If you’re in charge of a fleet of trucks or cars, understanding “OBD2 error codes” is essential, and it’s simpler than you might think. OBD2 codes are essentially messages from your vehicles, communicating what’s happening internally. For fleet managers and vehicle owners alike, grasping these codes can significantly improve vehicle care and ensure smooth operations.
This guide will clarify what OBD2 error codes are, how they function, and their importance for managing your vehicles. We’ll also explore effective strategies for handling OBD2 codes for your fleet, regardless of its size.
What are OBD2 Error Codes?
Onboard diagnostics (OBD2 error codes) are alphanumeric codes generated by your vehicle’s computer system. They serve as a communication method, alerting you to detected problems within the vehicle’s various systems.
Components throughout your vehicle, including the engine, transmission, and emissions systems, constantly exchange data with the onboard computer. When an anomaly occurs in your vehicle’s operation, the computer generates a corresponding error code.
These codes indicate a range of issues, from minor inconsistencies to potentially serious problems. For example, the illumination of the “Check Engine” light usually signifies that a system or component within the vehicle’s engine is not performing as expected.
To diagnose the issue, you can connect an OBD2 code reader to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard. This reader will display a diagnostic trouble code that pinpoints the underlying problem.
This code provides valuable guidance, helping you or a mechanic identify the precise source of the issue. It’s a crucial tool for effective troubleshooting and informed decision-making in fleet operations.
Understanding the Types of OBD2 Error Codes
When an OBD2 error code appears in one of your fleet vehicles, it’s important to determine its specific type to understand the general area of the problem.
These codes are categorized into four primary types, and understanding these categories will aid in efficient diagnosis and resolution.
Powertrain Codes
A powertrain code is an OBD2 code that signals issues within the vehicle’s engine, transmission, and drivetrain. These codes offer critical insights into problems affecting your vehicle’s power and performance.
For instance, consider the powertrain code P0101. This code suggests a potential problem with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor. The MAF sensor measures the air entering the engine, helping the vehicle’s computer calculate the correct fuel-air mixture for optimal performance. A malfunctioning MAF sensor can lead to issues like reduced fuel efficiency and diminished engine performance.
Body Codes
A body code is a specific OBD2 code type that indicates potential problems within the vehicle’s body systems, such as lighting, airbags, and climate control.
For example, the body code B0020 indicates a fault in the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit. If this circuit is not functioning correctly, the driver’s side airbag might not deploy properly in a collision. This poses a significant safety hazard, as airbags are vital for occupant protection during accidents.
Chassis Codes
A chassis code is a distinct OBD2 code type that identifies potential issues within the vehicle’s chassis and related systems, including the suspension, steering, and brakes.
For example, the chassis code C1234 indicates a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor. A malfunctioning wheel speed sensor can have several negative impacts. It can compromise the vehicle’s stability and handling, making it unsafe to drive, especially in adverse conditions. Additionally, it can interfere with the anti-lock braking system (ABS), reducing braking effectiveness.
Network Communication Codes
Network communication codes are a specific type of OBD2 code that identifies potential problems within the vehicle’s communication networks, including modules and sensors that exchange information.
Consider the network communication code U0100, which indicates a loss of communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM). This issue is often related to a weak or failing battery. When the U0100 code appears, you might experience symptoms like reduced engine power, slow acceleration, and decreased fuel economy. In some cases, this communication failure can even cause the engine to stall while driving, creating a serious safety risk.
Decoding OBD2 Error Codes: Understanding the Structure
OBD2 codes are composed of five characters – a letter followed by four digits – each carrying specific information.
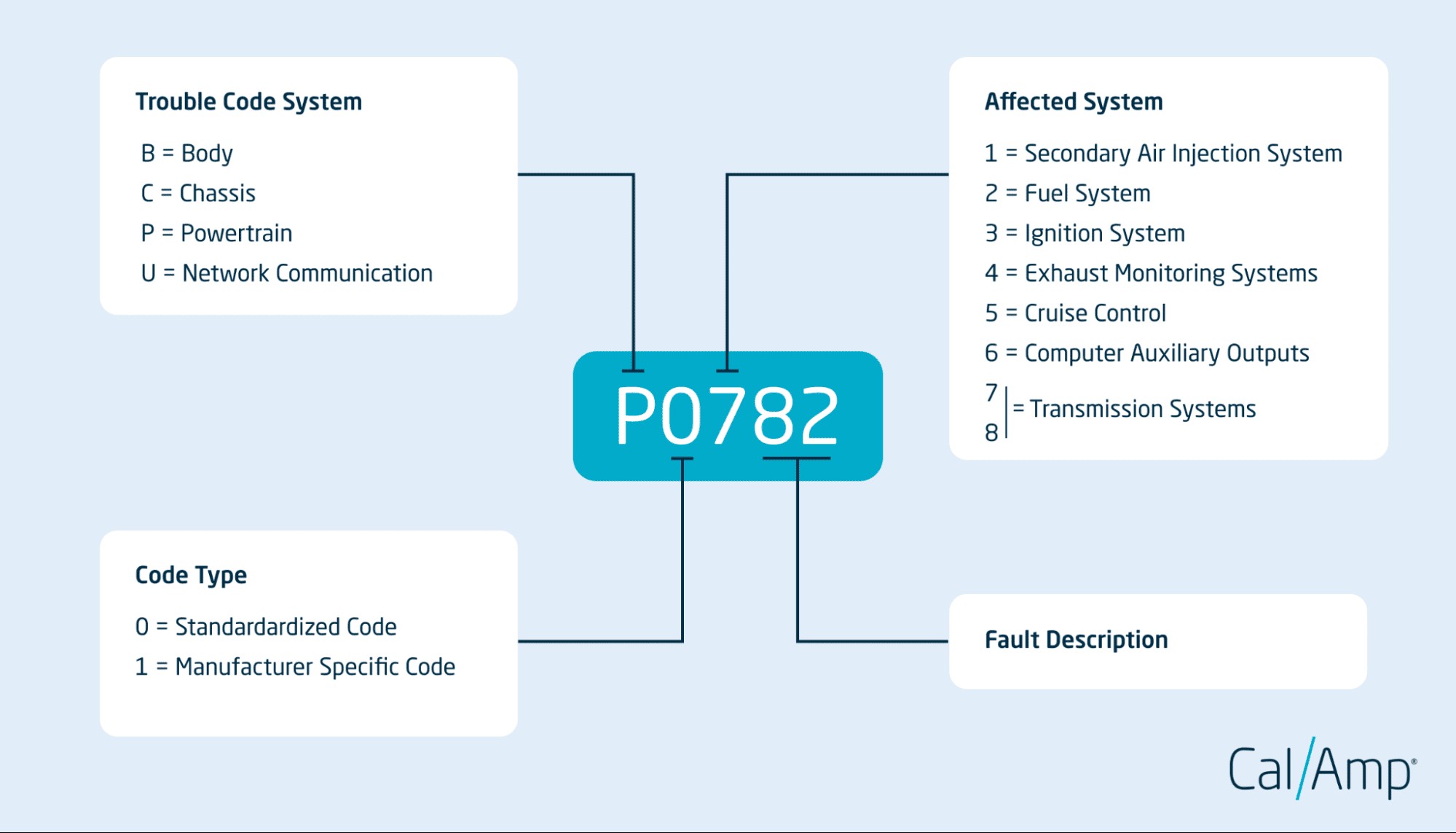 Diagram showing the structure of an OBD2 code and the meaning of each character
Diagram showing the structure of an OBD2 code and the meaning of each character
Each element, including the trouble code system, code type, affected system, and specific code, is crucial for accurately diagnosing the problem.
Trouble Code System: The First Letter
The first letter of an OBD2 code identifies the primary system affected:
- P (Powertrain): Relates to the engine, transmission, and associated drivetrain components.
- C (Chassis): Indicates issues with chassis-related systems like brakes, suspension, and steering.
- B (Body): Pertains to body systems such as airbags, power windows, and lighting.
- U (Network Communication): Signals communication issues between different vehicle modules and systems.
Code Type: The Second Character (Digit)
The second character, a digit, specifies whether the code is a standardized or manufacturer-specific code:
- 0 (Standardized Code): These are generic codes defined by SAE International and are common across all vehicle makes and models. For example, ‘P0420’ is a standardized code typically indicating a catalytic converter issue.
- 1 (Manufacturer-Specific Code): These codes are defined by the vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information specific to that brand. For instance, ‘P1101’ might be a manufacturer-specific code related to the air intake system in a particular vehicle brand.
Affected System: The Third Character (Digit)
The third character, a digit, denotes the specific subsystem within the broader system (powertrain, body, chassis, or network) that is experiencing the problem. Common affected systems include:
- 1: Secondary Air Injection System: Issues with the system that injects air into the exhaust to reduce emissions.
- 2: Fuel System: Problems related to fuel delivery, metering, or emissions from the fuel system.
- 3: Ignition System: Malfunctions in the system responsible for spark generation and ignition.
- 4: Exhaust Monitoring System: Issues with components monitoring and controlling exhaust emissions (e.g., oxygen sensors, catalytic converter).
- 5: Cruise Control & Idle Control System: Problems within the cruise control or idle speed regulation systems.
- 6: Computer & Auxiliary Outputs: Difficulties with the vehicle’s computer or outputs controlling various functions.
- 7 & 8: Transmission System: Concerns within the automatic transmission, including shift solenoids and gear selection.
Specific Code: The Last Two Characters (Digits)
The last two digits provide a highly specific identifier of the fault within the affected system. For example, in the code “P0420”, the “20” further specifies the problem as related to the catalytic converter’s efficiency in the powertrain system.
Reading OBD2 Error Codes: Tools and Techniques
Reading OBD2 error codes requires a diagnostic tool, commonly known as an OBD2 scanner or code reader. These devices connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and retrieve the stored error codes.
Using an OBD2 Scanner:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port.
- Turn Ignition to “ON”: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This powers up the vehicle’s computer systems.
- Read Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read and display the stored OBD2 error codes.
- Record Codes: Note down the displayed codes for diagnosis and repair.
OBD2 scanners range from basic, handheld units that only read and clear codes to more advanced, professional-grade tools that offer live data streaming, detailed diagnostics, and repair information. For fleet management, investing in a capable OBD2 scanner can significantly streamline maintenance and diagnostics.
Clearing OBD2 Error Codes: Methods and Precautions
While clearing OBD2 error codes might seem like a quick fix, it should generally be done after addressing the underlying issue. However, there are situations where clearing codes is necessary or helpful. Here are three methods:
OBD2 Scanner Method
OBD2 scanners not only read codes but also offer the functionality to clear them.
- Procedure: After reading the codes and addressing the problem (or deciding to clear them for other reasons), use the scanner’s “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” function.
- Caution: Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The code and light will likely reappear if the underlying issue persists.
Drive Cycle Method
Some OBD2 codes may clear themselves after a successful “drive cycle.” This involves driving the vehicle under specific conditions that allow the vehicle’s computer to re-evaluate the system and clear the code if the problem is no longer detected.
- Procedure: Drive cycles vary by manufacturer and code. Generally, they involve a combination of city and highway driving at varying speeds and engine temperatures. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or online resources for the specific drive cycle for your vehicle.
- Limitations: Drive cycles are not effective for all types of codes and can be time-consuming and not always reliable.
Professional Mechanic Method
Consulting a professional mechanic is always a reliable option, especially if you are unsure about the cause of the OBD2 code or how to properly address it.
- Procedure: A mechanic will use professional diagnostic tools to read and clear codes, but more importantly, they will diagnose the root cause of the problem. They can then perform necessary repairs and ensure the codes are cleared correctly after the repair.
- Benefits: Mechanics have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and fix complex issues, preventing further damage and ensuring long-term vehicle reliability.
Preventing OBD2 Error Codes: Proactive Maintenance
Preventing OBD2 error codes is crucial for avoiding costly repairs and maintaining the uptime of your fleet vehicles.
Two key strategies for preventing OBD2 codes are regular vehicle maintenance and using quality fuel and fluids.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Regular maintenance is the cornerstone of preventing OBD2 error codes. Routine inspections, fluid changes, and timely repairs can address minor issues before they escalate and trigger error codes.
- Routine Tasks: Include regular oil changes, air filter replacements, spark plug inspections, brake system checks, tire rotations, and inspections of belts and hoses.
- Scheduled Timing: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule outlined in the vehicle’s owner’s manual. This schedule considers mileage and time intervals for specific maintenance tasks.
- Professional Service: Consider utilizing professional mechanics for comprehensive maintenance services. They can conduct thorough inspections, identify potential problems early, and perform preventative maintenance to minimize the risk of OBD2 codes.
Use of Quality Fuel and Fluids
Using high-quality fuel and fluids is equally important for preventing OBD2 codes. Low-quality fluids can lead to inadequate lubrication, increased wear, and potential engine or transmission codes. Inferior fuel can cause incomplete combustion, leading to performance issues and emissions-related codes.
- Fuel Quality: Choose reputable gas stations and use fuel that meets or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended octane rating.
- Fluid Quality: Use manufacturer-recommended fluids, including engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, and brake fluid. These fluids are formulated to meet specific vehicle requirements and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Regular Fluid Checks: Periodically check fluid levels, especially engine oil and coolant, and top them off as needed to maintain proper lubrication and cooling.
Managing OBD2 Error Codes for Your Fleet: Efficient Strategies
For fleet managers, effectively managing OBD2 error codes across a fleet of vehicles requires a systematic and streamlined approach. Standardization and automation can significantly improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
Centralized Code Tracking Systems
Centralizing OBD2 code tracking involves aggregating diagnostic data from all fleet vehicles into a single, accessible system. This simplifies data management and provides a comprehensive overview of vehicle health. Solutions like the CalAmp iOn offer real-time insights into code occurrences, vehicle performance metrics, and maintenance needs.
- Real-time Visibility: Centralized systems provide immediate notifications of OBD2 codes as they occur, enabling prompt responses.
- Historical Data Analysis: Analyzing historical code data can reveal patterns and trends, helping identify recurring issues with specific vehicles or systems. This data-driven approach supports proactive maintenance planning and targeted repairs.
Ongoing Fleet Monitoring with Telematics
Implementing ongoing fleet monitoring using telematics systems provides continuous data collection from fleet vehicles, including location, performance data, and OBD2 error codes.
- Real-time Detection: Telematics systems enable immediate detection of OBD2 codes and associated issues, allowing for rapid response and minimizing vehicle downtime.
- Proactive Maintenance: Continuous monitoring facilitates proactive maintenance by identifying potential problems early, before they escalate into major breakdowns.
- Cost Reduction: By preventing breakdowns and optimizing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency, ongoing monitoring contributes to significant cost savings in fleet operations.
Prioritized Repair Scheduling
Fleet managers should implement a system for prioritizing repairs based on the severity of OBD2 codes and their potential impact on vehicle operation.
- Severity-Based Prioritization: Categorize codes based on their urgency, from critical codes requiring immediate attention to less severe codes that can be addressed during scheduled maintenance.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Prioritizing repairs ensures that resources are allocated effectively, focusing on addressing critical issues first to minimize vehicle downtime and maintain operational continuity.
In Summary: Leveraging OBD2 Error Codes for Vehicle Health
OBD2 error codes are invaluable diagnostic messages from your vehicle’s computer, signaling a wide range of potential issues, from minor sensor glitches to significant mechanical problems. Recognizing and understanding these codes is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicles.
While basic OBD2 scan tools are useful for reading codes and diagnosing problems, comprehensive fleet management solutions like CalAmp offer enhanced capabilities. These systems not only read codes but also provide real-time data on vehicle performance, location tracking, and proactive maintenance alerts.
Request a demo today to discover how CalAmp iOn can provide complete visibility and control over your fleet, optimizing maintenance and ensuring vehicle uptime.