The car battery is essential for starting your vehicle and powering electrical components. But have you ever wondered how this battery stays charged while you drive? The answer lies in a crucial component: the alternator. This is the primary part of your car responsible for charging the battery and ensuring your vehicle’s electrical systems run smoothly.
The Alternator: Your Car’s Battery Charger
The alternator is essentially a generator driven by your engine. It converts mechanical energy from the engine’s rotation into electrical energy. Located typically at the front of the engine and driven by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft, the alternator spins as the engine runs. This spinning motion is what generates the electricity needed to recharge your car battery and power your vehicle’s electrical accessories while driving.
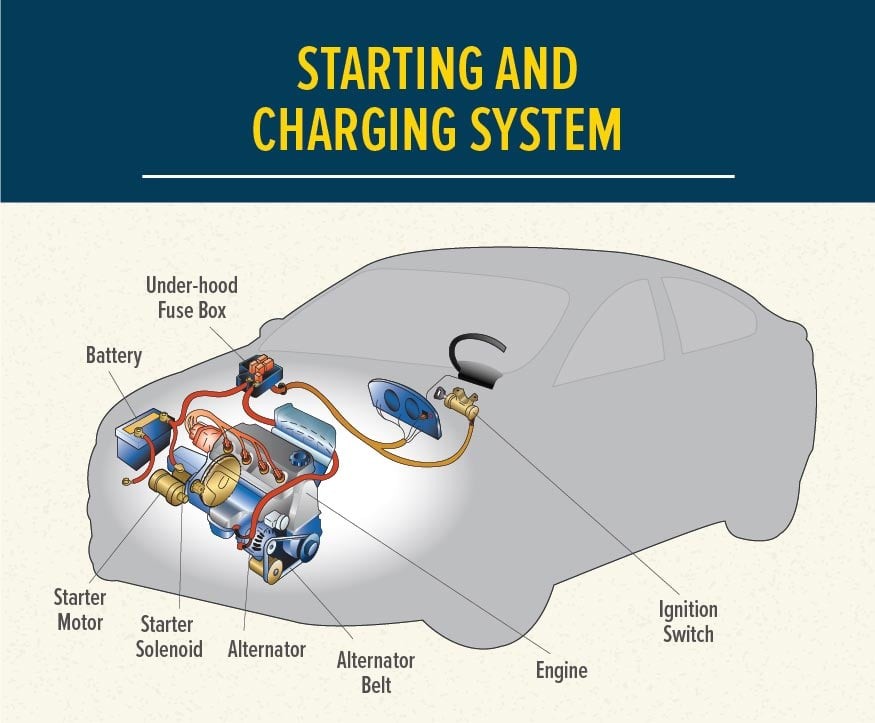 Vehicle Starting and Charging System
Vehicle Starting and Charging System
Alt text: Diagram illustrating a vehicle’s starting and charging system, highlighting the battery, alternator, ignition switch and starter motor and their connections.
The electricity produced by the alternator is not just a raw output; it’s regulated to ensure it’s suitable for your car’s electrical system and battery. This regulation is handled by the voltage regulator, often integrated into the alternator itself. The voltage regulator’s job is to maintain a consistent voltage level, protecting the battery from overcharging and ensuring that all electrical components receive the correct amount of power. Without this regulation, the battery could be damaged by excessive charging, and sensitive electronics could malfunction.
The Car Battery and the Charging Cycle
While the alternator is the charging component, the car battery itself plays a vital role in the overall charging system. The battery’s primary function is to provide the initial surge of power needed to start the engine. It also acts as a stabilizer in the electrical system, smoothing out voltage fluctuations and providing резерв power for short-term use of accessories when the engine is off.
When you start your car, the battery discharges to power the starter motor. Once the engine is running and the alternator kicks in, the charging process begins. The alternator supplies power to run systems like headlights, windshield wipers, the radio, and importantly, it replenishes the energy used from the battery during starting and operation. This continuous cycle of discharge and recharge is fundamental to how your car’s electrical system operates.
Alt text: Close-up interior view of a lead-acid car battery showing the internal plates and electrolyte solution, illustrating the technology used for energy storage and chemical reactions.
Maintaining a Healthy Charging System
To ensure your car battery remains properly charged and your electrical system functions reliably, regular maintenance is beneficial. Periodically checking your battery terminals for corrosion and cleaning them can improve electrical conductivity. Having your battery and charging system tested, especially before long trips or seasonal changes, can identify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns.
Understanding the role of the alternator as the “Part Of Car That Charges Battery” is crucial for car owners. A functioning alternator is essential for a healthy car battery and a dependable vehicle. By recognizing its importance and performing regular checks, you can help ensure your car starts reliably and runs smoothly for years to come.
