As a vehicle owner or fleet manager, encountering an illuminated check engine light can be concerning. Often, this signal is accompanied by an OBD2 powertrain code, a diagnostic message from your vehicle’s onboard computer indicating an issue within the powertrain system. Understanding these codes is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and repair, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
This guide will delve into the world of Obd2 Powertrain Codes, explaining what they are, how to interpret them, and why they are essential for maintaining your vehicles. We will explore the intricacies of powertrain codes, their impact on vehicle operation, and how to effectively manage them for both personal vehicles and entire fleets.
What are OBD2 Powertrain Codes?
OBD2 powertrain codes are a subset of On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) codes, specifically designed to report problems within your vehicle’s powertrain. The powertrain is the heart of your vehicle’s operation, encompassing the engine, transmission, and related systems that generate and deliver power to the wheels.
When the vehicle’s computer, also known as the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM), detects a malfunction within the powertrain, it generates a specific powertrain code. These codes are standardized alphanumeric identifiers that provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
Think of powertrain codes as specific error messages. They can range from minor issues like a loose gas cap (which can trigger an emissions-related powertrain code) to more significant problems within the engine or transmission. Recognizing and understanding these codes is the first step towards diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues efficiently.
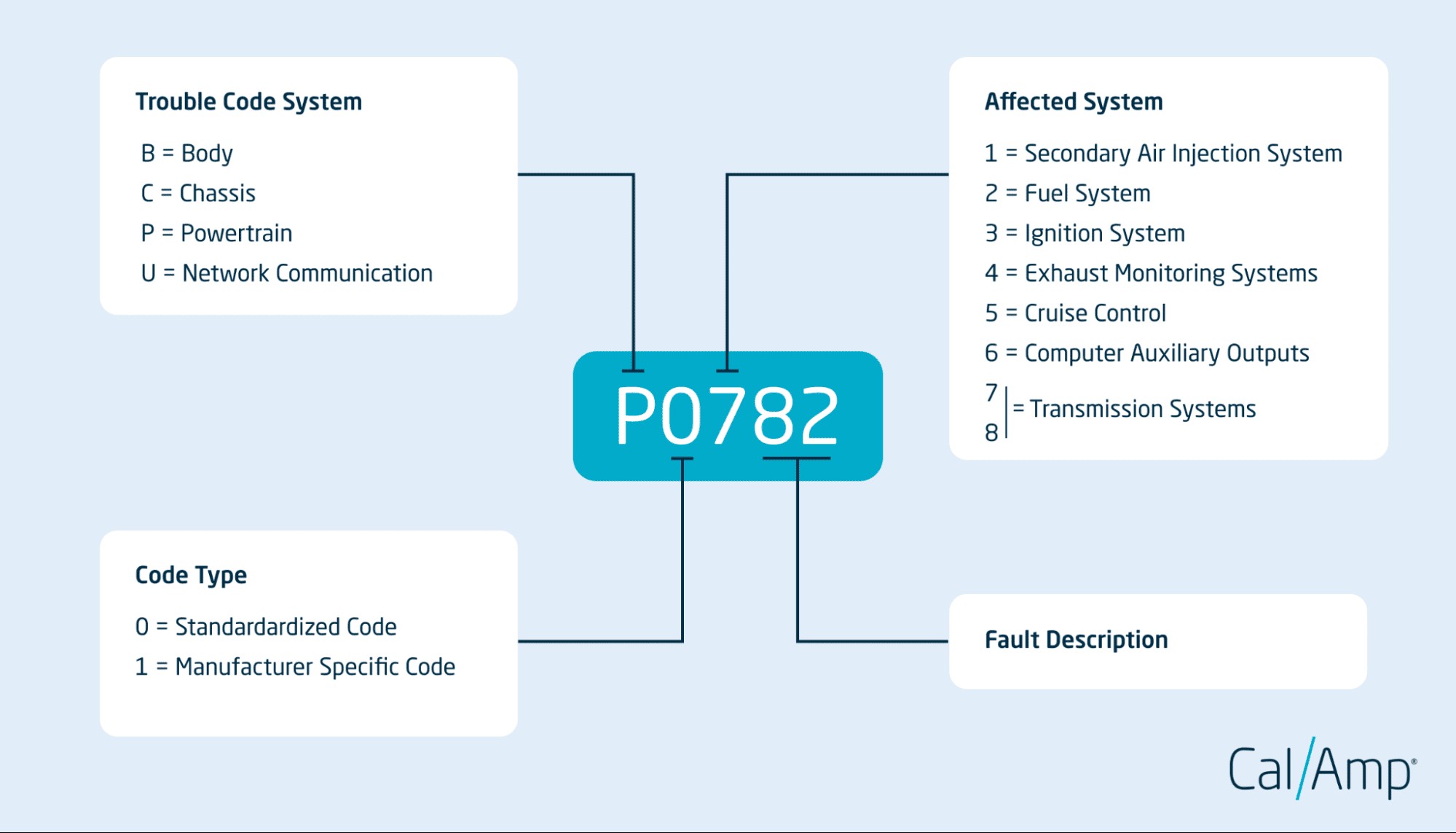 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Decoding the “P” in OBD2 Powertrain Codes
OBD2 codes are structured in a five-character format. The very first character is a letter that designates the system where the fault has occurred. For powertrain codes, this letter is always “P”. This “P” immediately tells you that the detected issue is related to the engine, transmission, or drivetrain.
For example, codes starting with “P” could indicate problems with:
- Engine Performance: Issues with fuel delivery, air intake, ignition, or exhaust systems.
- Transmission Function: Problems with gear shifting, transmission fluid pressure, or internal transmission components.
- Emissions Control: Malfunctions in sensors or components designed to reduce vehicle emissions, often directly linked to engine performance.
- Drivetrain Components: Although less common, some powertrain codes can point to issues in the transfer case or differentials in four-wheel-drive vehicles if they are electronically controlled and monitored by the PCM.
Knowing that a code starts with “P” narrows down the potential problem area significantly, helping you or a mechanic focus diagnostic efforts on the powertrain system.
Understanding the Numbering System of Powertrain Codes
After the “P”, the subsequent four characters in an OBD2 powertrain code provide further details about the specific problem. Let’s break down the meaning of each position:
-
Second Character (Digit): Code Type
- 0: Indicates a generic or standardized code. These codes are common across all vehicle makes and models and are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
- 1, 2, or 3: Indicates a manufacturer-specific code. These codes are defined by the vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information specific to that brand’s systems and components.
-
Third Character (Digit): Subsystem
This digit further categorizes the area within the powertrain system that is experiencing the problem. Common categories for powertrain codes include:- 1: Fuel and Air Metering (e.g., MAF sensor, O2 sensors, fuel injectors)
- 2: Fuel and Air Metering – Injector Circuit
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire (e.g., spark plugs, ignition coils)
- 4: Auxiliary Emission Controls (e.g., EGR system, secondary air injection)
- 5: Vehicle Speed Controls & Idle Control System
- 6: Computer Output Circuit
- 7, 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters (Digits): Specific Fault
These last two digits pinpoint the exact component or circuit malfunction within the subsystem identified by the third digit. For example, within the “Fuel and Air Metering” subsystem (digit 1), codes like P0101, P0102, and P0103 all relate to the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor but indicate different specific issues like range/performance problems, low input, or high input, respectively.
Example: Let’s take the powertrain code P0301.
- P: Powertrain
- 0: Generic (Standardized) Code
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire
- 01: Specific Fault – Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
This code clearly tells you there is a misfire occurring in cylinder number 1 of the engine. This information is incredibly valuable for a mechanic to start diagnosing the root cause, which could be a faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, or other related issues in cylinder 1.
Common OBD2 Powertrain Codes and Their Meanings
While there are thousands of possible OBD2 powertrain codes, some are more frequently encountered than others. Here are a few common examples and their general meanings:
- P0171 / P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 1 / Bank 2): Indicates that the engine is running with too much air and not enough fuel. This could be due to vacuum leaks, fuel delivery issues, or faulty sensors.
- P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected: Signifies that the engine is misfiring in one or more cylinders randomly. Possible causes include worn spark plugs, faulty ignition coils, or vacuum leaks.
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1): Points to a problem with the catalytic converter’s efficiency in reducing emissions. This could indicate a failing catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensors, or exhaust leaks.
- P0700 – Transmission Control System Malfunction: A general transmission fault code indicating that the transmission control system has detected a problem. Further diagnosis with a more advanced scanner or professional mechanic is usually required to pinpoint the specific transmission issue.
- P0741 – Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off: Indicates a problem with the torque converter clutch in the automatic transmission. This can affect fuel economy and driving performance.
It’s important to remember that these are just general descriptions. The exact meaning and potential causes of a specific code can vary slightly depending on the vehicle make, model, and year. Always consult a reliable OBD2 code database or repair information specific to your vehicle for accurate interpretation.
Diagnosing and Addressing OBD2 Powertrain Codes
When an OBD2 powertrain code appears, prompt diagnosis and repair are crucial to prevent further damage and maintain vehicle performance. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
-
Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the stored powertrain code(s) from your vehicle’s computer. These scanners are readily available for purchase or can be used at most auto parts stores or repair shops.
-
Research the Code: Once you have the code, research its meaning. Online OBD2 code databases, repair manuals, and websites like Carparteu.com are valuable resources. Understand the potential symptoms and common causes associated with the specific code.
-
Visual Inspection: Before jumping to conclusions, perform a visual inspection of the engine bay and related powertrain components. Check for:
- Loose gas cap
- Vacuum leaks (hoses that are cracked, disconnected, or broken)
- Damaged wiring or connectors to sensors and actuators
- Fluid leaks (oil, coolant, transmission fluid)
-
Basic Troubleshooting (If Comfortable): For some simpler codes, you might be able to perform basic troubleshooting yourself. For example, if you have a code related to a specific sensor, you could check its wiring and connections. However, for complex powertrain issues, it’s generally best to consult a professional.
-
Professional Diagnosis and Repair: For most powertrain codes, especially those related to engine or transmission internals, seeking professional help from a qualified mechanic is recommended. Mechanics have the expertise, specialized tools, and diagnostic equipment to accurately pinpoint the root cause and perform the necessary repairs.
Preventing OBD2 Powertrain Codes Through Proactive Maintenance
Prevention is always better (and cheaper) than cure. Regularly maintaining your vehicle’s powertrain system is the most effective way to minimize the occurrence of OBD2 powertrain codes.
- Regular Oil Changes: Engine oil lubricates and cools engine components. Regular oil changes with the correct type and viscosity are crucial for engine health and preventing wear and tear that can trigger codes.
- Transmission Fluid Service: Automatic transmissions require regular fluid changes to ensure proper lubrication and cooling. Neglecting transmission fluid service can lead to transmission overheating and failures, resulting in powertrain codes.
- Air and Fuel Filter Replacement: Clean air and fuel filters are essential for proper engine operation and fuel efficiency. Clogged filters can restrict airflow and fuel delivery, leading to performance issues and potentially triggering powertrain codes.
- Spark Plug and Ignition System Maintenance: Spark plugs have a limited lifespan and need to be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Faulty spark plugs or ignition components can cause misfires and trigger powertrain codes.
- Regular Inspections: Routine vehicle inspections, including checking hoses, belts, fluids, and sensors, can help identify potential problems early before they escalate and trigger OBD2 codes.
![Picture #5]
Managing OBD2 Powertrain Codes in Fleet Operations
For fleet managers, effectively managing OBD2 powertrain codes is crucial for minimizing vehicle downtime, controlling maintenance costs, and ensuring operational efficiency.
- Centralized Code Monitoring: Implementing a system for centralized OBD2 code monitoring across the fleet can provide real-time visibility into vehicle health. Telematics systems can automatically collect and report OBD2 codes, allowing fleet managers to proactively identify and address issues.
- Prioritized Maintenance Scheduling: Based on the severity of the powertrain codes and their impact on vehicle operation, fleet managers can prioritize maintenance schedules. Critical powertrain issues should be addressed immediately to prevent breakdowns and safety risks, while less severe codes can be scheduled for maintenance during routine service intervals.
- Data-Driven Maintenance Decisions: Analyzing historical OBD2 powertrain code data can reveal trends and patterns, helping fleet managers identify common issues across specific vehicle models or operational conditions. This data can inform preventative maintenance strategies and optimize fleet maintenance schedules.
- Integration with Fleet Management Software: Integrating OBD2 code data with comprehensive fleet management software can streamline maintenance workflows, automate repair scheduling, and track repair costs associated with specific powertrain codes.
In Summary
OBD2 powertrain codes are vital diagnostic tools that provide insights into the health of your vehicle’s engine, transmission, and related systems. Understanding how to interpret these codes, performing proactive maintenance, and leveraging technology for fleet management are key to ensuring vehicle reliability, optimizing performance, and minimizing repair costs. By taking a proactive approach to OBD2 powertrain codes, you can keep your vehicles running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
For advanced fleet management solutions that integrate OBD2 powertrain code monitoring and provide real-time vehicle health insights, consider exploring telematics systems designed for commercial fleets. They offer a comprehensive approach to vehicle maintenance and operational efficiency.
