The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system in modern vehicles, mandated in the United States for all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996. While the general OBD2 standard applies across manufacturers, understanding the specifics of the Vw Obd2 Protocol is crucial for accurate diagnostics and repair of Volkswagen vehicles. This guide will delve into the essential aspects of OBD2 protocols relevant to VWs, ensuring you have a solid grasp on this critical system.
What is OBD2 and Why is it Important for VWs?
OBD2 is designed to provide vehicle owners and technicians with access to the health information of a car. It monitors various systems, including engine, transmission, and emissions, and reports diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) when issues arise. For VW owners and mechanics working on Volkswagens, familiarity with the vw obd2 protocol is indispensable for efficient troubleshooting and maintenance. It allows for accurate identification of problems, reducing guesswork and saving time in the repair process.
OBD2 Communication Protocols Used in VW Vehicles
OBD2 compliance dictates the use of specific communication protocols to transmit diagnostic data. While the original article mentions five protocols, it’s important to understand how these apply to VW vehicles. Initially, OBD2 allowed for protocols like J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW, ISO9141-2, and ISO14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000). However, the landscape has evolved, and modern VWs primarily utilize ISO15765-4/SAE J2480, which is based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol.
While older VW models might have employed some of the earlier protocols, especially before the widespread adoption of CAN, it’s safe to assume that most VW vehicles from the early 2000s onwards, and certainly all newer models, communicate using the CAN protocol for OBD2 diagnostics. The CAN protocol became mandatory for all vehicles in the US from model year 2008, and VW, being a global manufacturer, adopted this standard broadly.
Location and Types of VW OBD2 Connectors (DLC)
The diagnostic link connector (DLC) is the physical interface point to access the vw obd2 protocol. SAE J1962 defines two types of DLCs: Type A and Type B. Both are 16-pin connectors, but they differ in their alignment tab shape.
Type A DLCs, as per J1962 standards, are typically located within the driver’s compartment, ranging from the instrument panel to about 300mm beyond the vehicle’s centerline. The preferred location in most VWs is often beneath the steering column or in the dashboard area, easily accessible from the driver’s seat.
Fig. 1 – Type A OBD2 Connector in a VW Vehicle
Type B DLCs are also found in the passenger or driver’s compartment but can be located further out, up to 750mm beyond the vehicle centerline. These are also designed for easy access, potentially from the driver’s seat, co-driver’s seat, or even from outside the vehicle. While Type A is more common in passenger vehicles, it’s good to be aware of Type B as a possibility in some VW models.
Fig. 2 – Type B OBD2 Port Example for VW Cars
Identifying the VW OBD2 Protocol Through Pinouts
While modern VWs predominantly use CAN, understanding how to identify the protocol via the DLC pinout can be helpful, especially when dealing with older vehicles or for verification purposes. The pinout configuration of the OBD2 connector can indicate the communication protocol in use.
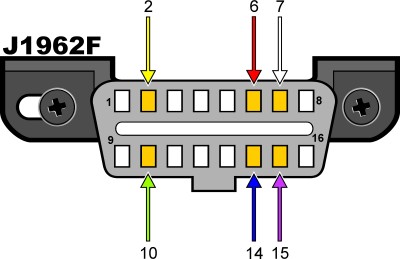
The following diagram illustrates the standard OBD2 connector pinout, which is consistent across OBD2 compliant vehicles, including VWs.
Fig. 3 – Standard OBD2 Pinout for VW Protocol Identification
To determine the protocol, focus on specific pins in the DLC. The table below, adapted for relevance to identifying vw obd2 protocol, outlines how pin presence relates to the communication standard:
| Pin 2 | Pin 6 | Pin 7 | Pin 10 | Pin 14 | Pin 15 | Protocol Indication for VW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| must have | – | – | must have | – | – | J1850 PWM (Older VWs – unlikely) |
| must have | – | – | – | – | – | J1850 VPW (Older VWs – unlikely) |
| – | – | must have | – | – | may have* | ISO9141/14230 (Older VWs – possible) |
| – | must have | – | – | must have | – | ISO15765 (CAN) – Common in modern VWs |
*Pin 15, the “L-line,” is optional in newer vehicles using ISO9141-2 or ISO14230-4. However, for CAN-based VWs, pins 6 and 14 are the key indicators.
Therefore, for most modern VW vehicles, you should find pins 4 (Chassis Ground), 5 (Signal Ground), 6 (CAN High), 14 (CAN Low), and 16 (Battery Positive) populated in the OBD2 connector, confirming the use of the CAN protocol, which is the standard vw obd2 protocol for diagnostics.
In Summary:
Understanding the vw obd2 protocol is essential for anyone working with Volkswagen vehicles. While the OBD2 system provides a standardized approach to vehicle diagnostics, knowing that modern VWs primarily utilize the CAN protocol and understanding the DLC connector and pinouts enhances diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. This knowledge empowers VW owners and technicians to effectively diagnose and maintain these vehicles.