, affected system, and specific code, is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Decoding the Structure of OBD2 Error Codes
OBD2 codes are not just random strings of characters; they follow a structured format that provides valuable diagnostic information. Each code consists of five characters: a letter followed by four digits. Understanding this structure can significantly aid in deciphering the problem.
-
First Character: Trouble Code System – This letter indicates the primary system affected:
- P – Powertrain (Engine, Transmission)
- B – Body (Comfort and Safety Systems)
- C – Chassis (Suspension, Steering, Brakes)
- U – Network Communication
-
Second Character: Code Type – This digit specifies whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0 – Generic or Standardized Code: These codes are common across all makes and models and are defined by SAE standards. For example, P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold) is a generic code.
- 1 – Manufacturer-Specific Code: These codes are defined by the vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information specific to a particular make or model. For example, P1101 might be a manufacturer-specific code related to the air intake system in a particular vehicle brand.
-
Third Character: Affected System – This digit indicates the subsystem affected. The common categories are:
- 1 – Fuel and Air Metering
- 2 – Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
- 3 – Ignition System or Misfire
- 4 – Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5 – Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
- 6 – Computer Output Circuit
- 7 & 8 – Transmission
4 & 5. Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Code – These final two digits provide a more specific number that, combined with the preceding characters, pinpoints the exact nature of the problem. For example, in the code P0420, ’20’ specifies the exact nature of the catalytic converter issue within the powertrain and emissions system.
By understanding this structure, you can begin to interpret OBD2 codes more effectively, narrowing down the potential problem area even before consulting a repair manual or mechanic.
Clearing OBD2 Codes: When and How
While clearing an OBD2 code might seem like a quick fix, it’s crucial to understand when it’s appropriate and how to do it correctly. Generally, simply clearing a code without addressing the underlying issue is not recommended as the problem, and the “Check Engine” light, will likely return. However, there are situations where clearing a code can be useful, such as after performing a repair to confirm the issue is resolved, or in cases of intermittent errors. Here are three common methods for clearing OBD2 codes:
Using an OBD2 Scanner to Clear Codes
OBD2 scanners are not only useful for reading codes but also for clearing them. Most scanners have a “clear codes” or similar function. Once you’ve diagnosed and addressed the issue causing the code, you can use the scanner to clear it. This will turn off the “Check Engine” light. If the problem is genuinely fixed, the light should stay off. If the light comes back on shortly after clearing, it indicates the underlying issue persists and requires further attention. Using an OBD2 scanner to clear codes is a convenient method for DIYers and car owners who want to manage minor issues themselves.
The Drive Cycle Method
In some instances, particularly for less severe or intermittent issues, an OBD2 code might clear itself after a “drive cycle.” A drive cycle is a specific set of driving conditions that allows the vehicle’s computer to re-run diagnostics and confirm if the problem is no longer present. This typically involves driving at varying speeds and conditions over a set period. The exact drive cycle procedure can vary by vehicle manufacturer, and it’s usually detailed in the vehicle’s service manual. While drive cycles can sometimes clear codes, they are not a guaranteed solution for all types of problems and are less effective for serious mechanical or electrical faults.
Seeking Professional Mechanic Assistance
If you are unsure about the cause of an OBD2 code, or if the code returns immediately after clearing, it’s always best to consult a professional mechanic. Mechanics have the expertise, diagnostic tools, and experience to accurately identify the root cause of the problem. They can perform thorough inspections, not just read and clear codes, ensuring that the underlying issue is properly resolved and not just masked by clearing the code. Furthermore, mechanics can advise on necessary repairs and maintenance to prevent future issues. For complex OBD2 errors or persistent “Check Engine” lights, professional help is the most reliable approach to ensure your vehicle is correctly diagnosed and repaired.
Preventing OBD2 Codes: Proactive Vehicle Maintenance
Preventing OBD2 codes is always better than reacting to them. Proactive vehicle maintenance is key to minimizing the occurrence of error codes and ensuring your vehicle operates reliably and efficiently. Here are two fundamental strategies for preventing OBD2 codes:
Regular Vehicle Maintenance Schedules
Regular maintenance is the cornerstone of preventing many vehicle problems, including those that trigger OBD2 codes. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual, is crucial. This schedule includes routine tasks like oil changes, filter replacements (air, fuel, cabin), spark plug inspections and replacements, fluid checks and top-ups (coolant, brake fluid, transmission fluid), and regular inspections of brakes, tires, and other critical components. Addressing minor issues during routine maintenance, such as replacing worn spark plugs or changing dirty filters, can prevent these small problems from escalating into larger issues that trigger OBD2 codes and potentially lead to costly repairs.
Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
The quality of fuel and fluids you use in your vehicle significantly impacts its performance and longevity. Using high-quality fuel from reputable stations ensures proper combustion and minimizes deposits that can affect engine and emission system components. Similarly, using manufacturer-recommended, high-quality fluids like engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, and brake fluid is essential. These fluids are formulated to provide optimal lubrication, cooling, and protection for your vehicle’s systems. Using low-quality or incorrect fluids can lead to increased wear and tear, overheating, and malfunctions that can trigger OBD2 codes. Regularly checking fluid levels and ensuring they are topped up with the correct, high-quality fluids is a simple yet effective way to prevent many common OBD2 error codes related to engine and transmission performance.
By adopting these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering OBD2 error codes, maintain your vehicle in optimal condition, and avoid unexpected repairs.
Conclusion: Empower Yourself with OBD2 Code Knowledge
OBD2 error codes are a vital communication tool from your vehicle, providing insights into its health and potential issues. Understanding what these codes mean, how to interpret their structure, and how to respond appropriately is crucial for every car owner. While tools like OBD2 scanners and basic maintenance can empower you to handle minor issues, remember that professional mechanic assistance is invaluable for complex or persistent problems. By being proactive in vehicle maintenance and informed about OBD2 codes, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable, efficient, and on the road for longer.
