Wheels are more than just aesthetic features on your vehicle; they are crucial for performance and safety. Upgrading to a new set of wheels can dramatically change your car’s appearance and handling. However, navigating the world of wheels can be confusing, especially when understanding the different parts and terminology. While many people refer to the entire wheel as the “rim,” the rim is actually just one component of the complete wheel assembly. Understanding the Parts Of A Car Rim is essential for anyone looking to upgrade, repair, or simply learn more about their vehicle.
This guide will delve into the specific parts of a car rim, clarifying the terminology and helping you understand the function of each component. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or a curious car owner, this breakdown will equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently discuss and understand your car’s wheels.
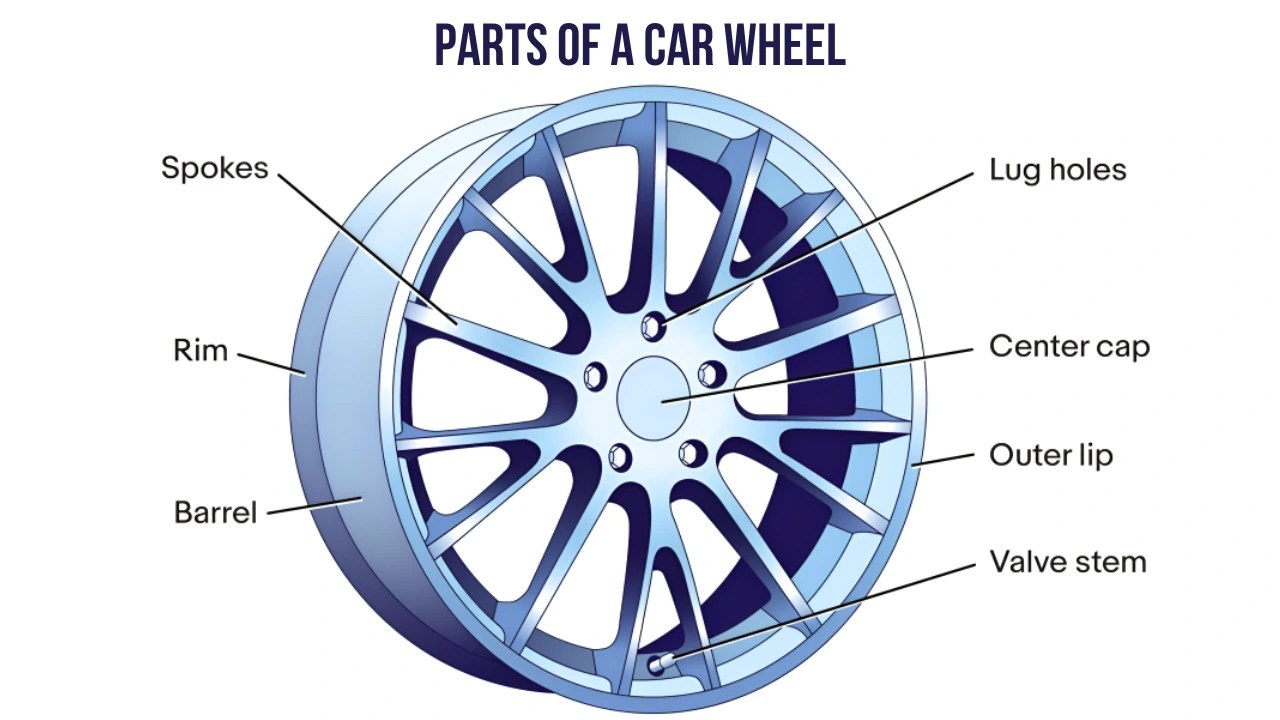 Parts Of A Car Wheel Diagram
Parts Of A Car Wheel Diagram
Key Components: Exploring the Parts of a Car Rim
While the terms “wheel” and “rim” are often used interchangeably, it’s important to understand that the rim is a specific part of the wheel. The car rim is the outer edge of the wheel that holds the tire. It’s the circular metal component to which the tire is mounted. Let’s break down the essential parts of a car rim:
1. Rim Flange: The Outer Edge
The rim flange is the outermost lip of the rim, the part that you see and often admire. It’s designed to provide strength and prevent the tire from rolling off the rim, especially during cornering or under heavy loads. The flange is crucial for maintaining tire bead retention and ensuring safe driving conditions. Different rim designs can feature varying flange styles, impacting both aesthetics and performance.
2. Bead Seat: Where Tire Meets Rim
The bead seat is the critical surface on the rim where the tire bead rests and seals. This area is precision-engineered to ensure an airtight seal between the tire and the rim. A clean and undamaged bead seat is vital for maintaining proper tire pressure and preventing air leaks. When mounting tires, technicians pay close attention to the bead seat to ensure correct tire seating and inflation.
3. Drop Center: Facilitating Tire Mounting
The drop center is a recessed area in the center of the rim’s barrel. This ingenious design makes tire mounting and demounting possible. The drop center allows one bead of the tire to be positioned deeper into the rim, providing enough slack to stretch the opposite bead over the rim flange. Without the drop center, installing tires, particularly low-profile ones, would be extremely difficult, if not impossible.
4. Outer Lip & Inner Lip: Defining Rim Edges
The outer lip of the rim is the visible edge on the outside of the wheel, contributing significantly to the wheel’s style. The inner lip, on the other hand, is the edge on the inside of the wheel, facing the car’s suspension and brake components. Both lips play a role in tire retention and rim integrity. The design and depth of the outer lip are often key styling features in aftermarket wheels.
5. Valve Stem Hole: Access for Inflation
The valve stem hole is a precisely drilled opening in the rim designed to accommodate the valve stem. This small but essential part allows for tire inflation and deflation. The valve stem, when installed through this hole, creates an airtight seal, allowing you to add or release air to adjust tire pressure. The valve stem hole is strategically placed for easy access when checking and adjusting tire pressure.
6. Lug Nut Holes: Securing the Wheel
Lug nut holes, or bolt holes in some designs, are located on the center disc of the wheel, extending into the rim structure. These holes are designed to align with the wheel studs on the car’s hub. Lug nuts (or wheel bolts) are then tightened through these holes, securely fastening the wheel to the vehicle. The number and pattern of lug nut holes are crucial and must match the vehicle’s specifications for safe wheel mounting.
7. Center Bore: Centering on the Hub
The center bore is the large hole in the very center of the rim. It’s designed to fit precisely over the vehicle’s hub flange, ensuring the wheel is centered correctly on the axle. Proper center bore sizing is vital for vibration-free driving. If a wheel’s center bore is larger than the hub flange, hub-centric rings are used to fill the gap and maintain proper centering and weight distribution.
8. Safety Humps: Enhancing Tire Security
Safety humps are raised ridges located just inside the bead seat area of the rim. These humps are designed to provide an extra measure of tire bead retention, particularly in run-flat tire systems or during sudden air loss. Safety humps help to keep the tire bead seated in the event of a puncture, allowing for better vehicle control and safer stopping.
Understanding these parts of a car rim provides a comprehensive view of this critical wheel component. While the rim works in conjunction with other parts of the wheel assembly like the hub, spokes and tire, its individual components are key to tire safety, performance, and overall wheel functionality.
Beyond the Rim: Other Essential Wheel Components
While this article focuses on the parts of a car rim, it’s helpful to remember that the rim is part of a larger wheel assembly. Here’s a brief overview of other key wheel parts to provide a complete picture:
- Hub: The central part of the wheel that attaches to the vehicle’s axle. It houses components like wheel bearings and connects to the braking system.
- Spokes (or Disc): Connect the rim to the hub. Spokes provide structural support and contribute significantly to the wheel’s style. Some wheels, particularly steel wheels, may have a solid disc instead of spokes.
- Tire: The rubber component mounted on the rim, providing traction, cushioning, and contact with the road surface.
- Valve Stem: A spring-loaded valve inserted into the valve stem hole of the rim, used for inflating and deflating the tire.
- Wheel Weights: Small weights attached to the rim to balance the wheel and tire assembly, preventing vibrations.
- Center Cap: A decorative cap that covers the center bore and sometimes the lug nuts, enhancing wheel aesthetics.
FAQs About Car Rims
Q: What is the difference between a wheel and a rim?
A: While often used interchangeably, the “rim” is specifically the outer circular part of the “wheel” to which the tire is mounted. The “wheel” is the complete assembly, including the rim, hub, and spokes (or disc).
Q: Can I replace just the rim of my wheel?
A: In most cases, wheels are sold and replaced as complete units. While technically some multi-piece wheels allow for component replacement, it’s generally not practical or recommended to replace just the rim section of a standard wheel. Damage to the rim often necessitates replacing the entire wheel for safety and structural integrity.
Q: What materials are car rims made of?
A: Car rims are commonly made from steel or aluminum alloys. Steel rims are typically found on standard vehicles due to their durability and lower cost. Alloy rims (aluminum) are lighter, offer better heat dissipation, and allow for more intricate designs, often used for performance and aesthetic upgrades.
Q: How do I know what size rim my car needs?
A: The correct rim size for your car is specified by the vehicle manufacturer. You can find this information in your owner’s manual, on a sticker on the driver’s side doorjamb, or by consulting tire size guides online. It’s crucial to use rims that are compatible with your vehicle’s specifications to ensure proper fitment, safety, and performance.
Q: What are aftermarket car rims?
A: Aftermarket car rims are wheels manufactured by companies other than the original vehicle manufacturer. They offer a wide range of styles, sizes, and materials, allowing car owners to personalize their vehicles and enhance performance or aesthetics. When choosing aftermarket rims, it’s important to ensure they meet safety standards and are compatible with your vehicle.
Understanding the parts of a car rim and the broader wheel assembly empowers you to make informed decisions about wheel maintenance, upgrades, and replacements. Whether you’re dealing with tire changes, considering new wheels, or simply interested in car mechanics, this knowledge is invaluable for any car owner.