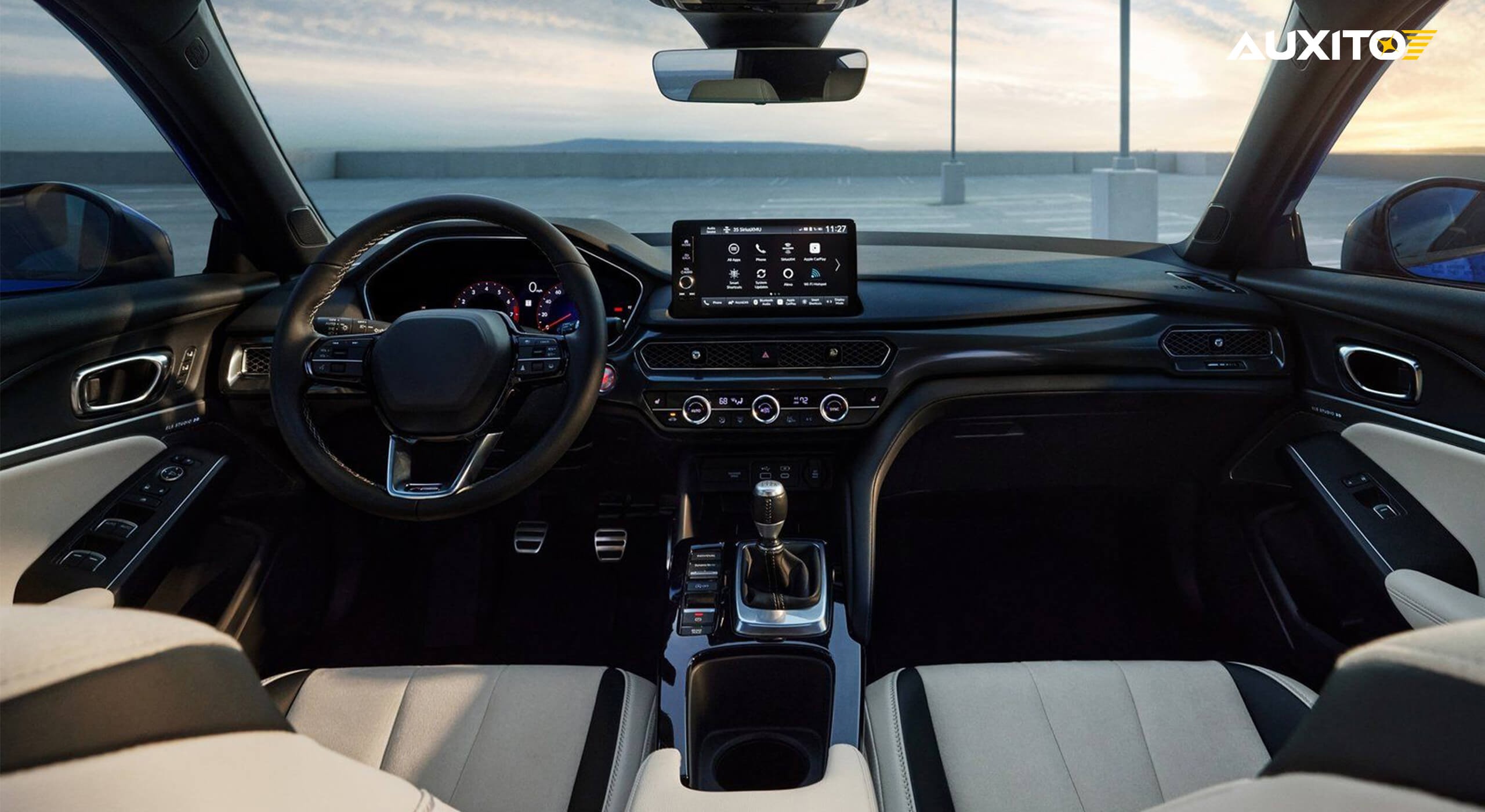
After exploring the exterior components of a vehicle, it’s natural to be curious about what’s inside. This guide dives into the Parts Of A Car Interior, explaining their names and functions. Understanding these components is essential for informed car shopping, maintenance, and upgrades, ensuring a safer and more comfortable driving experience.
Interior Components Breakdown
Section 1: Driving Controls and Performance
Section 2: Safety and Signaling Features
Section 3: Convenience and Utility
Section 4: Entertainment and Connectivity
Section 5: Comfort and Cabin Environment
Conclusion
FAQ
Section 1: Driving Controls and Performance {#driving-controls-performance}
Steering Wheel and Horn
The steering wheel is the primary control for directing the vehicle. Often called a hand wheel or drive wheel, it allows drivers to manually control the car’s direction. Integrated into the steering wheel is the car horn, typically located in the center. The horn is a crucial safety feature, producing a loud sound to alert pedestrians and other vehicles, enhancing road safety.
Modern steering wheels often include additional controls for features like lights and audio systems. Furthermore, advancements in automotive technology have led to systems like Electric Power Steering (EPS) and Adaptive Steering, offering improved handling and responsiveness.
Ignition System
The ignition is where you initiate your car’s engine start, typically by inserting the key. It’s usually found on the steering column or dashboard. Turning the ignition key or pressing a start button activates the ignition switch, powering up the engine and enabling the vehicle to move.
Pedals
Car pedals are foot-operated controls that allow the driver to manage the vehicle’s speed and braking. Designed for responsiveness and ease of modulation, they ensure smooth and controlled driving. Proper pedal operation is crucial for safe and efficient driving. However, wet or snowy conditions can cause pedals to become slippery. Upgrading with brake pedal covers can enhance grip and safety by adding wear resistance and anti-slip properties.
Most cars feature three primary pedals:
- Accelerator Pedal (Gas Pedal): Controls fuel flow to the engine, regulating vehicle speed.
- Brake Pedal: Used to decelerate or stop the vehicle by activating the braking system, applying pressure to brake pads or shoes.
- Clutch Pedal (Manual Transmissions): Found in manual cars, it disengages the engine from the transmission for smooth gear changes.
These pedals work together, enabling the driver to precisely control the car’s speed and movement.
Gear Shift
The gear shift, or gear lever, allows the driver to select gears in both manual and automatic transmissions. Automatic transmissions use sensors to shift gears automatically, eliminating the clutch pedal and manual gear lever operation. Typically located on the center console or steering column for easy access, proper gear shifting improves driving safety and efficiency. Incorrect gear shifting can damage the transmission or engine.
Section 2: Safety and Signaling Features {#safety-signaling}
Dashboard and Instrument Cluster
The dashboard, centrally located in the console, is a vital control panel displaying critical vehicle information. It monitors performance, speed, engine status, and other key indicators, enabling drivers to manage the car effectively. Key components include:
- Fuel Gauge: Indicates the amount of fuel remaining, helping drivers plan refueling stops.
- Speedometer: Displays the vehicle’s current speed, assisting drivers in maintaining safe and legal speeds.
- Tachometer (RPM Gauge): Measures engine revolutions per minute, ensuring the engine operates within safe limits and aiding gear shifting in manual vehicles.
- Temperature Gauge: Shows the engine’s operating temperature, warning of overheating issues that may require coolant or indicate potential problems.
Dashboards also include warning and indicator lights that signal potential vehicle system issues or malfunctions.
Emergency Flasher (Hazard Lights)
Emergency flashers, or hazard lights, are crucial for signaling emergencies or hazardous situations to other road users. Usually located centrally near air vents or on the dashboard, activating the emergency flasher button causes all four turn signals to flash simultaneously. This highly visible signal alerts drivers, pedestrians, and emergency services to potential hazards or distress.
Seat Belts and Airbags
Seat belts are essential safety devices designed to protect occupants during sudden stops or accidents. They prevent occupants from being thrown forward or ejected in a collision. Airbags are supplemental safety features that provide additional protection during crashes or sudden deceleration. They deploy rapidly upon impact, cushioning the head, chest, and other vulnerable body parts, reducing the risk of serious injury.
Airbags and seatbelts work in tandem to maximize occupant safety and minimize collision impact. Airbags are supplementary restraints and do not replace seat belts; occupants should always wear seat belts correctly and ensure they are in good working order.
Rearview Mirrors
Rearview mirrors are angled mirrors attached to the windshield’s interior. Their design allows drivers to see vehicles behind without turning around. Most rearview mirrors offer manual adjustment for tilt and swivel, accommodating different driver heights and seating positions to ensure optimal rear visibility.
Emergency Brake (Parking Brake)
The emergency brake, also known as the parking brake or handbrake, is a safety feature used to secure a parked vehicle, preventing unintended movement. It typically consists of a lever or pedal, cables or linkages, and rear brakes.
To engage the emergency brake, pull the handle or depress the pedal fully. A warning light on the dashboard usually indicates engagement. Disengaging involves releasing a button or pushing the lever/pedal back to its resting position, at which point the warning light should turn off.
Turn Signal Lever (Indicator Stalk)
The turn signal lever, or indicator stalk, is located on the steering column and activates turn signals or indicators. Essential for signaling intended direction changes, it’s a crucial part of the vehicle’s safety system, communicating driver intentions to other road users.
Section 3: Convenience and Utility {#convenience-utility}
Center Console
The center console is the area between the front seats, serving as a functional and organizational hub. It provides storage, houses controls, and enhances convenience for drivers and passengers. Common features include:
- Cup Holders: Integrated holders for beverages, preventing spills.
- Armrests: Comfortable rests for the driver and front passenger’s arms, reducing fatigue on long drives.
- Storage Compartments: Bins with lids for storing personal items like phones, wallets, keys, and sunglasses.
Some consoles include removable trays or organizers for enhanced storage. Center consoles vary in shape, size, and style depending on vehicle make and model, and may include electrical outlets, charging ports, climate control, and audio system controls.
Glove Compartment (Glove Box)
The glove compartment, or glove box, is a small storage area located in the dashboard on the passenger side. Usually a hinged compartment with a locking mechanism, it provides convenient storage for documents, personal items, and essentials accessible to the driver and front passenger.
Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Power window and door lock controls are standard in modern vehicles, typically located on door armrests. They allow independent operation of each window and door lock, increasing vehicle comfort and safety. Power windows add convenience, while door locks enhance passenger safety, especially for children. Control designs vary; some cars have both power and manual door handles, while others rely solely on power controls. If window controls become unresponsive or buttons are damaged, replacing the power window switch may be necessary, ensuring compatibility with your vehicle model.
Interior Door Handles
Interior door handles, located inside each door, allow occupants to open and close doors from within the vehicle, providing essential convenience and accessibility. Designs vary across car models. Worn or damaged interior handles can be replaced with new, matching handles.
Section 4: Entertainment and Connectivity {#entertainment-connectivity}
Audio System (Car Stereo)
A car audio system provides in-vehicle audio entertainment and sound reproduction. It enables occupants to enjoy music, podcasts, radio, and other audio content while driving. Systems include components like a main unit, speakers, subwoofers, amplifiers, and equalizers.
The main unit, typically in the center console or dashboard, controls the audio system. Frequent use of radio button logos can cause fading. Button stickers offer a simple repair solution, avoiding costly replacements. Specific audio system features vary by vehicle make, model, and trim level.
Central Control Screen (Infotainment System)
The central control screen, or infotainment system, is a prominent feature in modern cars, acting as a hub for various functions and information. It includes entertainment systems for audio and video, navigation with real-time maps, and integration with cameras and sensors for enhanced visibility and safety. Features and interfaces vary by model and manufacturer, but the core purpose is a centralized, user-friendly control interface.
Section 5: Comfort and Cabin Environment {#comfort-cabin}
Ventilation Control and Air Vents
Car ventilation systems manage airflow, circulating fresh outside air to create a comfortable and healthy cabin environment. These systems adjust temperature, humidity, and air quality via the air conditioning switch knob on the control panel. Air vents, located throughout the cabin, direct airflow from the climate control system. Front vents are typically in the center and sides of the dashboard, while rear vents can be in the roof, center console, or under front seats. Adjustable vents allow passengers to direct airflow as needed.
Sun Visors
Sun visors, positioned above the windshield, adjust to block sunlight and glare, protecting the driver and passengers from harmful UV rays. Some visors include built-in mirrors or lights.
Car Seats
Car seats are designed for support and comfort with a strong frame and padding. Frames are typically metal or high-strength materials, and padding provides cushioning and shock absorption. Adjustable components like seat height, back angle, and lumbar support, controlled by seat handles, allow for personalized comfort.
Seat maintenance includes regular vacuuming to remove dirt and dust and applying leather or fabric conditioner to prevent cracking or fading. Car seat covers are a popular, easy-to-maintain alternative for seat protection and comfort, offering easy replacement and cleaning, especially leather seat covers.
Floor Mats
Car floor mats are protective accessories placed on the vehicle floor to shield the carpet from dirt, spills, and wear. They prevent shoe debris from spreading inside the car, maintaining a cleaner and healthier environment. Made from durable, easy-to-clean materials, floor mats can also enhance vehicle aesthetics and provide underfoot comfort.
Roof and Headliner
Car roofs and headliners are integral to the interior, providing structural support, insulation, and aesthetic appeal. The roof provides structural rigidity, protecting occupants in rollovers and crashes and withstanding weather elements. The headliner offers sound absorption and insulation, regulating cabin temperature and enhancing comfort. Together, they create a functional, comfortable, and visually appealing cabin space.
Conclusion {#conclusion}
From the dashboard to the pedals, and the center console to the roof, each car interior part plays a crucial role. These components work in harmony to create a safe and comfortable driving environment. Understanding their functions is vital for informed decisions when purchasing or upgrading a vehicle, ensuring an optimal driving experience.
For more information on vehicle exteriors, read our guide: Detail Guide to Exterior Car Parts: Exploring and What They Do
FAQ {#faq}
Q: What are car interior panels?
A: Car interior panels are components forming the vehicle’s interior, typically made of plastic, fabric, or leather. They provide functionality, aesthetics, and protection, mounted on interior surfaces. Examples include instrument panel panels, center console panels, door panels, roof liner panels, and column panels like A-pillars and B-pillars.
Q: What are the different types of car interiors?
A: Car interiors vary by design, material, and use. Common types include:
- Nylon Interior: Durable and porous, common, requires regular cleaning.
- Polyester Upholstery: Soft, comfortable, suede-like, stains easily, steam cleaning recommended.
- Vinyl Upholstery: Non-porous, waterproof, easy to clean with water, low maintenance.
- Leather Upholstery: Luxurious, elegant, high maintenance, used in luxury vehicles.
Q: What can I use to clean my car interior?
A: Recommended cleaning tools and products:
- Vacuum Cleaner: For loose dirt and debris on carpets and upholstery.
- Microfiber Cloths: For wiping dashboards, door panels, and delicate surfaces.
- Multi-purpose Cleaners: For general interior cleaning.
- Glass Cleaner: Specifically for windows and mirrors.
- Upholstery Cleaner: For stains and odors on fabric upholstery and carpets.
Q: How often should I clean my car interior?
A: Cleaning frequency depends on driving conditions and lifestyle. Regular cleaning is needed with frequent passengers or cargo. A general guideline is deep cleaning twice yearly, such as in spring to remove winter dirt and late summer to prepare for colder months.